Introduction to Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Elbow tendon inflammation is a pervasive condition affecting individuals engaging in repetitive activities. This introduction provides an overview of the complexities surrounding elbow tendon inflammation, setting the stage for in-depth exploration of its multifaceted aspects;
Definition and Prevalence of Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Characterized by inflammation of tendons, elbow tendon inflammation is a musculoskeletal disorder. Affecting individuals worldwide, its prevalence varies among populations, necessitating comprehensive understanding of its definition and epidemiological aspects for effective management.
2.1 Definition of Tendonitis and Tendinosis
Tendonitis and tendinosis are two distinct yet interconnected conditions affecting the tendons. Tendonitis refers to the inflammation of tendons, typically resulting from acute injuries or repetitive strain. This condition is characterized by the presence of inflammatory cells, pain, and swelling in the affected area.
On the other hand, tendinosis is a chronic degenerative condition marked by the deterioration of tendon tissue. Unlike tendonitis, tendinosis is not typically accompanied by significant inflammation. Instead, it involves the gradual breakdown of collagen fibers, leading to loss of tendon strength and function.
A thorough understanding of these definitions is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment of elbow tendon inflammation. By distinguishing between tendonitis and tendinosis, healthcare professionals can develop targeted interventions to address the underlying causes of the condition and promote optimal recovery.
2.2 Prevalence of Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Elbow tendon inflammation is a common condition affecting individuals across various demographics and occupations. According to epidemiological studies, the prevalence of elbow tendonitis ranges from 1% to 3% in the general population.
Certain groups, however, are more susceptible to developing elbow tendon inflammation. For instance, individuals engaged in repetitive manual labor, athletes participating in racquet sports, and musicians are at a higher risk of developing the condition. Additionally, the prevalence of elbow tendonitis increases with age, peaking between the fourth and sixth decades of life.
Understanding the prevalence of elbow tendon inflammation is essential for developing targeted prevention strategies and allocating healthcare resources effectively. By recognizing the scope of the issue, healthcare professionals can work towards reducing the incidence and impact of this debilitating condition on affected individuals and communities.
Causes and Risk Factors of Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Elbow tendon inflammation arises from a complex interplay of intrinsic and extrinsic factors. This section elucidates the underlying causes and risk factors contributing to the development of elbow tendonitis, providing a comprehensive framework for understanding the condition.
3.1 Repetitive Strain Injury
Repetitive strain injury is a primary contributor to elbow tendon inflammation, resulting from prolonged and recurrent exposure to stressful movements. This type of injury occurs when the tendons and muscles surrounding the elbow joint are subjected to repetitive strain, leading to micro-tears and subsequent inflammation. Activities involving repetitive flexion, extension, or rotation of the elbow, such as tennis, golf, or rowing, increase the risk of developing repetitive strain injury. Furthermore, occupations requiring manual labor, assembly line work, or computer use also pose a significant risk. The cumulative effect of repetitive strain can lead to chronic inflammation, degeneration, and eventual rupture of the affected tendons. A comprehensive understanding of repetitive strain injury is essential for early diagnosis, prevention, and effective management of elbow tendon inflammation;
3.2 Overuse Injury
Overuse injury is a significant contributing factor to elbow tendon inflammation, resulting from excessive and intense physical activity without adequate recovery time. This type of injury occurs when the tendons and muscles surrounding the elbow joint are subjected to prolonged periods of stress, leading to fatigue, degeneration, and subsequent inflammation. Overuse injuries can be acute or chronic, with the latter being more prevalent in athletes and individuals engaging in strenuous activities. Insufficient warm-up and cool-down exercises, inadequate training techniques, and poor equipment use can exacerbate the risk of overuse injury. A thorough understanding of overuse injury mechanisms and prevention strategies is crucial for mitigating the risk of elbow tendon inflammation. By recognizing the early warning signs of overuse injury, individuals can take proactive measures to prevent further damage and promote optimal recovery.
3.3 Poor Technique and Biomechanics
Poor technique and biomechanics play a pivotal role in the development of elbow tendon inflammation. Aberrant movement patterns, such as incorrect grip, stance, or swing mechanics, can lead to uneven distribution of forces across the elbow joint, resulting in excessive stress on the tendons and muscles. Furthermore, inadequate core strength, flexibility, and proprioception can compromise optimal movement patterns, increasing the risk of injury. Individuals engaging in activities that involve repetitive throwing, lifting, or twisting motions are particularly susceptible to poor technique-related injuries. A thorough analysis of an individual’s biomechanics and technique can help identify potential flaws and facilitate targeted interventions to mitigate the risk of elbow tendon inflammation. By addressing these issues, individuals can optimize their movement patterns, reduce the risk of injury, and enhance overall performance.
Types of Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Elbow tendon inflammation encompasses various distinct conditions, each with unique characteristics and etiologies. This section provides an overview of the primary forms of elbow tendon inflammation, highlighting their differences and similarities.
4.1 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a prevalent condition characterized by inflammation of the extensor tendons in the forearm. This condition typically affects individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive wrist extension, such as tennis players and manual laborers.
The primary symptoms of tennis elbow include pain and tenderness on the lateral aspect of the elbow, which can radiate to the forearm and wrist. In severe cases, individuals may experience weakness in the affected arm, making everyday activities challenging.
A thorough diagnosis of tennis elbow involves a comprehensive physical examination and imaging studies, such as X-rays or MRI scans, to rule out other potential causes of elbow pain. A well-structured treatment plan, incorporating rest, physical therapy, and pain management, is essential for alleviating symptoms and promoting recovery.
4.2 Golfer’s Elbow (Medial Epicondylitis)
Golfer’s elbow, or medial epicondylitis, is a condition characterized by inflammation of the flexor tendons in the forearm. This condition typically affects individuals who engage in activities that involve repetitive wrist flexion, such as golfers, rowers, and manual laborers.
The primary symptoms of golfer’s elbow include pain and tenderness on the medial aspect of the elbow, which can radiate to the forearm and wrist. In severe cases, individuals may experience weakness in the affected arm, making everyday activities challenging. A thorough diagnosis involves a comprehensive physical examination and imaging studies to rule out other potential causes of elbow pain.
Treatment for golfer’s elbow typically involves a combination of rest, physical therapy, and pain management. In some cases, orthotics or assistive devices may be recommended to reduce strain on the affected tendons. Early intervention and proper treatment are essential for alleviating symptoms and promoting recovery.
Consequences of Untreated Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Neglecting elbow tendon inflammation can lead to severe and irreversible damage. This section highlights the potential consequences of untreated elbow tendon inflammation, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention and proper management strategies.
5.1 Tendon Rupture
A tendon rupture is a severe and debilitating consequence of untreated elbow tendon inflammation. This occurs when the inflamed tendon becomes weakened, leading to a complete or partial tear. The severity of the rupture can vary, with some cases requiring immediate surgical intervention.
The symptoms of a tendon rupture can be sudden and dramatic, often accompanied by a loud popping sound. Severe pain, swelling, and bruising are common, along with reduced mobility and strength in the affected arm. In some cases, the rupture may be preceded by warning signs such as increased pain and stiffness.
Prompt medical attention is essential in the event of a suspected tendon rupture. A thorough diagnosis will be performed to determine the extent of the damage, followed by a treatment plan tailored to the individual’s needs. In severe cases, surgery may be necessary to repair or reattach the ruptured tendon.
5.2 Chronic Joint Pain and Muscle Strain
Chronic joint pain and muscle strain are common consequences of untreated elbow tendon inflammation. As the condition progresses, the inflamed tendon can cause persistent pain and stiffness in the affected joint, leading to reduced mobility and function.
The surrounding muscles may also become strained, leading to further pain and discomfort. This can create a vicious cycle, where the individual avoids using the affected arm due to pain, leading to muscle atrophy and decreased strength.
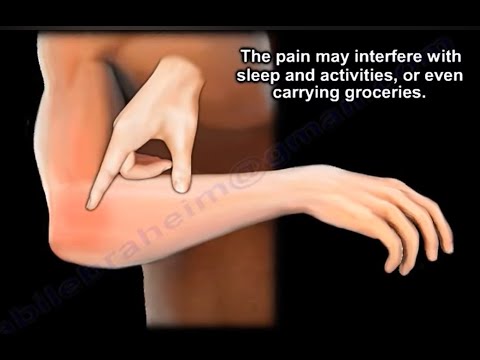
If left unaddressed, chronic joint pain and muscle strain can significantly impact daily activities and overall quality of life. Simple tasks, such as gripping or lifting, can become daunting challenges. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A comprehensive treatment plan can help alleviate chronic joint pain and muscle strain, promoting optimal recovery and preventing long-term damage.
Prevention and Treatment of Elbow Tendon Inflammation
Effective prevention and treatment strategies for elbow tendon inflammation are crucial to mitigate its debilitating effects. This section provides an overview of evidence-based approaches to prevent and manage this condition, ensuring optimal recovery and functionality.
6.1 Prevention Strategies
Implementing prevention strategies is essential to reduce the risk of developing elbow tendon inflammation. A well-structured warm-up and cool-down routine, incorporating exercises that enhance flexibility and strength, can significantly mitigate the onset of this condition. Furthermore, adopting proper techniques and biomechanics when engaging in activities that involve repetitive strain on the elbow joint is crucial. Additionally, utilizing equipment with ergonomic design, such as grips and handles, can also help to minimize the stress exerted on the elbow tendons. Regular breaks and adequate rest periods are also vital to prevent overuse injuries. It is equally important to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to ensure overall musculoskeletal well-being. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can substantially reduce their susceptibility to elbow tendon inflammation and related conditions, thereby promoting optimal elbow health and function.
The section on prevalence was informative, but I felt that it could have been strengthened with more specific data on how different demographics are affected by elbow tendon inflammation. Additionally, it would have been helpful to discuss how occupation-specific activities contribute to this condition.
I appreciate the emphasis on distinguishing between tendonitis and tendinosis, as this distinction is crucial for accurate diagnosis and effective treatment. However, I would have liked to see more discussion on the specific causes and risk factors associated with each condition.
I appreciated the discussion on the importance of distinguishing between acute injuries versus repetitive strain as causes of tennis elbow versus golfer’s elbow respectively; however there could still stand even greater emphasis being placed here given just how critical proper identification truly becomes when talking treatments moving forward down line later after initial onset symptoms subside somewhat.
As an orthopedic specialist, I found this article to be a useful resource for patients seeking information on elbow tendon inflammation. The explanations were clear and concise, making it easy for non-experts to understand this complex topic.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of elbow tendon inflammation, including its definition, prevalence, and distinction between tendonitis and tendinosis. The language is clear and concise, making it accessible to both healthcare professionals and individuals affected by this condition.
This article provided a solid foundation for understanding elbow tendon inflammation; however I think further discussion regarding potential treatments options such physical therapy modalities along side perhaps certain pharmaceuticals utilized today when attempting manage these types painful disorders appropriately going forward.