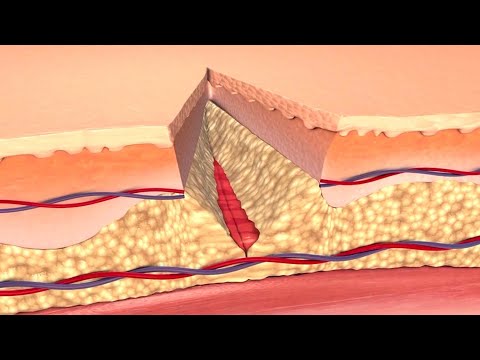
What is Wound Revival?
Wound revival refers to the process of a previously closed wound reopening, also known as wound dehiscence. This complication can arise due to various factors, including infection, poor wound care, or underlying medical conditions, leading to delayed healing and potential serious consequences.
Risk Factors for Wound Revival
Several factors contribute to the development of wound revival, making it essential to identify high-risk individuals. These include⁚
- Age⁚ Older adults are more prone to wound revival due to decreased collagen synthesis, reduced wound contraction, and age-related comorbidities.
- Diabetes⁚ Individuals with diabetes mellitus are at higher risk due to impaired wound healing, neuropathy, and peripheral vascular disease.
- Smoking⁚ Smoking hinders wound healing by reducing blood flow, oxygen delivery, and collagen synthesis.
- Obesity⁚ Excess weight increases the risk of wound revival due to compromised wound closure, reduced tissue oxygenation, and increased pressure on the wound site.
- Poor nutrition⁚ Inadequate nutrient intake impairs wound healing, making it essential to ensure sufficient protein, vitamin, and mineral consumption.
- Chronic diseases⁚ Conditions such as cardiovascular disease, respiratory disease, and renal failure can impede wound healing and increase the risk of wound revival.
Understanding these risk factors enables healthcare professionals to implement targeted interventions, minimizing the likelihood of wound revival and promoting optimal wound healing outcomes.
Delayed Healing⁚ A Precursor to Wound Revival
Delayed healing is a critical precursor to wound revival, as it creates an environment conducive to complications. Prolonged healing times can be attributed to various factors, including⁚
- Inadequate wound care and management
- Insufficient debridement and cleansing
- Poor tissue oxygenation and perfusion
- Infection or bacterial colonization
- Nutritional deficiencies and inadequate supplementation
When healing is delayed, the wound becomes increasingly susceptible to complications, such as infection, ischemia, and necrosis. Furthermore, the prolonged inflammatory response can lead to tissue damage, scarring, and adhesion formation.
The consequences of delayed healing can be mitigated through prompt intervention, including reassessment of wound management strategies, optimization of nutritional support, and implementation of evidence-based wound care practices. Early recognition of delayed healing and targeted interventions can help prevent wound revival and promote optimal wound outcomes.
Healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in monitoring wound progress, recognizing the signs of delayed healing, and taking prompt action to address potential complications and prevent wound revival.
Surgical Wound Complications⁚ A Major Concern
Surgical wound complications, including wound revival, pose significant risks to patient health and safety. Prompt recognition and management of complications, such as wound dehiscence, infection, and bleeding, are crucial to prevent long-term sequelae and optimize outcomes in the postoperative period.
Signs and Symptoms of Wound Revival
Identifying the signs and symptoms of wound revival is crucial for prompt intervention and preventing further complications. A comprehensive assessment of the wound and surrounding tissue is essential to detect any abnormalities.
Common signs and symptoms of wound revival may include increased pain, swelling, and redness around the wound site. The presence of pus, drainage, or a foul odor may indicate an underlying infection. Additional signs may comprise increased warmth, red streaks, swollen lymph nodes, fever, chills, malaise, decreased mobility, tenderness, and increased sensitivity.
It is essential to monitor the wound closely for any changes in its appearance, size, or drainage. Patients may also report a feeling of tightness or pulling around the wound site, which can be indicative of wound dehiscence. Furthermore, the presence of a gaping or open wound is a clear indication of wound revival.
Healthcare professionals should be vigilant in assessing patients for these signs and symptoms, particularly in the postoperative period or in individuals with underlying medical conditions that may impair wound healing; Early recognition and management of wound revival can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent long-term consequences.
A thorough understanding of the signs and symptoms of wound revival enables healthcare professionals to provide timely interventions, optimize wound care, and promote successful wound healing.
By recognizing the early warning signs of wound revival, healthcare professionals can mitigate the risk of complications and improve patient outcomes.
Wound Infection Signs⁚ A Key Indicator
Wound infection is a primary concern in wound revival, as it can significantly impede the healing process and lead to severe consequences. Identifying the signs of wound infection is crucial for prompt intervention and mitigating the risk of complications.
The classic signs of wound infection include increased redness, swelling, warmth, and pain around the wound site. The presence of pus, drainage, or a foul odor is a strong indication of infection. Additionally, the wound may appear inflamed, with increased erythema, edema, or induration.
In some cases, wound infection may manifest systemically, with symptoms such as fever, chills, malaise, and decreased mobility. Patients may also report increased tenderness or sensitivity around the wound site, which can be indicative of an underlying infection.
It is essential to note that some patients may not exhibit overt signs of infection, particularly those with compromised immune systems or underlying medical conditions. Therefore, healthcare professionals must remain vigilant and consider wound infection as a potential cause of delayed healing or wound revival.
A thorough assessment of the wound and surrounding tissue, combined with laboratory tests and diagnostic imaging, can confirm the presence of wound infection. Early recognition and management of wound infection can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent long-term consequences.
By recognizing the signs of wound infection, healthcare professionals can provide targeted interventions, optimize wound care, and promote successful wound healing.
Swelling and Redness⁚ Early Warning Signs
Increased swelling and redness around the wound site are early warning signs of potential complications. These symptoms can indicate inflammation, infection, or other underlying issues, warranting prompt attention from healthcare professionals to prevent wound revival and promote optimal healing.
Consequences of Untreated Wound Revival
Untreated wound revival can lead to severe and potentially life-threatening consequences. If left unaddressed, the wound can become a portal for bacteria to enter the bloodstream, causing sepsis, organ failure, and even death.
In addition to these severe outcomes, untreated wound revival can also result in significant morbidity, including prolonged hospitalization, surgical interventions, and extended periods of rehabilitation.
Furthermore, the chronic nature of untreated wound revival can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life, leading to decreased mobility, pain, and discomfort. This can result in significant emotional and psychological distress, affecting not only the individual but also their loved ones.
The financial burden of untreated wound revival should also not be underestimated. The cost of ongoing medical care, including hospitalizations, surgical procedures, and wound care supplies, can be substantial, placing a significant strain on individuals and healthcare systems.
It is essential that wound revival is recognized and treated promptly to prevent these severe consequences. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes, reduce morbidity and mortality, and promote optimal wound healing.
Healthcare professionals must remain vigilant in monitoring for signs of wound revival and take prompt action to address any concerns. By doing so, they can help mitigate the consequences of untreated wound revival and promote the best possible outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
Severe Consequences⁚ A Need for Prompt Intervention
Prompt intervention is crucial in preventing the severe consequences of wound revival. If left unaddressed, the condition can rapidly deteriorate, leading to life-threatening complications.
Sepsis, a potentially fatal condition, can arise when bacteria from the wound enter the bloodstream. Organ failure, including respiratory and cardiac failure, can also occur, necessitating immediate medical attention.
In extreme cases, wound revival can lead to necrotizing fasciitis, a rare but deadly bacterial infection that destroys tissue and requires prompt surgical intervention.
Furthermore, the risk of amputation is also a significant concern, particularly in individuals with underlying vascular disease or diabetes. Prompt intervention can help prevent these severe consequences and promote optimal wound healing.
Healthcare professionals must be aware of the signs and symptoms of wound revival and take immediate action to address any concerns. This includes administering antibiotics, performing surgical debridement, and providing wound care.
Individuals with wound revival require close monitoring and regular follow-up appointments to ensure that the condition does not deteriorate. By providing prompt intervention and ongoing care, healthcare professionals can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of severe consequences.
Early recognition and treatment of wound revival are essential in preventing these severe consequences and promoting optimal wound healing. Healthcare professionals must remain vigilant and take prompt action to address any concerns and prevent long-term damage.
Long-term Consequences⁚ A Concern for Healthcare Professionals
The long-term consequences of wound revival are a significant concern for healthcare professionals, as they can have a profound impact on an individual’s quality of life.
Chronic pain and discomfort are common long-term consequences of wound revival, affecting not only the individual’s physical well-being but also their mental health and emotional stability.
Scarring and disfigurement can also occur, leading to body image issues and decreased self-esteem. In some cases, wound revival can lead to permanent disability, rendering individuals unable to perform daily tasks or engage in activities they once enjoyed.
Furthermore, the financial burden of wound revival can be substantial, with ongoing medical expenses, lost wages, and reduced productivity all taking a toll on an individual’s economic stability.
Healthcare professionals must consider these long-term consequences when developing treatment plans for wound revival. A comprehensive approach that addresses not only the physical aspects of wound healing but also the emotional and psychological needs of the individual is essential.
By providing ongoing support and care, healthcare professionals can help mitigate the long-term consequences of wound revival and promote optimal outcomes for individuals affected by this condition.
Early intervention, education, and preventative measures can also play a crucial role in reducing the risk of long-term consequences and improving overall health and well-being.
As a healthcare professional working with older adults, I appreciate how this article highlights age-related comorbidities as contributing factors for wound revival.
The emphasis on adequate nutrition as essential for optimal wound healing outcomes cannot be overstated; I would have liked more specific guidance on nutritional recommendations.
The section on chronic diseases as risk factors for wound revival is particularly informative; I was not aware of the specific ways in which conditions like cardiovascular disease can impede wound healing.
This article would benefit from additional examples or case studies illustrating successful prevention or management strategies for wound revival.
I appreciate how this article highlights the impact of lifestyle factors such as smoking and obesity on wound revival risk; this information can inform targeted interventions.
While informative overall, this article could benefit from further discussion on emerging treatments or innovations aimed at preventing or managing wound revival.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of wound revival, its risk factors, and the importance of understanding delayed healing as a precursor to this complication.
I found this article well-researched and concise; however, some visuals or diagrams might enhance reader engagement.