Understanding Bone Infection
Bone infection, or osteomyelitis, is a severe condition characterized by bone inflammation and bone marrow infection. It occurs when bacteria or fungi invade the bone tissue, leading to a debilitating bone disease. Prompt recognition and treatment are crucial to prevent long-term damage.
Causes and Symptoms of Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis is typically caused by bacterial infection, with the most common culprits being Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Fungal infections, such as those caused by Candida and Aspergillus, can also lead to osteomyelitis.
The symptoms of osteomyelitis can vary depending on the location and severity of the infection. Common symptoms include⁚
- Pain and swelling in the affected area
- Redness and warmth around the infected site
- Fever and chills
- Weakness and fatigue
In cases of acute osteomyelitis, symptoms can develop rapidly, often within days of the initial infection. If left untreated, the infection can spread to surrounding tissues and lead to serious complications. In contrast, chronic osteomyelitis can persist for months or even years, causing ongoing pain and discomfort.
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Early diagnosis and treatment are critical in preventing long-term damage and promoting effective management of the condition.
A thorough understanding of the causes and symptoms of osteomyelitis is crucial for prompt recognition and treatment. By recognizing the warning signs, individuals can take the first step towards effective management and recovery.
Bacterial and Fungal Osteomyelitis⁚ What’s the Difference?
Bacterial osteomyelitis is typically caused by Staphylococcus aureus, while fungal osteomyelitis is often caused by Candida or Aspergillus. Bacterial osteomyelitis tends to be more acute, whereas fungal osteomyelitis is often chronic and more challenging to treat;
Diagnosis and Treatment of Osteomyelitis
A prompt and accurate diagnosis is crucial for effective treatment of osteomyelitis. A comprehensive approach, including clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies, is employed to confirm the diagnosis. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and type of osteomyelitis, as well as the patient’s overall health.
Osteomyelitis treatment typically involves a combination of antimicrobial therapy, surgery, and supportive care. Antimicrobial agents are selected based on the causative pathogen and its susceptibility pattern. Surgery may be necessary to drain abscesses, debride infected tissue, and stabilize affected bones.
In cases of acute osteomyelitis, early initiation of antimicrobial therapy can lead to a significant reduction in morbidity and mortality. Chronic osteomyelitis, however, requires a more complex treatment approach, often involving prolonged antimicrobial therapy, repeated surgical interventions, and ongoing supportive care;
A multidisciplinary team, including infectious disease specialists, orthopedic surgeons, and radiologists, works together to develop an individualized treatment plan for each patient. Effective communication and collaboration among healthcare providers are essential for achieving optimal outcomes in patients with osteomyelitis.
By combining advances in diagnostic techniques, antimicrobial therapy, and surgical interventions, clinicians can improve patient outcomes and reduce! the risk of long-term complications associated with osteomyelitis.
How is Osteomyelitis Diagnosed?
Diagnosing osteomyelitis requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating clinical evaluation, laboratory tests, and imaging studies. A thorough medical history and physical examination are essential to identify symptoms and signs suggestive of osteomyelitis, such as bone pain, swelling, and redness.
Laboratory tests play a crucial role in diagnosing osteomyelitis. Blood cultures and bone tissue cultures are used to isolate the causative pathogen; Elevated white blood cell counts, erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR), and C-reactive protein (CRP) levels can indicate the presence of an infection.
Imaging studies are also vital in diagnosing osteomyelitis. X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) help visualize the affected bone and surrounding tissues. These studies can reveal signs of bone destruction, abscess formation, and soft tissue involvement.
Bone biopsy is often necessary to confirm the diagnosis of osteomyelitis. This involves surgically removing a sample of bone tissue for histopathological examination and culture. A bone biopsy can provide definitive evidence of infection and help guide treatment decisions.
A diagnostic algorithm, combining clinical, laboratory, and imaging findings, is used to establish the diagnosis of osteomyelitis. This approach enables clinicians to accurately diagnose and manage this complex bone infection, reducing the risk of complications and improving patient outcomes.
Osteomyelitis Treatment Options
Treatment of osteomyelitis typically involves a combination of antibiotic therapy and surgical intervention. Antibiotics target the underlying infection, while surgery may be necessary to drain abscesses, debride infected tissue, and stabilize affected bones. A multidisciplinary approach ensures optimal patient outcomes.
Complications and Prevention of Osteomyelitis
Osteomyelitis can lead to severe complications if left untreated or inadequately managed. These may include chronic osteomyelitis, bone deformities, and disability. In rare cases, the infection can spread to other parts of the body, such as the bloodstream or nervous system, resulting in life-threatening conditions like sepsis or meningitis.
Prevention of osteomyelitis is crucial, particularly in individuals with compromised immune systems or those who have undergone recent trauma or surgery. Effective preventative measures include proper wound care, strict adherence to antibiotic regimens, and avoiding activities that may exacerbate the condition.
In addition, certain populations, such as those with diabetes, human immunodeficiency virus (HIV), or cancer, should be aware of their increased risk of developing osteomyelitis. Regular check-ups with healthcare professionals and prompt reporting of any symptoms can aid in early detection and treatment.
Furthermore, maintaining good hygiene practices, such as frequent handwashing, proper sterilization of medical equipment, and avoiding sharing personal items, can also help reduce the risk of osteomyelitis transmission.
By understanding the potential complications and taking proactive steps towards prevention, individuals can minimize their risk of developing osteomyelitis and ensure optimal outcomes if the condition does occur.
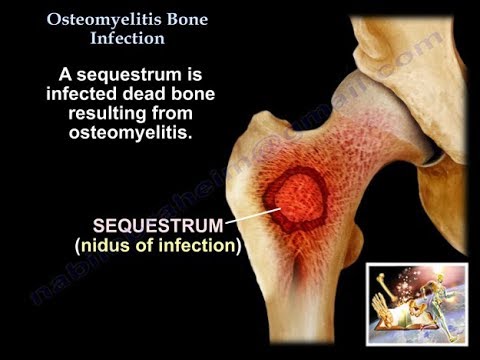
Chronic Osteomyelitis⁚ A Long-Term Battle
Chronic osteomyelitis is a persistent and relapsing form of bone infection that can last for months or even years. This condition often develops when acute osteomyelitis is not properly treated or when the underlying infection is not fully eradicated.
Characterized by recurring episodes of bone pain, swelling, and discharge, chronic osteomyelitis can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. The condition can also lead to bone deformation, limited mobility, and emotional distress.
Treatment of chronic osteomyelitis typically involves prolonged courses of antibiotics, which may be administered orally or intravenously. In some cases, surgical intervention may be necessary to remove infected bone tissue or repair damaged bone structures.
A comprehensive treatment plan for chronic osteomyelitis should also address related health issues, such as malnutrition and immunosuppression. Furthermore, patients with chronic osteomyelitis require ongoing monitoring and follow-up care to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Effective management of chronic osteomyelitis necessitates a multidisciplinary approach, involving collaboration between healthcare professionals, including infectious disease specialists, orthopedic surgeons, and physical therapists. By working together, individuals with chronic osteomyelitis can develop strategies to cope with this challenging condition and improve their overall well-being.
Preventing Osteomyelitis⁚ What You Can Do
To reduce the risk of developing osteomyelitis, practice good hygiene, avoid sharing personal items, and ensure proper wound care. Individuals with compromised immune systems or certain medical conditions should take extra precautions to prevent bone infection and promote overall bone health.
In conclusion, osteomyelitis is a severe and potentially debilitating condition that requires prompt recognition and treatment. Understanding the causes, symptoms, and treatment options is essential for individuals to take proactive steps in preventing and managing bone infections.
It is crucial to recognize the importance of proper wound care, good hygiene practices, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems or certain medical conditions should take extra precautions to prevent bone infections.
By staying informed and taking preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing osteomyelitis and promote overall bone health. Furthermore, advances in medical research and technology have improved diagnosis and treatment options, offering hope for those affected by this condition.
Ultimately, a comprehensive approach to osteomyelitis prevention, diagnosis, and treatment can significantly improve outcomes and quality of life for individuals affected by this condition. By working together, healthcare professionals, researchers, and individuals can combat osteomyelitis and promote optimal bone health.
Through continued education and awareness, we can empower individuals to take control of their bone health and reduce the incidence of osteomyelitis. By doing so, we can improve overall health outcomes and enhance the well-being of individuals and communities worldwide.
As an orthopedic specialist, I appreciate the accuracy of this article in describing osteomyelitis. However, I would have liked to see more emphasis on prevention strategies, such as proper wound care.
The section on bacterial vs fungal osteomyelitis was enlightening; however, I felt that some technical terms were not adequately explained for non-medical readers.
Overall, this article provides an excellent foundation for understanding bone infection; nonetheless, incorporating real-life examples or case studies could have enhanced reader engagement.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of bone infection, including its causes, symptoms, and treatment options. The distinction between bacterial and fungal osteomyelitis is particularly informative.
I found this article very helpful in understanding my recent diagnosis with osteomyelitis. The explanation of symptoms was spot-on, but I wish there was more information about managing chronic pain associated with this condition.