Effective Thalassemia Treatment⁚ An Overview
Effective thalassemia treatment requires a comprehensive approach, incorporating blood transfusion procedures, iron overload management, and symptom management․ A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals ensures optimal care for patients with thalassemia․
Understanding Thalassemia Treatment Options
Thalassemia treatment options vary depending on disease severity and patient needs․ A thorough diagnosis and assessment enable healthcare professionals to develop personalized treatment plans, ensuring optimal outcomes and improved quality of life․
Blood Transfusion Procedure⁚ A Lifeline for Thalassemia Patients
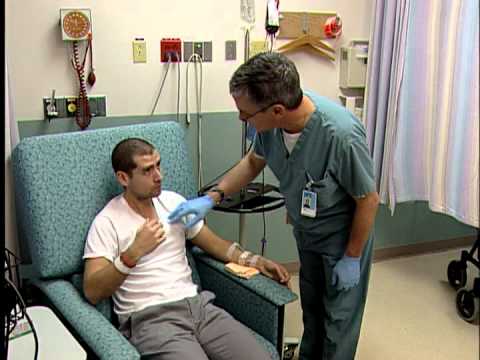
The blood transfusion procedure is a crucial component of thalassemia treatment, providing patients with the necessary red blood cells to alleviate anemia․ This procedure involves the intravenous infusion of donor blood, carefully matched to the patient’s blood type․
Prior to transfusion, patients undergo a series of tests to ensure compatibility and minimize the risk of adverse reactions․ The transfusion process typically takes several hours, during which time patients are closely monitored for any signs of complications․
The frequency and duration of blood transfusions vary depending on individual patient needs, with some requiring transfusions as frequently as every 2-4 weeks․ By replenishing red blood cells, blood transfusions enable thalassemia patients to maintain optimal hemoglobin levels, reducing symptoms and improving overall quality of life․
It is essential for patients to adhere to their prescribed transfusion schedule to maximize the effectiveness of this treatment and minimize potential complications․
Benefits and Risks of Blood Transfusions
The benefits of blood transfusions for thalassemia patients are numerous, including improved hemoglobin levels, reduced anemia symptoms, and enhanced overall quality of life․ Regular transfusions can also prevent long-term complications, such as organ damage and impaired growth and development․
However, as with any medical procedure, there are also risks associated with blood transfusions․ These may include adverse reactions to the donated blood, such as allergic reactions or transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI)․ Additionally, patients may be at risk of contracting blood-borne infections, although this risk is significantly minimized through rigorous donor screening and testing protocols․
Other potential risks include iron overload, which can occur due to the accumulation of excess iron from frequent transfusions, and alloimmunization, a condition in which the patient’s immune system reacts to the donated blood․ It is essential for patients to discuss these risks with their healthcare provider and carefully weigh the benefits and risks of blood transfusions․
Iron Overload Management⁚ A Crucial Aspect of Thalassemia Treatment
Effective iron overload management is vital for thalassemia patients, as excess iron accumulation can lead to organ damage and complications․ Prompt diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent long-term consequences and ensure optimal patient outcomes․
Iron Chelation Therapy⁚ Removing Excess Iron
Iron chelation therapy is a medical treatment that removes excess iron from the body, thereby preventing organ damage and complications․ This therapy involves administering chelating agents, either orally or intravenously, to bind with excess iron and facilitate its excretion․
There are several types of chelating agents available, each with its own advantages and disadvantages․ The choice of agent depends on factors such as the patient’s age, kidney function, and severity of iron overload․
Regular monitoring of iron levels and liver function is crucial during iron chelation therapy to ensure optimal efficacy and minimize side effects․ Adherence to treatment is essential for successful management of iron overload and prevention of long-term complications․
Patients undergoing iron chelation therapy must be closely monitored by a healthcare professional to adjust the treatment regimen as needed and address any concerns or side effects that may arise․
Effective iron chelation therapy can significantly improve the quality of life and life expectancy of thalassemia patients with iron overload․
Monitoring Iron Levels⁚ A Key to Effective Management
Regular monitoring of iron levels is crucial for effective management of iron overload in thalassemia patients․ This involves periodic blood tests to assess serum ferritin levels, liver iron concentration, and cardiac iron levels․
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) may also be used to assess iron deposition in organs such as the liver and heart․ These tests enable healthcare professionals to evaluate the efficacy of iron chelation therapy and adjust the treatment regimen as needed․
Frequent monitoring also helps identify potential complications, such as cardiac arrhythmias or liver dysfunction, allowing for prompt intervention and prevention of long-term damage․
A multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals should be involved in monitoring iron levels, including hematologists, cardiologists, and hepatologists, to ensure comprehensive care and optimal management of iron overload․
By closely monitoring iron levels, healthcare professionals can tailor treatment to individual patient needs, minimizing the risk of complications and improving overall outcomes․
Bone Marrow Transplant⁚ A Potential Cure for Thalassemia
A bone marrow transplant offers a potential cure for thalassemia by replacing defective stem cells with healthy ones, eliminating the need for lifelong blood transfusions and iron chelation therapy․
Eligibility and Procedure
To be eligible for a bone marrow transplant, thalassemia patients must meet specific criteria, including a suitable HLA-matched donor, adequate organ function, and a low risk of complications․ The procedure involves several steps⁚
- Pre-transplant preparation⁚ The patient undergoes chemotherapy and/or radiation therapy to destroy their existing bone marrow․
- Harvesting donor cells⁚ The donor’s bone marrow or stem cells are collected through a bone marrow harvest or peripheral blood stem cell collection․
- Infusing donor cells⁚ The donor cells are infused into the patient through a central line․
- Post-transplant care⁚ The patient receives immunosuppressive medications to prevent graft-versus-host disease and is closely monitored for complications․
A bone marrow transplant is a complex procedure that requires careful planning and execution by a multidisciplinary team of healthcare professionals․
Risks and Complications
A bone marrow transplant is a high-risk procedure that carries several potential complications, including⁚
- Graft-versus-host disease (GVHD)⁚ A condition in which the donor’s immune cells attack the patient’s tissues․
- Infection⁚ Patients are at increased risk of developing infections due to their compromised immune system․
- Organ damage⁚ The conditioning regimen can cause damage to the lungs, liver, and other organs․
- Rejection⁚ The patient’s immune system may reject the transplanted bone marrow or stem cells․
- Secondary cancers⁚ There is a small risk of developing secondary cancers, such as leukemia or lymphoma․
It is essential for patients to discuss the potential risks and complications with their healthcare provider and carefully weigh the benefits against the risks before undergoing a bone marrow transplant․
A thorough understanding of the potential complications enables patients to make informed decisions about their care and take an active role in managing their health․
Gene Therapy⁚ A Promising Future for Thalassemia Treatment
Gene therapy offers a promising solution for thalassemia patients, aiming to correct or replace the faulty HBB gene responsible for the disorder, potentially eliminating the need for lifelong transfusions and treatments․
Gene Editing Techniques⁚ A Potential Solution
CRISPR-Cas9 gene editing has emerged as a promising tool for treating thalassemia․ By precisely editing the HBB gene٫ scientists aim to correct the genetic mutation responsible for the disorder․ This technique involves using a small RNA molecule٫ known as a guide RNA٫ to locate the faulty gene and then cutting the DNA at that site․ The cell’s natural repair machinery is then activated٫ allowing researchers to supply a corrected version of the gene․
This approach has shown significant promise in laboratory studies, with edited cells demonstrating improved hemoglobin production․ While still in its infancy, gene editing holds tremendous potential for revolutionizing thalassemia treatment․ Ongoing research focuses on refining the technique, ensuring safety and efficacy, and exploring its applications in clinical settings․ As research advances, gene editing may become a viable treatment option for patients with thalassemia;
Current Research and Developments
Several clinical trials are currently underway to investigate the safety and efficacy of gene therapy for thalassemia․ These studies aim to evaluate the use of lentiviral vectors, gene editing techniques, and other approaches to modify or replace the faulty HBB gene․
Researchers are also exploring the use of induced pluripotent stem cells (iPSCs) to generate healthy red blood cells․ This approach involves reprogramming a patient’s own cells to produce functional red blood cells, potentially eliminating the need for blood transfusions․ Additionally, studies are investigating the role of small molecule therapies in increasing fetal hemoglobin production, which may help alleviate symptoms of thalassemia․
These ongoing research efforts hold promise for improving treatment options and quality of life for patients with thalassemia․ As new findings emerge, they will inform the development of innovative therapies and shape the future of thalassemia treatment․
Supportive Care⁚ Managing Thalassemia Symptoms
Supportive care plays a vital role in managing thalassemia symptoms, focusing on pain management, infection prevention, and nutrition counseling to improve quality of life for patients with thalassemia․
Hemoglobin Level Monitoring⁚ Tracking Progress
Hemoglobin level monitoring is a crucial aspect of thalassemia management, enabling healthcare professionals to track the effectiveness of treatment and make informed decisions․ Regular blood tests are performed to measure hemoglobin levels, which indicate the severity of anemia․
A complete blood count (CBC) is typically conducted every 2-3 months to assess hemoglobin levels٫ as well as other blood parameters․ This information helps healthcare providers adjust treatment plans٫ including blood transfusion schedules٫ to maintain optimal hemoglobin levels․
Accurate hemoglobin level monitoring also facilitates the early detection of complications, such as iron overload or transfusion-related reactions․ By closely tracking hemoglobin levels, healthcare professionals can provide personalized care and improve outcomes for patients with thalassemia․
Furthermore, hemoglobin level monitoring empowers patients to take an active role in their care, fostering a collaborative relationship between patients and healthcare providers․
Red Blood Cell Count⁚ Maintaining Healthy Levels
Maintaining a healthy red blood cell count is essential for individuals with thalassemia, as low levels can exacerbate anemia and related complications․ Regular monitoring of red blood cell counts enables healthcare professionals to assess the effectiveness of treatment and adjust transfusion schedules accordingly․
A normal red blood cell count ranges from 4․32 to 5․72 million cells per microliter (mcL) of blood․ In thalassemia patients٫ however٫ this number can be significantly lower due to ineffective erythropoiesis․ By closely tracking red blood cell counts٫ healthcare providers can identify trends and patterns that inform treatment decisions;
To maintain healthy red blood cell levels, patients may receive erythropoietin-stimulating agents or undergo regular blood transfusions․ Additionally, addressing underlying nutritional deficiencies, such as iron, folate, or vitamin B12 deficiencies٫ can also help support healthy red blood cell production․
By prioritizing red blood cell count maintenance, healthcare professionals can improve the overall health and well-being of patients with thalassemia․
Spleen Removal Surgery⁚ A Potential Option
Splenectomy, or spleen removal surgery, may be considered for certain individuals with thalassemia who experience significant splenomegaly (enlarged spleen) or hypersplenism (overactive spleen)․ In these cases, the spleen can become overly active, prematurely destroying red blood cells and exacerbating anemia․
The decision to undergo splenectomy is typically made on a case-by-case basis, taking into account factors such as disease severity, transfusion frequency, and overall health status․ The procedure can help reduce transfusion requirements and alleviate related symptoms․
However, splenectomy also carries risks, including increased susceptibility to infections and potential long-term complications․ Therefore, it is essential for patients to carefully discuss the potential benefits and risks with their healthcare provider to determine if splenectomy is a suitable treatment option for their specific situation․
Post-operative care and monitoring are crucial to minimize complications and ensure a successful outcome․
A thorough evaluation by a qualified healthcare professional is necessary to determine the appropriateness of splenectomy for individual patients with thalassemia․
In conclusion, effective thalassemia treatment requires a multifaceted approach, incorporating various medical interventions and supportive care measures․ While significant progress has been made in managing the disease, ongoing research and developments hold promise for improved treatment options and potential curative therapies․
It is essential for patients with thalassemia to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop personalized treatment plans tailored to their unique needs․ By fostering collaborative relationships and staying informed about the latest advancements, individuals with thalassemia can optimize their care and improve their overall quality of life․
Ultimately, the goal of thalassemia treatment is to enable patients to lead active, fulfilling lives despite the challenges posed by the disease․ With continued advances in medical science and a commitment to providing comprehensive, patient-centered care, this goal is increasingly within reach․
By promoting awareness, education, and advocacy, we can work together to support individuals affected by thalassemia and strive towards a brighter future for those living with this condition․
A better understanding of thalassemia and its treatment options empowers patients and families to navigate the complexities of the disease and make informed decisions about their care․
I appreciate the emphasis on personalized treatment plans for thalassemia patients. It
As a healthcare professional, I appreciate the attention to detail regarding pre-transfusion testing and monitoring for adverse reactions. This highlights the importance of careful planning and execution in transfusion therapy.
This article serves as a valuable resource for both healthcare professionals and patients seeking information on effective thalassemia treatment strategies. Well-written and informative!
This article effectively conveys the benefits of regular blood transfusions for thalassemia patients. However, it would be helpful to include more discussion on potential risks or complications associated with long-term transfusion therapy.
I found the section on iron overload management particularly insightful. It
This article provides a comprehensive overview of thalassemia treatment options, highlighting the importance of a multidisciplinary approach. The section on blood transfusion procedures is particularly informative.
The article does an excellent job explaining the blood transfusion process and its significance in managing thalassemia. However, I would have liked more information on emerging treatments or research developments.
Overall, this article demonstrates a clear understanding of thalassemia treatment principles. I appreciate the emphasis on adherence to prescribed transfusion schedules to optimize treatment outcomes.
While this article provides an excellent overview of current treatments, I believe it would benefit from additional discussion on innovative approaches or future directions in thalassemia research.