Introduction to Elbow Fracture
An elbow fracture refers to a break in one or more bones of the elbow joint, comprising the humerus, radius, and ulna, requiring prompt medical attention to prevent complications and ensure proper healing.
1.1. Definition and Overview
An elbow fracture is a type of orthopedic injury that involves a break or crack in one or more of the bones that comprise the elbow joint. The elbow joint is a complex structure that consists of the humerus, radius, and ulna bones, which work together to facilitate flexion, extension, and rotation of the arm. A fracture can occur in any of these bones, causing pain, swelling, and limited mobility in the affected arm. Elbow fractures can range from simple, non-displaced fractures to complex, comminuted fractures that require surgical intervention. Prompt medical attention is essential to diagnose and treat elbow fractures effectively, as untreated fractures can lead to long-term complications, such as arthritis, stiffness, and limited range of motion.
A comprehensive understanding of elbow fractures is crucial for developing effective treatment strategies and achieving optimal outcomes. This requires a thorough knowledge of the anatomy, classification, and management of elbow fractures.
Anatomy of the Elbow Joint
The elbow joint comprises the humerus, radius, and ulna bones, with key components including the olecranon, medial epicondyle, lateral condyle, and articular surfaces, all working in concert to facilitate flexion and extension.
2.1. Key Components of the Elbow Joint
The elbow joint consists of three bones⁚ the humerus, radius, and ulna. The humerus is the long bone of the upper arm, while the radius and ulna are the two bones of the forearm. The olecranon, located at the proximal end of the ulna, forms the bony prominence of the elbow. The medial epicondyle and lateral condyle are bony projections on the distal end of the humerus, serving as attachment points for muscles and ligaments. Articular surfaces, including the capitellum and trochlea, facilitate smooth movement between the bones. The radial head and neck also play crucial roles in elbow function. A thorough understanding of these key components is essential for diagnosing and treating elbow fractures. Each component interacts with others to enable flexion, extension, and rotation of the elbow joint. Precise alignment and coordination of these components are necessary for optimal elbow function.
Types of Elbow Fractures
Elbow fractures are classified into various types based on the bones involved, fracture patterns, and degree of displacement, including olecranon, radial head, and supracondylar fractures, among others, each with distinct characteristics.
3.1. Common Fracture Types
Several common fracture types occur in the elbow joint. Olecranon fractures involve the bony prominence at the elbow, while radial head fractures affect the radius bone. Supracondylar fractures occur above the condyles of the humerus. Lateral condyle fractures involve the bony projection on the outside of the elbow, whereas medial epicondyle fractures affect the bony projection on the inside. Capitellum fractures involve the rounded prominence at the end of the humerus; These fracture types can be further classified as nondisplaced, displaced, comminuted, or open, depending on the severity and complexity of the injury. Understanding the specific type of fracture is essential for determining the most effective treatment approach and achieving optimal outcomes.
- Olecranon fractures
- Radial head fractures
- Supracondylar fractures
- Lateral condyle fractures
- Medial epicondyle fractures
- Capitellum fractures
Symptoms of Elbow Fracture
Symptoms of an elbow fracture may include severe pain, swelling, bruising, limited mobility, and deformity of the affected arm, as well as numbness or tingling sensations in the hand or fingers.
4.1. Common Symptoms and Signs
Common symptoms and signs of an elbow fracture may include⁚
- Severe pain or tenderness in the elbow or surrounding areas
- Swelling, bruising, or redness around the elbow
- Limited mobility or stiffness in the elbow or arm
- Deformity or abnormal alignment of the elbow or arm
- Numbness or tingling sensations in the hand or fingers
- Weakness or difficulty moving the arm or hand
In some cases, patients may also experience more severe symptoms, such as difficulty rotating the arm or forearm, or a grinding or snapping sensation in the elbow. It is essential to seek immediate medical attention if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt treatment can significantly impact the outcome and recovery process.
A thorough evaluation by a medical professional is necessary to determine the severity and type of fracture, as well as the most effective course of treatment.
Causes of Elbow Fracture
Elbow fractures typically result from traumatic injuries, such as falls onto an outstretched hand, sports-related accidents, or direct blows to the elbow, causing stress and pressure on the joint.
5.1. Common Causes and Risk Factors
Common causes of elbow fractures include high-impact activities, such as football, hockey, and gymnastics, which increase the risk of injury. Falling onto an outstretched hand or directly onto the elbow can also cause fractures. Furthermore, individuals with osteoporosis or other bone diseases may be more susceptible to elbow fractures due to weakened bone density. Additionally, children and adolescents are at higher risk due to their developing bones and increased physical activity. Other risk factors include age, with older adults being more prone to fractures, and certain occupations, such as construction work or contact sports coaching. Understanding these common causes and risk factors can help individuals take preventive measures to minimize their risk of sustaining an elbow fracture.
Diagnosis of Elbow Fracture
Diagnosis of an elbow fracture involves a comprehensive evaluation, including physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies, such as X-rays, CT scans, or MRI, to confirm the presence and severity of the fracture.
6.1. Diagnostic Tests and Procedures
A thorough diagnostic evaluation is crucial to accurately diagnose an elbow fracture. The following diagnostic tests and procedures may be employed⁚
- X-rays⁚ To visualize the fracture and assess bone alignment
- CT scans⁚ To provide detailed cross-sectional images of the elbow joint
- MRI⁚ To evaluate soft tissue injuries, such as ligament or tendon damage
- Arthroscopy⁚ A minimally invasive procedure to visually inspect the joint
- Bone scans⁚ To detect bone fractures or abnormalities not visible on X-rays
A combination of these diagnostic tests and procedures enables healthcare professionals to determine the type, severity, and extent of the elbow fracture, guiding the development of an effective treatment plan.
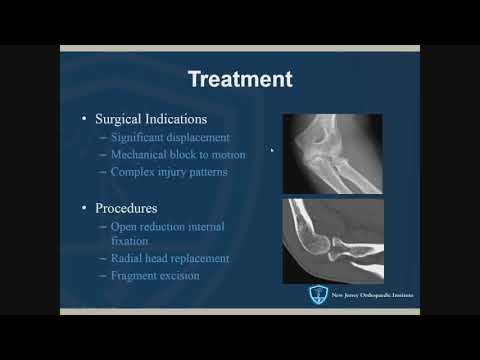
Treatment Options for Elbow Fracture
Treatment options for elbow fractures vary depending on the type, severity, and patient’s overall health, encompassing non-surgical methods, such as casting, and surgical interventions, including open reduction and internal fixation.
7.1. Non-Surgical and Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment options for elbow fractures include immobilization in a cast or splint, pain management with medication, and physical therapy to maintain range of motion. Surgical intervention is often necessary for more complex fractures, such as those involving the olecranon or coronoid process. Open reduction and internal fixation (ORIF) is a common surgical procedure, where the surgeon realigns and stabilizes the bone fragments using plates, screws, or wires. In some cases, a combination of both non-surgical and surgical methods may be employed. The choice of treatment depends on the specific characteristics of the fracture, as well as the patient’s overall health and activity level. A thorough evaluation by an orthopedic specialist is essential to determine the most effective treatment plan and achieve optimal outcomes.
Recovery Time and Rehabilitation
Following elbow fracture treatment, patients typically undergo a rehabilitation program to restore strength, flexibility, and function, with recovery times varying from several weeks to several months, depending on fracture severity.
8.1. Expected Recovery Time and Rehabilitation Process
The expected recovery time for an elbow fracture varies depending on the severity of the injury and the effectiveness of the treatment. Generally, patients can expect to regain full range of motion and strength within 3-6 months. The rehabilitation process typically begins with immobilization, followed by progressive mobilization and strengthening exercises. Patients may require physical therapy to restore function and mobility. A typical rehabilitation program includes exercises such as flexion, extension, pronation, and supination, as well as activities to improve grip strength and overall arm function. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are necessary to monitor progress and address any complications. With proper rehabilitation, most patients can achieve full recovery and return to their normal activities, including sports and heavy lifting, within 6-12 months after the injury.
The section on anatomy was informative! I particularly enjoyed learning about key components like olecranon & medial epicondyle – indeed these play vital roles! Maybe consider adding images/diagrams for enhanced comprehension?
Overall,a well-written & structured piece! Perhaps future installments might delve into classifications & corresponding treatments – doing so could offer readers even greater insight into complexities surrounding management/recovery processes.
I appreciate how this article emphasizes a comprehensive understanding of elbow fractures for effective treatment strategies! However,I would have liked more information on common causes or risk factors associated with this type of injury.
This piece presents solid foundational knowledge! Nevertheless,I think further discussion regarding potential complications arising from untreated or poorly managed cases could better reinforce urgency/importance surrounding timely interventions.
This article provides an excellent introduction to elbow fractures! I found it helpful how it clearly defined what an elbow fracture is and explained its importance in seeking medical attention promptly.