Introduction to Ferns
Ferns are ancient, vascular plants that comprise a diverse group of approximately 12٫000 species٫ exhibiting a wide range of morphologies and habitats٫ with fossil records dating back to the Devonian period․
Definition and Classification of Ferns
Ferns belong to the division Pteridophyta, a group of vascular plants that reproduce via spores․ They are characterized by the presence of fronds, which are leaves that arise from a central rhizome or stem․ The classification of ferns is complex and has undergone significant revisions in recent years․
The most widely accepted classification system recognizes four classes of ferns⁚ Polypodiopsida, Marattiopsida, Ophioglossopsida, and Psilotopsida․ These classes are further divided into orders, families, and genera, reflecting the diversity of fern morphology and evolutionary relationships․
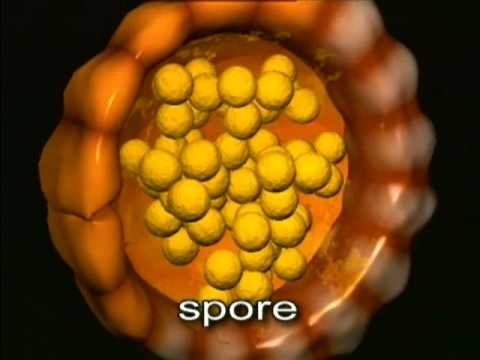
A key characteristic used in the classification of ferns is the arrangement and structure of their spores, as well as the morphology of their fronds and rhizomes․ Understanding the classification of ferns is essential for appreciating their diversity and evolutionary history, as well as for identifying and studying individual species․
Ethnobotany of Ferns
Ferns have been utilized by indigenous cultures worldwide for centuries, providing a rich source of traditional knowledge on their medicinal, food, and spiritual uses, reflecting their significance in human societies․
Traditional Uses of Ferns in Folk Remedies
Ferns have been employed in traditional medicine for centuries, with various species used to treat a range of ailments․ In many cultures, ferns are valued for their anti-inflammatory, antiseptic, and antiviral properties․ For example, the maidenhair fern (Adiantum spp․) has been used to treat respiratory issues, such as bronchitis and asthma, while the ostrich fern () has been used to treat fever and rheumatism․ In some Asian cultures, ferns are believed to possess spiritual significance, with certain species used in rituals to ward off evil spirits or bring good fortune․ The use of ferns in folk remedies is often passed down through generations, with traditional healers relying on observation, experimentation, and oral tradition to develop their knowledge of these plants’ medicinal properties․
Medicinal Properties of Ferns
Ferns possess a diverse range of bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, phenolic acids, and terpenoids, which contribute to their medicinal properties․ Many fern species have been found to exhibit antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and antimicrobial activities, making them potential candidates for the treatment of various diseases․ The Athyrium genus, for example, has been found to contain compounds with potent antiviral and anticancer properties․ Additionally, some ferns have been shown to possess cardiovascular-protective effects, such as reducing blood pressure and improving lipid profiles․ The unique chemical composition of ferns offers opportunities for the discovery of novel therapeutic agents, and further research is needed to fully elucidate the medicinal properties of these plants․ Studies have also highlighted the importance of considering the environmental and genetic factors that influence the production of bioactive compounds in ferns․
Herbalism and Ferns
Ferns have been a component of traditional herbalism for centuries, with various species utilized in the preparation of teas, tinctures, and infusions to promote health and well-being in diverse cultural contexts․
Using Ferns in Herbal Remedies
The utilization of ferns in herbal remedies is a longstanding practice, with various species employed to address a range of health concerns․ The fronds, rhizomes, and roots of ferns are commonly harvested for their medicinal properties․ To prepare herbal remedies, ferns may be dried, crushed, or steeped in hot water to create teas, tinctures, or infusions․ The specific preparation method can impact the efficacy and potency of the remedy․ For instance, drying ferns can help preserve their medicinal compounds, while steeping them in hot water may release bioactive ingredients․ Traditional herbalists often combine ferns with other plants to create synergistic blends that enhance their therapeutic effects․ The art of using ferns in herbal remedies requires a deep understanding of their unique properties and interactions, as well as a commitment to sustainable harvesting practices to ensure the long-term viability of these valuable plant resources․
Plant Extracts and Their Applications
Fern extracts have been found to possess a range of bioactive compounds with potential applications in various fields․ The extraction process typically involves the use of solvents, such as ethanol or hexane, to isolate specific constituents from the plant material․ These extracts can then be incorporated into pharmaceuticals, cosmetics, and food products․ For instance, fern-derived antioxidants may be used to enhance the stability and shelf life of food products, while their antimicrobial properties could be leveraged in the development of natural preservatives․ Additionally, fern extracts have been explored as potential ingredients in skincare products, owing to their anti-inflammatory and antiseptic properties․ The precise formulation and application of these extracts can significantly impact their efficacy, underscoring the need for rigorous research and testing to ensure their safe and effective utilization․
Modern Research on Ferns
Contemporary studies on ferns employ advanced techniques, such as molecular phylogenetics and bioinformatics, to elucidate their evolutionary relationships, genomic structure, and biochemical properties, yielding novel insights into their biology․
Pharmacological Studies on Ferns
Pharmacological investigations of ferns have led to the discovery of various bioactive compounds, including flavonoids, alkaloids, and phenolic acids․ These studies have employed in vitro and in vivo models to evaluate the efficacy and safety of fern extracts in treating diverse health conditions․
The results of these studies indicate that certain fern species possess significant anti-inflammatory, antimicrobial, and antioxidant properties, suggesting their potential as natural therapies for managing chronic diseases․ Furthermore, some fern-derived compounds have demonstrated cytotoxic activity against cancer cell lines, warranting further investigation into their anticancer potential․
Ongoing research aims to elucidate the molecular mechanisms underlying the pharmacological effects of ferns and to identify lead compounds for the development of novel medications․ The integration of traditional knowledge with modern pharmacology has the potential to unlock the therapeutic value of ferns and contribute to the advancement of botanical medicine․
Potential Therapeutic Applications of Ferns
Ferns have been found to possess a range of bioactive compounds with potential therapeutic applications in the prevention and treatment of various diseases․ The antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties of fern extracts suggest their suitability for managing chronic conditions such as arthritis, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease․
The antimicrobial activity of certain fern species has implications for the development of novel antimicrobial agents, while the cytotoxic properties of others indicate potential applications in cancer therapy․ Additionally, the neuroprotective effects of some fern-derived compounds suggest their potential in the treatment of neurodegenerative disorders such as Alzheimer’s and Parkinson’s diseases․
Further research is necessary to fully elucidate the therapeutic potential of ferns and to explore their applications in clinical settings․ The development of fern-based medications could provide novel treatment options for a range of diseases and contribute to the advancement of natural therapies and botanical medicine․
Conservation Status of Ferns
Ferns face numerous threats to their survival, with many species listed as Endangered or Vulnerable on the IUCN Red List, necessitating urgent conservation efforts to protect these ancient and ecologically vital plants․
Threats to Fern Populations and Habitats
Fern populations and habitats are facing numerous threats, including deforestation, urbanization, and infrastructure development, leading to habitat destruction and fragmentation․ Climate change is also altering the delicate ecological balance, making it challenging for ferns to adapt and survive․ Overcollection for the horticulture trade and medicinal purposes has led to the depletion of wild populations․ Invasive species, such as rats and goats, are causing significant damage to fern habitats, particularly on islands․ Furthermore, pollution from agricultural runoff and industrial activities is contaminating water sources and soil, affecting fern growth and reproduction․ Human activities, such as mining and logging, are also disrupting the natural habitats of ferns, leading to population decline and even extinction․ It is essential to address these threats to conserve fern populations and habitats․
Efforts to Protect and Conserve Ferns
Conservation efforts are underway to protect and conserve fern populations and habitats․ National parks and protected areas have been established to safeguard critical habitats and prevent further destruction․ Ex situ conservation programs, such as fern nurseries and botanical gardens, are being implemented to propagate and reintroduce endangered species․ Community-based conservation initiatives are also being promoted, engaging local communities in fern conservation and sustainable land-use practices․ Furthermore, research institutions and organizations are conducting studies on fern ecology, taxonomy, and conservation biology to inform effective conservation strategies․ International collaborations and agreements, such as the Convention on International Trade in Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), are regulating the trade of threatened fern species․ These concerted efforts aim to mitigate the decline of fern populations and ensure the long-term conservation of these unique and fascinating plants․
In conclusion, the study of ferns offers a fascinating glimpse into the diversity and complexity of plant life․ Through their unique characteristics, adaptations, and uses, ferns have captivated the interest of botanists, ethnobotanists, and conservationists alike․ As we continue to navigate the complexities of environmental sustainability and human well-being, the importance of preserving and understanding fern populations cannot be overstated․ By embracing a multidisciplinary approach that incorporates scientific research, traditional knowledge, and conservation efforts, we can work towards a future where these ancient plants continue to thrive․ Ultimately, the preservation of ferns serves as a testament to our commitment to protecting the natural world and promoting a deeper appreciation for the intricate relationships between humans, plants, and the environment․ By doing so, we ensure a lasting legacy of botanical heritage for generations to come․
This piece exceeded expectations! Intriguing historical tidbits scattered throughout made me want more!
The article does an excellent job explaining complex concepts such as spore arrangement and frond morphology in simple terms. Well done!
One area where I
Minor quibble – could benefit from clearer subheadings between sections! Nonetheless engaging content all around!
It
This article provides an excellent introduction to the world of ferns! The author
I was particularly impressed by the section on ethnobotany. It
Would love if future articles expanded upon modern-day applications! Perhaps touching upon contemporary research & innovations?