I. Introduction
Uterine fibroids are a common concern during pregnancy‚ affecting maternal health and fetal well-being. This article discusses the risks and complications associated with fibroids during pregnancy‚ emphasizing the importance of awareness and monitoring.
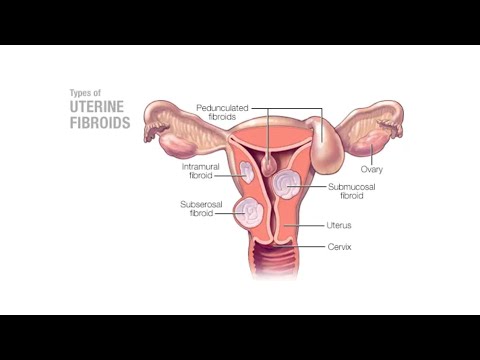
A. Definition and Prevalence of Uterine Fibroids
Uterine fibroids‚ also known as leiomyomas‚ are benign tumors that arise from the smooth muscle layer of the uterus. They can vary in size‚ shape‚ and location‚ and are often asymptomatic.
According to recent studies‚ uterine fibroids affect approximately 20-40% of women of reproductive age‚ with the prevalence increasing with age. Fibroids are more common among African American women‚ who are also more likely to experience symptoms and complications.
The exact cause of uterine fibroids remains unclear‚ but hormonal and genetic factors are thought to play a role. Estrogen and progesterone levels‚ in particular‚ may influence the growth and development of fibroids.
As fibroids can have significant implications for maternal health and fetal well-being during pregnancy‚ it is essential to understand their definition and prevalence. By acknowledging the scope of the issue‚ healthcare providers can better diagnose‚ manage‚ and treat fibroids‚ ultimately improving outcomes for pregnant women and their babies.
II. Risks Associated with Fibroids during Pregnancy
The presence of uterine fibroids during pregnancy can pose significant risks to maternal health and fetal well-being‚ necessitating careful monitoring and management to mitigate potential complications and adverse outcomes.
A. Maternal Health Risks
Women with uterine fibroids during pregnancy are at increased risk of developing various maternal health complications‚ including pelvic pain‚ vaginal bleeding‚ and pregnancy-induced hypertension. The presence of large or multiple fibroids can also lead to anemia‚ due to chronic blood loss‚ and a higher likelihood of requiring blood transfusions.
Furthermore‚ fibroids can cause ureteral obstruction‚ leading to urinary retention and potential renal impairment. Pregnant women with fibroids are also more likely to experience gastrointestinal symptoms‚ such as constipation and abdominal distension‚ due to the compression of adjacent organs by the growing uterus and fibroids.
It is essential for healthcare providers to closely monitor pregnant women with fibroids for these potential maternal health risks and provide timely interventions to prevent adverse outcomes and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Early detection and management of maternal health risks associated with fibroids are critical to preventing long-term health consequences and promoting optimal maternal well-being during pregnancy.
B. Fetal Growth Restriction
Fetal growth restriction (FGR) is a significant concern in pregnancies complicated by uterine fibroids. The presence of large or multiple fibroids can lead to placental insufficiency‚ resulting in inadequate fetal nutrition and oxygenation. This can cause FGR‚ which is associated with increased perinatal morbidity and mortality.
Studies have shown that pregnant women with fibroids are at higher risk of developing FGR‚ particularly if the fibroids are large or located near the placenta. FGR can be diagnosed through ultrasound evaluation of fetal growth parameters‚ such as abdominal circumference and femur length.
Close monitoring of fetal growth and well-being is essential in pregnancies complicated by fibroids. This includes regular ultrasound assessments and non-stress testing to detect any signs of fetal distress. In some cases‚ delivery may be recommended if FGR is severe or if there are concerns about fetal well-being.
Early detection and management of FGR are critical to optimizing fetal outcomes and reducing the risk of adverse perinatal events.
C. Placental Abruption
Placental abruption is a serious pregnancy complication that can occur in women with uterine fibroids. It is characterized by the premature separation of the placenta from the uterus‚ which can lead to severe bleeding‚ fetal distress‚ and even maternal death.
The presence of fibroids increases the risk of placental abruption‚ particularly if the fibroids are large or located near the placenta. This is because fibroids can cause inflammation and scarring in the uterine lining‚ leading to placental insufficiency and increased risk of abruption.
Symptoms of placental abruption may include sudden onset of vaginal bleeding‚ abdominal pain‚ and fetal distress. If suspected‚ placental abruption is typically diagnosed through ultrasound evaluation and laboratory tests.
Prompt medical attention is essential in cases of suspected placental abruption. Women with fibroids should be aware of the risks and report any symptoms to their healthcare provider immediately. Close monitoring and timely intervention can help mitigate the risks associated with placental abruption and ensure the best possible outcomes for both mother and fetus.
III. Pregnancy Complications and Fibroids
The presence of uterine fibroids during pregnancy increases the risk of various complications‚ including preterm labor‚ cesarean delivery‚ and fetal growth restriction‚ which can have significant implications for maternal and fetal health.
A. Preterm Labor and Delivery
Preterm labor and delivery are significant complications associated with uterine fibroids during pregnancy. Fibroids can cause pelvic pain‚ vaginal bleeding‚ and uterine contractions‚ leading to premature cervical dilation and effacement. Women with fibroids are more likely to experience preterm labor‚ particularly if the fibroids are large or located near the cervix.
Studies have shown that the presence of fibroids increases the risk of preterm birth by 20-30%. Furthermore‚ women with fibroids are more likely to require hospitalization for preterm labor‚ and may require tocolytic therapy to delay delivery. In some cases‚ preterm delivery may be necessary due to fetal distress or other complications. It is essential for women with fibroids to receive close prenatal care and monitoring to prevent and manage preterm labor and delivery.
Early detection and management of preterm labor are critical in preventing adverse outcomes for both the mother and the fetus. Healthcare providers should be aware of the increased risk of preterm labor in women with fibroids and take a proactive approach to managing these patients.
B. Cesarean Delivery
The presence of uterine fibroids during pregnancy increases the risk of cesarean delivery. Fibroids can cause fetal malposition‚ placental abruption‚ and uterine dystocia‚ making vaginal delivery more challenging. Additionally‚ large fibroids may obstruct the birth canal‚ necessitating a cesarean section.
Studies have shown that women with fibroids are 2-3 times more likely to require a cesarean delivery compared to those without fibroids. The likelihood of cesarean delivery is particularly high if the fibroids are large‚ multiple‚ or located near the cervix. In some cases‚ a cesarean delivery may be planned in advance due to concerns about fetal safety or the potential for complications during vaginal delivery.
A thorough evaluation of the uterus and fetus is essential in determining the best approach for delivery. Healthcare providers should carefully assess the size‚ location‚ and number of fibroids‚ as well as the overall health of the mother and fetus‚ when deciding whether a cesarean delivery is necessary.
C. Miscarriage and Stillbirth
The presence of uterine fibroids during pregnancy increases the risk of miscarriage and stillbirth. Fibroids can disrupt fetal development and increase the likelihood of placental insufficiency‚ which can lead to fetal demise. Additionally‚ large fibroids may compress or distort the uterine cavity‚ reducing blood flow to the fetus.
Studies have shown that women with fibroids are at a higher risk of miscarriage‚ particularly in the first trimester. The risk of stillbirth is also increased‚ especially if the fibroids are large or located near the placenta. Furthermore‚ fibroids can cause chronic inflammation and oxidative stress‚ which can contribute to fetal growth restriction and increased risk of stillbirth.
Close monitoring of fetal well-being and regular prenatal care are crucial for pregnant women with fibroids. Healthcare providers should be vigilant for signs of fetal distress or growth restriction‚ and intervene promptly if necessary to prevent adverse outcomes. In some cases‚ bed rest or other interventions may be recommended to reduce the risk of miscarriage or stillbirth.
IV. Managing Fibroids during Pregnancy
Effective management of fibroids during pregnancy involves a multidisciplinary approach‚ incorporating regular prenatal care‚ pain management strategies‚ and selective surgical interventions to minimize risks and optimize maternal-fetal outcomes.
A. Regular Prenatal Care
Regular prenatal care is essential for pregnant women with uterine fibroids. Frequent check-ups with a healthcare provider allow for close monitoring of the fibroids’ size‚ location‚ and potential impact on the pregnancy. This enables timely identification of any complications or concerns‚ facilitating prompt intervention and minimizing risks to both mother and fetus.
A thorough prenatal care plan should include⁚
- Routine ultrasound examinations to track fibroid growth and assess fetal well-being
- Blood pressure and urine protein monitoring to detect potential signs of preeclampsia
- Regular fetal movement assessments and non-stress tests to evaluate fetal health
- Open communication with the healthcare provider to address any concerns or symptoms
By prioritizing regular prenatal care‚ women with fibroids can better navigate their pregnancy and make informed decisions about their care‚ ultimately promoting a healthier outcome for both mother and baby.
B. Pain Management
Effective pain management is crucial for pregnant women with uterine fibroids‚ as these growths can cause significant discomfort‚ pelvic pain‚ and vaginal bleeding. A comprehensive pain management plan should be developed in collaboration with a healthcare provider to ensure the well-being of both mother and fetus.
Pain relief options may include⁚
- Acetaminophen (Tylenol) or other over-the-counter pain medications‚ under the guidance of a healthcare provider
- Prescription pain medications‚ such as opioids or muscle relaxants‚ when necessary and closely monitored
- Alternative therapies‚ like acupuncture‚ massage‚ or physical therapy‚ to alleviate pain and promote relaxation
- Lifestyle modifications‚ including rest‚ hydration‚ and stress reduction techniques
It is essential to carefully weigh the benefits and risks of each pain management option‚ as some may impact fetal development or interact with other medications; By prioritizing effective pain management‚ women with fibroids can better cope with their symptoms and maintain a healthier pregnancy.
C. Surgical Intervention
In some cases‚ surgical intervention may be necessary to manage uterine fibroids during pregnancy. However‚ surgery is typically reserved for severe cases where the fibroids pose a significant threat to maternal or fetal health.
Myomectomy‚ a procedure to remove the fibroids‚ is generally avoided during pregnancy due to the risk of complications‚ including⁚
- Preterm labor and delivery
- Fetal distress or growth restriction
- Maternal bleeding or infection
In rare instances‚ a cesarean myomectomy may be performed during a scheduled cesarean delivery. This approach is usually considered when the fibroid is pedunculated and easily accessible; It is essential for women to discuss the risks and benefits of surgical intervention with their healthcare provider‚ as each case requires individualized consideration and careful decision-making.
A thorough evaluation of the woman’s overall health and pregnancy status will inform the decision to pursue surgical intervention‚ always prioritizing the well-being of both mother and fetus.
V. Conclusion
Awareness and monitoring of uterine fibroids during pregnancy are crucial to mitigate associated risks and complications. Close collaboration between healthcare providers and expectant mothers ensures optimal maternal and fetal outcomes‚ promoting a healthy pregnancy experience.
A. Importance of Awareness and Monitoring
Vigilant awareness and monitoring of uterine fibroids during pregnancy are essential for early detection and management of potential complications. Expectant mothers should be educated on the risks associated with fibroids‚ enabling them to recognize warning signs and seek medical attention promptly.
Healthcare providers must maintain a high index of suspicion for fibroid-related complications‚ conducting regular ultrasounds and clinical assessments to monitor fetal growth and maternal well-being. This proactive approach facilitates timely interventions‚ reducing the risk of adverse outcomes and promoting a healthy pregnancy experience.
The section discussing risks associated with uterinefibroidsduringpregnancy particularly stood out me.Clear explanations enable readers grasp severity situation.I suggest inclusion patient testimonies future articles provide emotional context personal struggles.
While this article provides valuable insights into uterine fibroids,there seems little attention given causes or preventive measures.Further research exploring these aspects would greatly enhance our understanding prevention strategies.
I found this article very helpful in understanding my own condition.I was diagnosed with uterine fibroids during my second trimester, I wish I had access this information earlier.It would be great if future articles could delve into treatment options more extensively.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of uterine fibroids during pregnancy, highlighting the importance of awareness and monitoring. The discussion on the definition, prevalence, and risks associated with fibroids is thorough and informative.
As an obstetrician, I appreciate the emphasis on early detection and management of uterine fibroids during pregnancy.The article accurately outlines the potential risks to maternal health, such as pelvic pain, vaginal bleeding, which underscores need for close monitoring.