Food Tube Procedure⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
Gastrostomy involves creating an opening in the stomach to insert a feeding tube, providing essential nutritional support through enteral nutrition, necessitating a thorough understanding of the medical procedure and hospital stay requirements.
Introduction
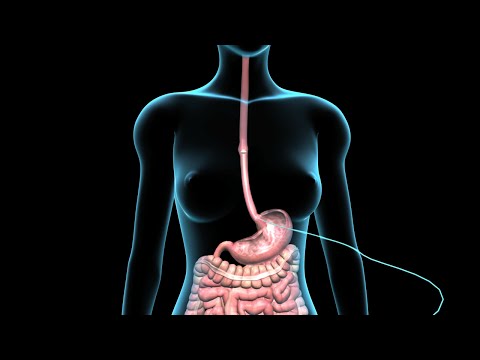
A food tube procedure, also known as gastrostomy, is a vital medical intervention aimed at providing nutritional support to individuals with compromised digestive systems or swallowing disorders. This procedure involves the insertion of a feeding tube directly into the stomach, bypassing the mouth and esophagus, to ensure adequate nutrition and hydration.
The goal of this comprehensive guide is to provide patients, families, and healthcare professionals with a thorough understanding of the food tube procedure, its indications, benefits, and potential complications. By exploring the various aspects of this medical intervention, we aim to empower individuals with the knowledge necessary to make informed decisions about their care and treatment options.
Throughout this guide, we will examine the key elements of the food tube procedure, from preparation to post-procedure care, highlighting the importance of patient-centered care and multidisciplinary collaboration in achieving optimal outcomes.
Indications for the Procedure
Clinical indications for gastrostomy include severe swallowing disorders, digestive system obstructions, and inadequate nutritional intake, necessitating enteral nutrition support to maintain optimal health and prevent malnutrition and related complications.
Swallowing Disorders
Swallowing disorders, also known as dysphagia, can significantly impact an individual’s ability to consume adequate nutrition, leading to malnutrition, dehydration, and related complications. Conditions such as stroke, cerebral palsy, and neurodegenerative diseases can cause dysphagia, necessitating the need for alternative nutritional support. A gastrostomy tube can provide a safe and effective means of delivering essential nutrients directly into the stomach, bypassing the oral cavity and esophagus. This can help alleviate symptoms of dysphagia, such as difficulty swallowing, choking, and aspiration, and ensure the individual receives the necessary nutrients for optimal health. In some cases, swallowing disorders may be temporary, and the gastrostomy tube can be removed once the underlying condition has been resolved. However, in cases where dysphagia is a chronic condition, the gastrostomy tube may be a long-term solution, requiring ongoing care and management to prevent complications.
Digestive System Issues
Certain digestive system issues can necessitate the use of a gastrostomy tube to ensure adequate nutritional support. Conditions such as Crohn’s disease, ulcerative colitis, and short bowel syndrome can lead to malabsorption of essential nutrients, resulting in malnutrition and related complications. A gastrostomy tube can provide a means of delivering nutrients directly into the stomach, bypassing affected areas of the digestive tract. Additionally, certain gastrointestinal motility disorders, such as gastroparesis, can cause food to remain in the stomach for extended periods, leading to nausea, vomiting, and malnutrition. A gastrostomy tube can help alleviate these symptoms by allowing for the direct delivery of nutrients into the stomach. In some cases, digestive system issues may be temporary, and the gastrostomy tube can be removed once the underlying condition has been resolved. Effective management of the gastrostomy tube is crucial to preventing complications and ensuring optimal nutritional support.
The Procedure
The gastrostomy procedure involves creating a stoma in the abdominal wall, allowing for the insertion of a feeding tube into the stomach, typically performed under local anesthesia or conscious sedation in a sterile environment.
Preparation
Prior to the gastrostomy procedure, patients undergo a comprehensive evaluation to determine the suitability of the intervention. This assessment includes a thorough review of their medical history, current medications, and underlying health conditions. A physical examination is also conducted to identify potential anatomical abnormalities or other factors that may impact the procedure.
Additionally, patients are instructed to refrain from eating and drinking for a specified period before the procedure to minimize the risk of aspiration. Any medications that may interfere with the procedure are also discontinued or adjusted as necessary. Blood tests and imaging studies, such as X-rays or computed tomography (CT) scans, may be ordered to evaluate the patient’s overall health status and identify any potential complications.
The healthcare team provides detailed explanations of the procedure, its benefits, and potential risks, ensuring that patients are fully informed and able to provide informed consent. Patients are also educated on post-procedure care and management to facilitate a smooth recovery.
Insertion of the Feeding Tube
The insertion of the feeding tube is typically performed under local anesthesia and conscious sedation to minimize discomfort and anxiety. The procedure involves making a small incision in the abdominal wall, through which the gastrostomy tube is carefully inserted into the stomach.
The tube is then secured in place using sutures or staples to prevent dislodgement. The position of the tube is verified through imaging studies, such as fluoroscopy or endoscopy, to ensure proper placement and prevent complications.
During the procedure, the patient’s vital signs are closely monitored to ensure stability and comfort. The entire process typically takes approximately 30-60 minutes to complete, depending on the complexity of the case and the expertise of the healthcare team. Upon successful insertion, the feeding tube is ready for use, allowing patients to receive the necessary nutritional support for optimal health outcomes.
A qualified healthcare professional performs the procedure, taking all necessary precautions to minimize risks and ensure a successful outcome.
Post-Procedure Care
Following the insertion of the feeding tube, patients require close monitoring and post-procedure care to ensure a smooth recovery and minimize potential complications. This includes regular assessment of the tube site for signs of infection, leakage, or dislodgement.
Pain management is also a crucial aspect of post-procedure care, with medications administered as needed to alleviate discomfort and promote relaxation. Patients are also educated on proper wound care and dressing changes to maintain a clean and dry environment around the tube site.
In addition, a comprehensive plan for enteral nutrition is developed, outlining the type and frequency of feedings, as well as any necessary supplements or medications. Healthcare professionals work closely with patients and their families to ensure a thorough understanding of post-procedure care instructions, promoting a successful transition to home care and reducing the risk of complications.
Regular follow-up appointments are also scheduled to monitor the patient’s progress and address any concerns or issues that may arise during the recovery period.
Hospital Stay and Recovery
Patients typically require a short hospital stay following the procedure, during which time they receive close monitoring and care to ensure a smooth and successful recovery from the gastrostomy and initiation of enteral nutrition.
Initial Recovery
The initial recovery period following a gastrostomy procedure is crucial for ensuring a smooth transition to enteral nutrition. During this time, patients are closely monitored by healthcare professionals for any signs of complications or adverse reactions. The patient’s vital signs, such as blood pressure, pulse, and oxygen saturation, are regularly checked to ensure stability. Additionally, the surgical site is assessed for any signs of bleeding, infection, or leakage. Patients may experience some discomfort, pain, or swelling at the surgical site, which can be managed with medication as prescribed by their doctor. It is essential for patients to follow their healthcare provider’s instructions regarding post-operative care, including wound care, medication management, and activity restrictions, to promote optimal healing and minimize the risk of complications. By adhering to these guidelines, patients can ensure a successful initial recovery and set the stage for a smooth transition to ongoing care.
Ongoing Care
To ensure optimal outcomes, patients with a gastrostomy tube require ongoing care and management. This includes regular check-ups with their healthcare provider إلى assess the tube’s placement and function, as well as the patient’s overall nutritional status and digestive health. Patients or caregivers must also learn how to properly care for the tube, including flushing and cleaning it to prevent blockages and infections. Additionally, patients may need to make adjustments to their diet and lifestyle to accommodate the tube and ensure adequate nutrition. This may involve working with a registered dietitian to develop a personalized meal plan. Furthermore, patients should be aware of potential complications, such as tube dislodgement or skin irritation, and know how to respond promptly if issues arise. By prioritizing ongoing care and maintenance, patients can minimize risks and maximize the benefits of their gastrostomy tube, promoting optimal health and well-being over the long term.
Complications and Risks
Gastrostomy tube insertion carries potential complications, including infection, bleeding, and bowel obstruction, emphasizing the need for careful risk assessment, close monitoring, and prompt intervention to mitigate adverse outcomes and ensure patient safety.
Potential Complications
Potential complications associated with gastrostomy tube insertion include infection, bleeding, and bowel obstruction. Additionally, patients may experience leakage around the tube site, skin irritation, or allergic reactions to the tube material. In some cases, the tube may become dislodged or clogged, requiring prompt intervention to prevent malnutrition and dehydration.
Furthermore, patients with certain underlying medical conditions, such as diabetes or immunosuppression, may be at increased risk for developing complications. It is essential for healthcare providers to closely monitor patients undergoing gastrostomy tube insertion and to take prompt action in the event of any adverse developments. By being aware of the potential complications and taking steps to mitigate them, healthcare providers can help minimize the risks associated with this medical procedure and ensure the best possible outcomes for their patients.
A thorough understanding of the potential complications and risks associated with gastrostomy tube insertion is crucial for providing informed patient care and optimizing treatment outcomes.
Minimizing Risks
To minimize the risks associated with gastrostomy tube insertion, healthcare providers should carefully evaluate patients prior to the procedure to identify any underlying conditions that may increase the risk of complications. This includes assessing the patient’s nutritional status, medical history, and current medications.
Additionally, strict sterile technique should be employed during the insertion procedure to reduce the risk of infection. Patients should also receive comprehensive education on tube care and maintenance, including proper cleaning and dressing changes, to prevent complications and promote optimal healing.
Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are also crucial to monitor the patient’s progress and address any concerns or issues promptly. By taking a proactive and multidisciplinary approach to patient care, healthcare providers can significantly minimize the risks associated with gastrostomy tube insertion and optimize treatment outcomes for their patients. This enables patients to receive the necessary nutritional support while minimizing the risk of adverse events.
This comprehensive guide provides a clear understanding of the food tube procedure and its indications. The language used is straightforward and accessible to both patients and healthcare professionals.
As a healthcare professional, I appreciate the thoroughness of this guide in covering all aspects of gastrostomy. The emphasis on patient-centered care and multidisciplinary collaboration is particularly noteworthy.
I found this article informative and helpful in understanding my mother
While generally well-written, I noticed some minor errors in formatting throughout the article. Nonetheless, it remains an excellent resource on gastrostomy.
This guide demonstrates a clear commitment to empowering patients with knowledge about their care options. I commend the authors on their efforts.
I appreciated how this article balanced technical information with accessible language suitable for non-experts like myself.
While this guide is comprehensive, I would have liked more information on potential complications associated with gastrostomy. Nevertheless, it remains a valuable resource.
As a caregiver for someone with dysphagia, I appreciate the attention given to swallowing disorders in this article. The explanation of enteral nutrition support was particularly helpful.