Hearing Loss⁚ Understanding the Causes and Consequences
Hearing loss is a pervasive and multifaceted health issue‚ affecting millions worldwide. It can result from various factors‚ including deafness‚ ear damage‚ and auditory nerve damage‚ impacting an individual’s quality of life and social interactions.
Introduction to Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a complex and multifaceted condition that affects individuals of all ages and backgrounds. It can manifest in various forms‚ ranging from mild to profound‚ and can be caused by a multitude of factors‚ including genetic predisposition‚ environmental influences‚ and certain medical conditions.
The human ear is a delicate and intricate system‚ comprising the outer‚ middle‚ and inner ear. Sound waves are transmitted through the air‚ causing the eardrum to vibrate‚ which in turn stimulates the cochlea‚ ultimately leading to the transmission of electrical signals to the brain.
When any part of this system is damaged or compromised‚ hearing loss can occur. This can have significant consequences on an individual’s daily life‚ causing difficulties with communication‚ social interactions‚ and overall well-being.
Understanding the causes‚ symptoms‚ and effects of hearing loss is crucial in developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. By shedding light on this often-overlooked condition‚ we can work towards creating a more inclusive and supportive environment for individuals affected by hearing loss.
Through advances in medical research and technology‚ we have made significant strides in addressing hearing loss. However‚ continued awareness and education are essential in promoting hearing health and mitigating the impact of this condition.
Types of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can be broadly categorized into three main types⁚ conductive‚ sensorineural‚ and mixed. Each type has distinct characteristics and underlying causes‚ requiring specialized diagnosis and treatment approaches to effectively address the specific needs of individuals affected.
Sensorineural Hearing Loss
Sensorineural hearing loss (SNHL) is a type of hearing impairment that occurs due to damage to the inner ear or the auditory nerve. This damage disrupts the transmission of sound waves to the brain‚ resulting in permanent hearing loss.
The causes of SNHL can be diverse‚ including exposure to loud noises‚ certain medications‚ and age-related degeneration. Additionally‚ conditions such as otosclerosis and viral infections like rubella or meningitis can also contribute to the development of SNHL.
Individuals with SNHL often experience difficulty perceiving high-frequency sounds and may struggle with speech recognition‚ particularly in noisy environments. Tinnitus‚ a ringing or buzzing sensation in the ears‚ may also be present.
A comprehensive audiological evaluation‚ including pure-tone audiometry and speech audiometry‚ is necessary to diagnose SNHL. While medical treatment options are limited‚ individuals with SNHL can benefit from amplification devices‚ such as hearing aids‚ and communication therapy to improve their overall quality of life.
Early detection and intervention are crucial in addressing SNHL‚ as they can significantly impact an individual’s social‚ emotional‚ and cognitive well-being. A thorough understanding of the underlying causes and effects of SNHL is essential for developing effective management strategies.
Causes of Hearing Loss
Hearing loss can result from a complex interplay of genetic‚ environmental‚ and lifestyle factors. Noise-induced hearing loss‚ ear infections‚ and earwax buildup are among the common causes‚ underscoring the need for proactive prevention and timely intervention strategies.
Age-Related Hearing Loss
Age-related hearing loss‚ also known as presbycusis‚ is a common condition affecting millions of individuals worldwide. It is characterized by a progressive decline in hearing acuity‚ particularly in the high-frequency range‚ making it challenging to understand speech and other sounds.
The exact causes of age-related hearing loss are multifaceted and not fully understood. However‚ research suggests that it may be attributed to a combination of factors‚ including the degeneration of hair cells in the cochlea‚ changes in the auditory nerve‚ and decreased blood flow to the ear.
Age-related hearing loss typically begins in the fifth or sixth decade of life and may progress gradually over time. While it is a natural part of the aging process‚ there are steps that can be taken to mitigate its effects‚ such as regular hearing assessments and the use of assistive listening devices.
It is essential for individuals experiencing age-related hearing loss to seek professional evaluation and treatment to address any underlying conditions and improve their overall quality of life. By doing so‚ they can better manage their hearing loss and maintain their independence and social connections.
Noise-Induced Hearing Loss
Noise-induced hearing loss (NIHL) is a preventable and irreversible condition caused by prolonged exposure to high levels of sound. Prolonged exposure to decibel levels exceeding 85 decibels can lead to permanent damage to the hair cells in the cochlea‚ resulting in hearing loss.
NIHL can occur suddenly or gradually‚ depending on the duration and intensity of the noise exposure. Individuals working in noisy environments‚ such as construction sites or factories‚ are at a higher risk of developing NIHL.
Additionally‚ recreational activities like attending concerts‚ shooting firearms‚ or listening to music at high volumes through personal audio devices can also cause NIHL. It is essential to take preventative measures‚ such as wearing ear protection‚ turning down the volume‚ or taking regular breaks in quiet environments‚ to mitigate the risk of NIHL.
Early detection and prevention are crucial in addressing NIHL. By promoting awareness and education about the risks associated with noise exposure‚ individuals can take proactive steps to protect their hearing and prevent this type of hearing loss. By doing so‚ they can safeguard their auditory health and overall quality of life.
Treatment Options for Hearing Loss
Effective treatment options are available to manage hearing loss‚ including hearing aids‚ cochlear implants‚ and other assistive listening devices. A comprehensive evaluation by an audiologist or hearing specialist is crucial in determining the most suitable treatment approach.
Hearing Aids
Hearing aids are a primary treatment option for individuals with hearing loss‚ designed to amplify sound waves and improve communication. They consist of a microphone‚ amplifier‚ and receiver‚ which work together to process and deliver sound to the ear.
There are various types of hearing aids available‚ including behind-the-ear (BTE)‚ in-the-ear (ITE)‚ and completely-in-canal (CIC) models. Each type has its unique features and benefits‚ catering to different individual needs and preferences.
Advancements in technology have led to the development of digital hearing aids‚ which offer improved sound quality‚ noise reduction‚ and speech recognition capabilities. Some models also feature Bluetooth connectivity‚ allowing users to stream audio directly from their devices.
A thorough evaluation by an audiologist or hearing specialist is necessary to determine the most suitable hearing aid model and configuration for each individual. Proper fitting and adjustment of the device are crucial to ensure optimal performance and user satisfaction.
Regular maintenance and follow-up appointments are also essential to ensure the hearing aid continues to function effectively and address any potential issues or concerns that may arise.
Cochlear Implants
A cochlear implant is a medical device designed to bypass damaged or non-functioning parts of the ear and directly stimulate the auditory nerve. It consists of an external sound processor‚ a cochlear implant‚ and an electrode array inserted into the cochlea.
The sound processor captures and converts sound waves into electrical signals‚ which are then transmitted to the implant and electrode array. These signals stimulate the auditory nerve‚ allowing the brain to interpret them as sound.
Cochlear implants are typically recommended for individuals with severe to profound sensorineural hearing loss who have limited benefit from traditional hearing aids. The implantation procedure is usually performed on an outpatient basis‚ and the device is activated several weeks after surgery.
While cochlear implants do not restore natural hearing‚ they can significantly improve speech recognition and communication skills. Many recipients experience improved ability to understand speech in quiet environments and participate in conversations with greater ease. Additionally‚ cochlear implants can also help reduce the perceived severity of tinnitus in some individuals.
Post-implantation rehabilitation and follow-up appointments with an audiologist or hearing specialist are essential to optimize device performance and ensure maximum benefit from the cochlear implant.
In conclusion‚ addressing hearing loss requires a comprehensive approach‚ encompassing education‚ prevention‚ and treatment. By promoting awareness and taking proactive steps‚ individuals can mitigate the impact of hearing loss and maintain a better quality of life.
Prevention and Protection
Preventing hearing loss is crucial‚ as it can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life. To achieve this‚ it is essential to adopt proactive measures that protect the ears from damage.
Limiting exposure to loud sound waves is vital‚ especially in environments where decibel levels exceed 85 dB. Using earplugs or earmuffs in such situations can help mitigate potential harm.
Regular ear check-ups are also important for identifying potential issues‚ such as earwax buildup‚ before they cause significant harm. Furthermore‚ avoiding insertion of objects into the ear canal can help prevent damage to the eardrum.
In addition‚ maintaining a healthy lifestyle‚ including a balanced diet and regular exercise‚ can contribute to overall auditory well-being. By taking these preventative measures‚ individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing hearing loss and maintain optimal ear health.
Moreover‚ education and awareness are key components in preventing hearing loss. Informing others about the importance of hearing protection can inspire a collective effort to prioritize auditory well-being.
Ultimately‚ by prioritizing prevention and protection‚ individuals can safeguard their hearing and enjoy a lifetime of healthy auditory function.
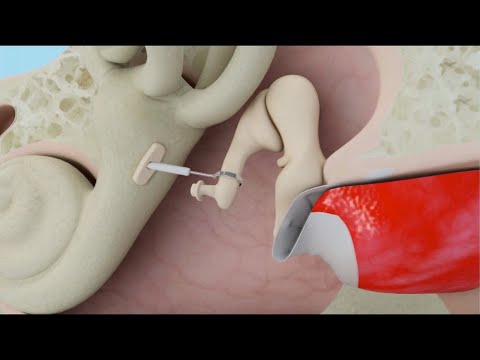
The section on the human ear system is informative, but I think it would benefit from additional diagrams or illustrations to help readers visualize the process.
I would like to see more discussion on prevention strategies, such as protecting one
This article provides a comprehensive overview of hearing loss, its causes, and consequences. The introduction effectively sets the stage for the rest of the article, highlighting the complexity of the condition.
Overall, this article provides a solid foundation for understanding hearing loss, but could benefit from additional resources or references for readers seeking further information.
“I commend the author for tackling this important topic, raising awareness about a condition that affects so many people worldwide.
I appreciate how the article breaks down the different types of hearing loss, making it easier for readers to understand the nuances of each category.
I appreciate how the article acknowledges advances in medical research and technology, offering hope for those affected by hearing loss.
The emphasis on awareness and education is crucial in promoting hearing health, as many people underestimate the impact of hearing loss on daily life.
The article highlights the importance of early detection and treatment, but could explore current treatments options in more depth.