Understanding Hoarseness⁚ Definition and Prevalence
Harness is characterized by an abnormal voice quality, often described as hoarse, raspy, breathy, or strained․ According to epidemiological studies, approximately 20% of the adult population experiences hoarseness at some point in their lives, affecting both men and women equally․
Causes of Hoarseness
The etiology of hoarseness is multifactorial, involving various factors that affect the vocal cords and surrounding tissues․ Common causes include vocal cord lesions, medical conditions, environmental exposures, and lifestyle choices, which can be further categorized into distinct subgroups․
Vocal Cord Lesions and Strain
Vocal cord lesions are a primary cause of hoarseness, often resulting from vocal strain, misuse, or overuse․ Prolonged vocal exertion, such as singing or public speaking, can lead to the formation of vocal cord nodules or polyps, which disrupt normal vocal cord closure and vibration․
Other vocal cord lesions, including cysts, papillomas, and granulomas, can also cause hoarseness․ These lesions may be benign or malignant, and their presence can be detected through laryngoscopy or other diagnostic techniques․
Vocal strain, in the absence of an apparent lesion, can also contribute to hoarseness․ This strain may result from poor vocal technique, inadequate breath support, or excessive vocal use․ The consequences of vocal strain can be exacerbated by factors such as acid reflux, allergies, or sinus infections, which can further compromise vocal cord function and overall voice quality․
A comprehensive evaluation by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or a speech-language pathologist is essential for determining the underlying cause of hoarseness and developing an effective treatment plan to address vocal cord lesions or strain․
Medical Conditions and Hoarseness
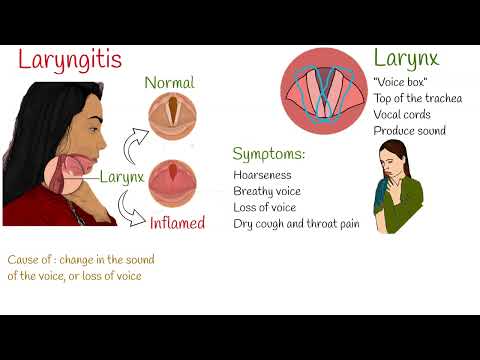
Certain medical conditions can contribute to the development of hoarseness, including laryngitis, thyroid problems, and hormonal imbalances․ Laryngitis, an inflammation of the larynx, can be caused by a viral or bacterial infection, and may result in hoarseness, vocal fatigue, and throat pain․
Thyroid disorders, such as hypothyroidism or hyperthyroidism, can also affect the voice, leading to changes in vocal quality, pitch, or volume․ Hormonal imbalances, particularly those experienced during menopause or pregnancy, can also impact the voice, causing hoarseness, breathiness, or vocal strain․
More serious medical conditions, such as throat cancer or neurological disorders, can also manifest as hoarseness․ Throat cancer, which includes cancers of the larynx, pharynx, or esophagus, may cause persistent hoarseness, vocal changes, or difficulty swallowing․ Neurological disorders, such as Parkinson’s disease or multiple sclerosis, can affect the nerve supply to the larynx, leading to vocal tremors, weakness, or hoarseness․
A thorough medical evaluation is essential for identifying underlying medical conditions that may be contributing to hoarseness, as early detection and treatment can significantly improve voice quality and overall health outcomes․
Environmental and Lifestyle Factors
Vocal abuse, misuse, or overuse can also lead to hoarseness․ This can occur due to prolonged talking, shouting, or singing without adequate rest periods, or using an improper speaking or singing technique․ Additionally, working in noisy environments or being exposed to loud sounds can strain the voice, leading to hoarseness․
Allergies and sinus infections can also affect the voice, causing postnasal drip, throat irritation, and subsequent hoarseness․ Furthermore, exposure to environmental pollutants, such as dust, chemicals, or pollutants, can irritate the vocal cords and contribute to hoarseness․
Acid reflux, also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), can also cause hoarseness by exposing the vocal cords to stomach acid, leading to inflammation and scarring․ Making healthy lifestyle choices, such as quitting smoking, managing allergies, and avoiding vocal strain, can help prevent and alleviate hoarseness caused by environmental and lifestyle factors․
Diagnosing Hoarseness
Diagnosing the underlying cause of hoarseness requires a comprehensive evaluation by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or a primary care physician․ The diagnostic process typically begins with a thorough medical history to identify potential causes, such as recent illnesses, allergies, or exposure to environmental irritants․
A physical examination of the head and neck is also performed to assess for any abnormalities, such as vocal cord lesions, nasal congestion, or sinusitis․ The physician may use a laryngoscope to visually examine the vocal cords and larynx for any signs of inflammation, scarring, or lesions․
In some cases, additional tests may be ordered to confirm the diagnosis, such as a thyroid function test to rule out hypothyroidism or a gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) test to assess for acid reflux․ Imaging studies, such as a computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scan, may also be used to evaluate the larynx and surrounding tissues․
A thorough diagnosis is essential to determine the underlying cause of hoarseness and develop an effective treatment plan․ A proper diagnosis can help to identify potential health risks and prevent long-term damage to the vocal cords and surrounding tissues․
Treatments for Hoarseness
Treatment options for hoarseness vary depending on the underlying cause, and may include medications, lifestyle modifications, speech therapy, or surgical interventions․ A healthcare professional will develop a personalized treatment plan to address the specific needs of each individual․
Conservative Treatments
Conservative treatments for hoarseness focus on addressing the underlying cause of the condition, while minimizing the risk of complications․ These approaches may include⁚
- Vocal rest⁚ Avoiding vocal strain by refraining from speaking or singing․
- Hydration⁚ Drinking plenty of water to keep the vocal cords hydrated and lubricated․
- Humidification⁚ Using a humidifier to add moisture to the air, helping to soothe the vocal cords․
- Speech therapy⁚ Working with a speech-language pathologist to develop healthy vocal habits and techniques․
- Medications⁚ Using medications such as antacids, antihistamines, or corticosteroids to treat underlying conditions․
These conservative treatments are often effective in resolving hoarseness, especially when caused by vocal strain, allergies, or acid reflux․ A healthcare professional will work with the individual to develop a personalized treatment plan, tailoring the approach to their specific needs and circumstances․
In many cases, conservative treatments can help to resolve hoarseness without the need for more invasive interventions․ However, if symptoms persist or worsen, further evaluation and treatment may be necessary․
Surgical Interventions
In some cases, surgical interventions may be necessary to treat underlying conditions causing hoarseness; These procedures are typically performed by an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist or a laryngologist․
- Vocal cord lesion removal⁚ Surgical excision of vocal cord nodules, polyps, or cysts that are causing hoarseness․
- Laryngoscopy⁚ A procedure in which a flexible or rigid scope is inserted through the mouth to visualize the vocal cords and surrounding tissues․
- Micro-laryngoscopy⁚ A surgical procedure that uses a microscope to examine and remove lesions from the vocal cords․
- Thyroid surgery⁚ In cases where hoarseness is caused by a thyroid condition, surgical removal of part or all of the thyroid gland may be necessary․
Surgical interventions are usually reserved for cases where conservative treatments have been ineffective or when a more serious underlying condition is suspected․ A thorough evaluation and consultation with a healthcare professional will help determine if surgery is the best course of treatment for an individual’s specific case of hoarseness․
It is essential to note that surgical interventions carry risks and complications, and should only be considered under the guidance of a qualified healthcare professional․
Preventing Hoarseness
To minimize the risk of developing hoarseness, several preventive measures can be taken․ These include⁚
- Vocal hygiene practices⁚ Avoid screaming, shouting, or making excessive noise, as these can strain the vocal cords․
- Stay hydrated⁚ Drink plenty of water to keep the vocal cords and surrounding tissues well-lubricated․
- Avoid irritants⁚ Refrain from smoking and avoid exposure to pollutants, dust, and other substances that can irritate the throat․
- Maintain good posture⁚ Proper posture can help reduce strain on the vocal cords and surrounding muscles․
- Warm up and cool down⁚ Before and after speaking or singing, perform simple vocal exercises to loosen up the vocal cords and prevent strain․
By incorporating these habits into daily life, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing hoarseness․ Additionally, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, can also help to support overall vocal health and prevent hoarseness․
By taking proactive steps to protect and care for the voice, individuals can enjoy optimal vocal health and minimize the risk of hoarseness and related voice disorders․
When to Seek Medical Attention
If hoarseness persists or worsens over time, it is essential to seek medical attention to rule out any underlying conditions that may be causing the symptoms․ Individuals should consult a healthcare professional if they experience⁚
- Persistent hoarseness lasting more than two weeks
- Sudden onset of hoarseness without a clear cause
- Difficulty swallowing or breathing
- Pain or discomfort in the throat or neck
- Coughing up blood or rust-colored mucus
A prompt medical evaluation can help identify potential underlying conditions, such as vocal cord lesions, thyroid problems, or throat cancer, and ensure timely treatment․ Early intervention can significantly improve treatment outcomes and prevent long-term damage to the vocal cords․
Additionally, individuals with a history of smoking, acid reflux, or previous vocal cord injuries should be particularly vigilant about seeking medical attention if they experience hoarseness, as these factors can increase the risk of developing more serious conditions․
A healthcare professional can provide personalized guidance and recommendations for addressing hoarseness and promoting optimal vocal health․
In conclusion, hoarseness is a common condition that can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life․ Effective management of hoarseness requires a comprehensive understanding of its causes, diagnosis, and treatment options․
A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating the expertise of healthcare professionals from various fields, is essential for providing optimal care and achieving successful outcomes․
By staying informed about the latest advances in the diagnosis and treatment of hoarseness, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their vocal health and address any concerns they may have․
Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of vocal health and the prevention of hoarseness can help reduce the prevalence of this condition and promote a healthier society․
Ultimately, a thorough understanding of hoarseness, combined with a commitment to maintaining good vocal hygiene and seeking medical attention when necessary, can help individuals restore their voice and improve their overall well-being․
It is our hope that this information has provided valuable insights into the complex issue of hoarseness and has empowered readers to take control of their vocal health․
We encourage individuals to consult with a healthcare professional if they have any questions or concerns about hoarseness․
This article effectively underscores the complexity involved in diagnosing & treating hoarssness given its multifactorial nature.One potential area for improvement involves incorporating patient testimonials/case studies illustrating effective management/treatment plans following accurate diagnoses.
I appreciated how this article discussed both physical causes (e.g., vocal cord lesions) as well as lifestyle choices that contribute to hoarseness (e.g., smoking). However,I felt that some sections were too technical for non-experts; perhaps incorporating simpler explanations alongside technical terms could improve accessibility.
As an ENT specialist myself, I found this article to be well-researched and accurate. The section on vocal cord lesions was particularly informative. One suggestion I might make is including more visual aids such as diagrams or images to help illustrate key concepts.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the definition and prevalence of hoarseness. I appreciate how it breaks down the causes into distinct subgroups. However, I would have liked to see more detailed information on the specific treatments available for each type of cause.
The section on medical conditions causing hoarseness was enlightening; many people might not associate thyroid issues with voice changes.I agree with another reviewer that visual aids would enhance comprehension.It
I found this article helpful in understanding my own experiences with hoarseness after years of singing in a band without proper training.I wish there was more discussion about preventative measures individuals could take before experiencing symptoms; perhaps future articles could explore these topics.