Understanding Prostate Cancer Treatment Options
Understanding prostate cancer treatment options is crucial for patients to make informed decisions about their care. Various treatments are available, each with its benefits and risks, and suitability depending on the cancer stage, grade, and individual health.
Overview of Treatment Approaches
Treatment approaches for prostate cancer are diverse and depend on various factors, including the cancer’s stage, grade, and the patient’s overall health. The primary goal of treatment is to control the growth of cancer cells, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life.
A multidisciplinary approach is often employed, involving a team of healthcare professionals, including urologists, radiation oncologists, medical oncologists, and supportive care specialists. Treatment plans may involve a single modality or a combination of therapies.
Patient preferences, lifestyle, and personal values also play a significant role in determining the most suitable treatment approach. Understanding the potential benefits, risks, and side effects of each treatment option is essential for patients to make informed decisions about their care.
A comprehensive discussion with a healthcare provider is necessary to determine the best course of treatment for each individual, taking into account their unique circumstances and priorities.
Surgical Treatment Options
Surgical treatment options for prostate cancer involve the removal of the prostate gland, offering a potential cure for localized disease. Surgery is often considered for patients with early-stage cancer, and various techniques are available to minimize side effects.
Prostatectomy⁚ Surgical Removal of the Prostate
A prostatectomy is a surgical procedure that involves the removal of the prostate gland. This treatment option is often considered for patients with localized prostate cancer, as it offers a potential cure for the disease. The surgery is typically performed by a urologist and can be done using various techniques.
The primary goal of a prostatectomy is to remove the entire prostate gland, including the tumor, while preserving surrounding tissues and nerves. This is crucial in minimizing potential side effects, such as urinary incontinence and erectile dysfunction. A prostatectomy can be performed using traditional open surgery or newer minimally invasive techniques, which offer reduced recovery time and less post-operative pain.
Following a prostatectomy, the patient will require hospitalization for several days to monitor for complications and ensure proper healing. A catheter is typically inserted during the surgery and remains in place for a few weeks after discharge. Patients are advised to follow a strict post-operative care plan to minimize the risk of complications and ensure optimal recovery.
Robotic Surgery⁚ A Minimally Invasive Approach
Robotic surgery is a minimally invasive approach that utilizes advanced robotic technology to assist in the surgical removal of the prostate gland. This technique allows for precise dissection and removal of the prostate, while minimizing damage to surrounding tissues and nerves.
The robotic system consists of a console, where the surgeon sits and controls the robotic arms, and a patient-side cart, which holds the instruments. The robotic arms are equipped with high-definition cameras, allowing the surgeon to visualize the operating site in 3D. This enhanced visualization enables the surgeon to perform complex maneuvers with increased precision and dexterity.
Robotic surgery offers several benefits, including reduced blood loss, less post-operative pain, and a shorter hospital stay. Additionally, the minimally invasive nature of the procedure allows for faster recovery and reduced risk of complications. With its advanced technology and precision, robotic surgery has become a popular treatment option for patients with prostate cancer, offering a high level of efficacy and minimal morbidity.
Laparoscopic Surgery⁚ A Less Invasive Alternative
Laparoscopic surgery is a less invasive alternative to traditional open surgery for prostate cancer treatment. This technique involves making several small incisions in the abdomen, through which a laparoscope (a thin, lighted tube with a camera) and specialized instruments are inserted.
The laparoscope allows the surgeon to visualize the operating site on a video monitor, while the instruments enable precise dissection and removal of the prostate gland. Laparoscopic surgery is often performed under general anesthesia and typically requires a shorter hospital stay compared to open surgery.
The benefits of laparoscopic surgery include reduced blood loss, less post-operative pain, and a faster recovery time. Additionally, the smaller incisions result in less scarring and a lower risk of complications. Laparoscopic surgery is a viable option for patients with localized prostate cancer, offering a high level of efficacy and minimal morbidity. However, it may not be suitable for all patients, and a thorough evaluation by a qualified surgeon is necessary to determine its feasibility.
Radiation Therapy Options
Radiation therapy is a non-surgical treatment for prostate cancer, utilizing high-energy rays to kill cancer cells. Two primary types of radiation therapy are available, each with distinct benefits and potential side effects, offering patients alternative treatment choices.
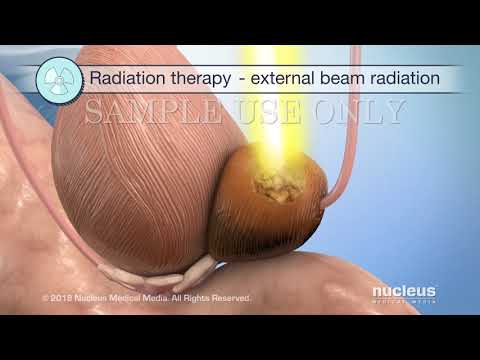
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT)⁚ A Non-Invasive Approach
External Beam Radiation Therapy (EBRT) is a widely used, non-invasive treatment for prostate cancer. This method involves directing high-energy rays from outside the body to target and destroy cancer cells within the prostate gland. EBRT is typically administered in multiple sessions over several weeks, with each session lasting only a few minutes.
A linear accelerator is used to generate and focus the radiation beams, allowing for precise targeting of the tumor while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues. The accuracy and effectiveness of EBRT have been significantly enhanced by advances in imaging technologies, such as 3D conformal radiation therapy and intensity-modulated radiation therapy (IMRT).
EBRT offers several benefits, including minimal recovery time and the avoidance of surgical risks. However, potential side effects may include fatigue, urinary changes, and bowel irritation. It is essential for patients to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of EBRT with their healthcare provider to determine if this treatment option is suitable for their specific needs.
Overall, External Beam Radiation Therapy provides an effective, non-invasive treatment option for prostate cancer patients, offering improved outcomes and enhanced quality of life.
Brachytherapy⁚ Internal Radiation Therapy
Brachytherapy is a type of internal radiation therapy that involves the placement of small, radioactive seeds or implants directly into the prostate gland. This approach allows for the delivery of high doses of radiation to the tumor site while minimizing exposure to surrounding healthy tissues.
There are two primary forms of brachytherapy⁚ low-dose rate (LDR) and high-dose rate (HDR). LDR brachytherapy involves the permanent implantation of radioactive seeds, which emit low levels of radiation over an extended period. HDR brachytherapy, on the other hand, utilizes temporary implants that deliver high doses of radiation in a short duration.
Brachytherapy offers several benefits, including reduced damage to surrounding tissues and a lower risk of long-term side effects. However, potential complications may arise, such as urinary retention, frequency, or urgency. It is essential for patients to discuss the advantages and disadvantages of brachytherapy with their healthcare provider to determine if this treatment option is suitable for their specific needs and medical history.
A thorough evaluation and consultation with a qualified healthcare professional are necessary to determine the feasibility of brachytherapy as a treatment option for prostate cancer.
Non-Surgical Treatment Options
Non-surgical treatment options offer patients a range of choices for managing prostate cancer without undergoing surgery. These alternatives can provide effective disease control, alleviate symptoms, and improve quality of life for individuals with prostate cancer.
Hormone Therapy⁚ Androgen Deprivation Therapy (ADT)
Hormone therapy, also known as androgen deprivation therapy (ADT), is a treatment approach that aims to reduce the levels of male hormones, such as testosterone, which can fuel the growth of prostate cancer cells.
ADT can be achieved through various methods, including medication, surgery, or a combination of both. Medications used in ADT work by blocking the production or action of testosterone, thereby slowing down the growth of cancer cells.
The benefits of ADT include reducing tumor size, alleviating symptoms, and slowing disease progression. However, ADT can also cause side effects, such as hot flashes, fatigue, and decreased libido.
ADT is often used in conjunction with other treatments, such as radiation therapy or chemotherapy, to enhance treatment efficacy. It is essential for patients to discuss the potential benefits and risks of ADT with their healthcare provider to determine if this treatment approach is suitable for their individual needs.
Chemotherapy⁚ Systemic Treatment for Advanced Cancer
Chemotherapy is a systemic treatment approach that utilizes medications to target and destroy rapidly dividing cancer cells. In the context of prostate cancer, chemotherapy is typically reserved for patients with advanced disease that has spread to other parts of the body.
Chemotherapy medications can be administered orally or intravenously, and treatment regimens vary depending on the specific medication and individual patient needs. The primary goal of chemotherapy in prostate cancer is to alleviate symptoms, slow disease progression, and improve quality of life.
Common chemotherapy medications used in prostate cancer treatment include docetaxel and cabazitaxel. While chemotherapy can be effective in managing advanced prostate cancer, it can also cause side effects, such as fatigue, nausea, and hair loss.
Patients undergoing chemotherapy require regular monitoring to assess treatment efficacy and manage potential side effects. A healthcare provider will work closely with the patient to develop a personalized treatment plan and provide ongoing support throughout the chemotherapy process.
Active Surveillance⁚ Monitoring Cancer Progression
Active surveillance is a management approach that involves closely monitoring prostate cancer progression, rather than immediately initiating treatment. This approach is often recommended for patients with low-risk prostate cancer, as it allows them to avoid potential treatment side effects.
Patients under active surveillance undergo regular check-ups with their healthcare provider, which include digital rectal examinations (DREs), prostate-specific antigen (PSA) blood tests, and periodic biopsies. These assessments help track the cancer’s growth and aggressiveness.
If test results indicate that the cancer is progressing or becoming more aggressive, the patient may be transitioned to active treatment. Alternatively, if the cancer remains stable or slow-growing, active surveillance can continue, sparing the patient from unnecessary interventions.
Active surveillance requires a high degree of patient commitment and adherence to scheduled follow-up appointments. By choosing this approach, patients can delay or potentially avoid treatment-related complications, while still ensuring prompt intervention if the cancer becomes more aggressive.
A comprehensive understanding of prostate cancer treatment options empowers patients to make informed decisions about their care. By considering individual needs and circumstances, patients can choose the most effective treatment approach for optimal outcomes.
Choosing the Right Treatment Option
Choosing the right treatment option for prostate cancer is a complex decision that requires careful consideration of various factors. Patients should discuss their individual situation, health status, and personal preferences with their healthcare provider to determine the most suitable treatment approach.
A thorough evaluation of the cancer’s stage, grade, and aggressiveness, as well as the patient’s overall health and potential side effects, is crucial in making an informed decision. Patients should also consider seeking a second opinion from a specialist or participating in clinical trials to explore innovative treatments.
Ultimately, the goal is to select a treatment option that balances cancer control with quality of life. By engaging in open and informed discussions with their healthcare team, patients can make empowered decisions about their care and achieve optimal outcomes. It is essential to approach this decision with patience, understanding, and a commitment to prioritizing individual needs and well-being.
The section on surgical treatment options was informative and well-written. However, I felt that the article could have benefited from more visual aids or diagrams to help illustrate complex concepts such as prostatectomy procedures.
This article does an excellent job highlighting the importance of considering individual patient needs when selecting a treatment approach. I appreciate how it emphasizes shared decision-making between patients and healthcare providers.
I appreciate how this article emphasizes patient-centered care and encourages individuals to take an active role in decision-making about their treatment plans. However, I would have liked to see more detailed information about emerging treatments and clinical trials.
I found this article to be well-researched and informative overall; however, I would have liked to see more discussion about managing side effects associated with different treatments.
This article provides an excellent overview of prostate cancer treatment options. The emphasis on a multidisciplinary approach to care is particularly important, as it highlights the need for collaboration among healthcare professionals to provide comprehensive care.