Understanding the Human Papillomavirus (HPV)
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a viral infection with multiple strains‚ some of which are associated with increased risk of developing oral cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 are considered high-risk strains. Understanding HPV transmission and its connection to oral cancer is crucial.
What is HPV and how is it transmitted?
Human Papillomavirus (HPV) is a highly contagious viral infection that affects millions of people worldwide. It is primarily spread through skin-to-skin contact‚ including oral‚ anal‚ and vaginal sex. HPV can also be transmitted through non-penetrative contact‚ such as genital-to-genital or oral-to-genital contact.
In addition to sexual transmission‚ HPV can also be spread through vertical transmission from mother to child during childbirth. In rare cases‚ HPV can be transmitted through non-sexual contact‚ such as sharing personal care items or through organ transplantation.
It is essential to note that anyone can contract HPV‚ regardless of age‚ sex‚ or sexual orientation. The virus can remain dormant for years‚ making it challenging to determine the exact time of transmission. Practicing safe sex‚ getting vaccinated‚ and maintaining good hygiene are crucial steps in reducing the risk of HPV transmission.
Awareness and education about HPV transmission can help prevent the spread of the virus and reduce the risk of developing HPV-related diseases‚ including oral cancer.
Healthcare providers recommend regular check-ups and screenings to monitor for HPV infection and related conditions.
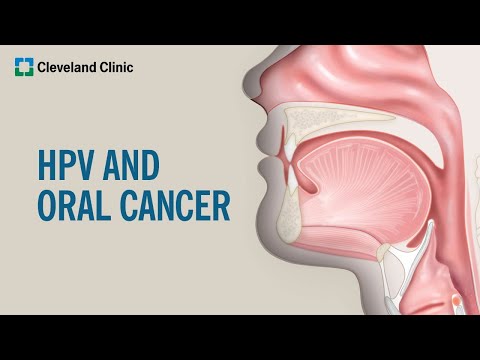
The Connection between HPV and Oral Cancer
Research has established a strong link between Human Papillomavirus (HPV) infection and the development of oral cancer. HPV types 16 and 18 are the most common high-risk strains associated with oral cancer.
When HPV infects the cells in the mouth‚ throat‚ or tongue‚ it can cause genetic mutations that lead to cancerous tumor growth. The virus can remain dormant for years‚ making it challenging to detect and treat oral cancer in its early stages.
Studies have shown that individuals with HPV-positive oral cancer have a higher survival rate than those with HPV-negative oral cancer. However‚ early detection and treatment are crucial in improving treatment outcomes.
The connection between HPV and oral cancer highlights the importance of practicing safe sex‚ getting vaccinated‚ and maintaining good oral hygiene. Regular dental check-ups and screenings can help identify potential oral cancer risks and prevent the development of this devastating disease.
As the medical community continues to research the connection between HPV and oral cancer‚ it is essential to stay informed about the latest findings and recommendations for prevention and treatment.
By understanding the link between HPV and oral cancer‚ individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and well-being.
Oral Cancer⁚ A Growing Concern
Oral cancer is an escalating health issue worldwide‚ with increasing incidence rates and mortality. The disease affects various populations‚ regardless of age‚ sex‚ or socioeconomic status‚ necessitating awareness and proactive measures to mitigate its impact.
The Rise of Oral Cancer Cases
The incidence of oral cancer has been steadily increasing over the past few decades‚ with a notable rise in cases among younger individuals. According to recent statistics‚ oral cancer accounts for approximately 3% of all cancer diagnoses worldwide.
This upward trend is attributed to various factors‚ including changes in lifestyle and behaviors‚ such as increased tobacco consumption‚ excessive alcohol use‚ and the growing prevalence of human papillomavirus (HPV) infections. Additionally‚ advances in diagnostic techniques and screening methods have contributed to the detection of more cases.
The surge in oral cancer cases highlights the need for enhanced awareness and education about the disease‚ its risk factors‚ and the importance of early detection. Healthcare professionals‚ policymakers‚ and the general public must collaborate to develop and implement effective prevention strategies and promote healthy behaviors to combat this growing health concern.
Addressing the rising incidence of oral cancer requires a multifaceted approach‚ encompassing improved access to screening and diagnostic services‚ enhanced patient education‚ and continued research into the causes and consequences of the disease. By working together‚ we can mitigate the impact of oral cancer and improve treatment outcomes for those affected.
The Importance of Early Detection
Early detection of oral cancer is crucial for improving treatment outcomes and patient survival rates. When diagnosed at an early stage‚ oral cancer is more likely to be treated effectively‚ resulting in better prognosis and quality of life.
Studies have shown that patients who receive timely treatment for oral cancer tend to experience fewer complications‚ reduced morbidity‚ and lower mortality rates compared to those whose diagnosis is delayed. Furthermore‚ early intervention often minimizes the need for aggressive treatments‚ preserving oral function and aesthetics.
To facilitate early detection‚ regular dental check-ups and screenings are essential. Healthcare providers should perform thorough oral examinations‚ including visual inspections and tactile assessments‚ to identify potential abnormalities. Patients must also be aware of their own oral health and report any suspicious symptoms or changes to their healthcare provider promptly.
By prioritizing early detection‚ we can enhance patient care‚ reduce the burden of oral cancer‚ and ultimately save lives. A multidisciplinary approach‚ involving healthcare professionals‚ patients‚ and communities‚ is necessary to promote awareness and drive progress in the fight against oral cancer.
Through collective efforts‚ we can ensure that oral cancer is diagnosed and treated in its earliest stages‚ maximizing the chances of successful treatment and improved patient outcomes.
Mouth Cancer Symptoms to Watch Out For
Recognizing mouth cancer symptoms is crucial for early detection and treatment. Be aware of unusual changes in your mouth‚ such as lumps‚ sores‚ or discoloration. Nine key signs can indicate mouth cancer‚ and identifying them can save lives.
9 Signs of Mouth Cancer You Should Know
Mouth cancer can manifest in various ways‚ and being aware of the following signs can aid in early detection⁚
- Persistent mouth ulcers that do not heal within 2-3 weeks
- Red or white patches on the gums‚ tongue‚ or lining of the mouth
- Lumps or thickening on the cheek‚ lips‚ or tongue
- Pain or discomfort when eating‚ speaking‚ or swallowing
- Bleeding or numbness in the mouth
- Loose teeth or tooth sockets that do not heal
- Pain or stiffness in the jaw or face
- Difficulty opening the mouth or moving the jaw
- Unexplained bad breath or changes in speech
If you experience any of these symptoms‚ it is essential to consult a healthcare professional for proper evaluation and diagnosis. Early detection significantly improves treatment outcomes.
Remember‚ some of these signs may have other causes‚ but if you notice any unusual changes or persistent issues‚ do not hesitate to seek medical attention.
HPV Infection and Oral Sex Risks
Engaging in oral sex increases the risk of contracting HPV infection‚ particularly strains associated with oral cancer. Practicing safe sex and maintaining good oral hygiene can help mitigate this risk. Awareness of oral sex risks is crucial.
Understanding the Risks of Oral Sex
Oral sex has become increasingly common in modern society‚ but it’s essential to acknowledge the associated risks. Engaging in oral sex can lead to the transmission of HPV‚ HIV‚ and other STDs. The human papillomavirus (HPV) is particularly concerning due to its connection to oral cancer.
The risk of HPV transmission through oral sex is higher when there is an open wound or sore in the mouth. Additionally‚ individuals with weakened immune systems are more susceptible to infection. It’s crucial to maintain good oral hygiene and avoid engaging in oral sex if you have any oral health issues.
While the risk of HPV transmission through oral sex cannot be eliminated entirely‚ practicing safe sex can help reduce the likelihood. Using protection‚ such as dental dams or condoms‚ can significantly lower the risk of transmission. Vaccination against HPV can also provide protection against certain strains. By understanding the risks associated with oral sex‚ individuals can take informed steps to protect their health.
Reducing the Risks of HPV Infection
To minimize the risk of HPV infection‚ it’s essential to adopt a proactive approach. One of the most effective ways to reduce the risk is to get vaccinated against HPV. The HPV vaccine is available for both males and females and can provide protection against certain high-risk strains.
In addition to vaccination‚ practicing safe sex is crucial. Using protection‚ such as dental dams or condoms‚ can significantly lower the risk of transmission. It’s also essential to maintain good oral hygiene‚ including regular brushing and flossing‚ to reduce the risk of oral health issues.
Lifestyle choices can also play a role in reducing the risk of HPV infection. Avoiding tobacco and limiting alcohol consumption can help minimize the risk. Furthermore‚ maintaining a healthy diet rich in fruits‚ vegetables‚ and whole grains can help boost the immune system. By taking these steps‚ individuals can significantly reduce their risk of HPV infection and associated health complications.
Regular health check-ups and screenings can also help identify any potential issues early on‚ allowing for prompt treatment and reducing the risk of complications.
The Cervical Cancer Connection
A well-established link exists between HPV infection and cervical cancer. Certain high-risk HPV strains‚ particularly types 16 and 18‚ are responsible for approximately 70% of cervical cancer cases worldwide‚ highlighting the significance of HPV in cervical cancer development.
The Link between HPV and Cervical Cancer
The connection between Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and cervical cancer is well-documented; Research has consistently shown that persistent infection with high-risk HPV strains‚ particularly types 16 and 18‚ is a necessary step in the development of cervical cancer.
HPV-induced carcinogenesis is a complex process involving the disruption of normal cellular mechanisms‚ leading to uncontrolled cell growth and tumor formation. The E6 and E7 proteins produced by high-risk HPV strains play a crucial role in this process‚ as they interfere with the host cell’s ability to regulate cell division and repair DNA damage.
Epidemiological studies have demonstrated a strong association between HPV infection and cervical cancer‚ with certain populations‚ such as young women and those with weakened immune systems‚ being at increased risk. The implementation of HPV vaccination programs and cervical cancer screening initiatives has significantly reduced the incidence of cervical cancer in many countries‚ underscoring the importance of prevention and early detection in controlling this disease.
Further research into the molecular mechanisms underlying the HPV-cervical cancer link is necessary to develop more effective prevention and treatment strategies‚ ultimately reducing the burden of cervical cancer worldwide.
In conclusion‚ the relationship between Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and oral cancer is a pressing concern that warrants attention from healthcare professionals and the general public alike. By understanding the risks associated with HPV infection and the signs of mouth cancer‚ individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health.
Early detection and prevention are crucial in combating oral cancer. Regular dental check-ups‚ HPV vaccinations‚ and safe sex practices can significantly reduce the risk of developing this disease. Furthermore‚ being aware of the 9 signs of mouth cancer can facilitate prompt medical attention‚ improving treatment outcomes and survival rates.
Healthcare providers play a vital role in educating patients about the risks of HPV-related oral cancer and promoting preventive measures. By working together‚ we can mitigate the impact of this disease and create a healthier future for generations to come.
Ultimately‚ awareness and education are key in the fight against HPV-related oral cancer. We must continue to promote research‚ prevention‚ and early detection to reduce the burden of this devastating disease and improve the lives of those affected.
One area where this article could improve is by providing more detailed statistics on HPB infections rates globally.
As someone who works in healthcare, I appreciate how this article stresses the importance of regular check-ups and screenings for monitoring HPB infection.
This article provides an excellent overview of Human Papillomavirus (HPV) and its connection to oral cancer. The explanation of how HPV is transmitted is clear and concise, making it accessible to readers who may not have prior knowledge on the topic.
The section on vertical transmission from mother to child during childbirth was particularly informative for me, as I had not previously known about this mode of transmission.
While this article provides a solid foundation for understanding HPB, I would have liked more information on current research into treatments for HPB-related diseases.
I appreciate how this article emphasizes the importance of practicing safe sex, getting vaccinated, and maintaining good hygiene in reducing the risk of HPV transmission. These preventive measures are crucial in preventing the spread of HPB.