Laryngitis⁚ An Overview
Laryngitis is a medical condition characterized by inflammation of the larynx, leading to vocal cord damage and respiratory issues, affecting individuals of all ages, with various causes and symptoms.
Causes of Laryngitis
Laryngitis is caused by a variety of factors, including viral and bacterial infections, such as the common cold and flu. Additionally, exposure to allergens, pollutants, and irritants like tobacco smoke, dust, and chemicals can trigger laryngitis.
Vocal strain and misuse, such as screaming, shouting, or prolonged singing, can also lead to laryngitis. Furthermore, gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), sinus infections, and postnasal drip can contribute to the development of laryngitis.
In some cases, laryngitis may be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as thyroid disorders, autoimmune diseases, or neurological conditions like Parkinson’s disease. Moreover, certain medications, such as corticosteroids and chemotherapy, can increase the risk of developing laryngitis.
It is essential to identify and address the underlying cause of laryngitis to ensure effective treatment and prevent future occurrences. A thorough medical evaluation and diagnosis are necessary to determine the root cause of laryngitis.
Symptoms of Laryngitis
Symptoms of laryngitis include a hoarse or raspy voice, vocal fatigue, and throat discomfort, which can range from mild to severe, and may be accompanied by coughing, wheezing, or shortness of breath.
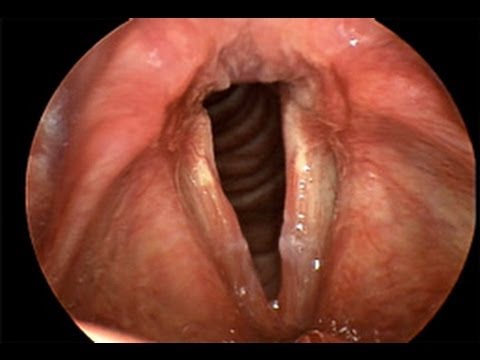
Vocal Cord Inflammation and Hoarseness
Vocal cord inflammation is a hallmark symptom of laryngitis, resulting in hoarseness or a raspy voice. This inflammation can be acute or chronic, depending on the underlying cause. When the vocal cords become inflamed, they swell and stiffen, disrupting normal vocal cord vibration and leading to changes in voice quality.
The severity of hoarseness can vary widely, ranging from a mild, breathy voice to a severely strained or barely audible voice. In some cases, individuals with laryngitis may experience vocal fatigue, struggling to speak for extended periods without straining their voice. Vocal cord inflammation and hoarseness can significantly impact daily life, affecting communication, work, and social interactions.
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated vocal cord inflammation can lead to long-term damage and scarring, potentially affecting voice quality permanently.
Sore Throat and Vocal Strain
A sore throat is a common symptom of laryngitis, often accompanied by vocal strain. The inflammation of the larynx can cause discomfort, pain, or tenderness in the throat, making it difficult to swallow or speak. Vocal strain occurs when the vocal cords are overused or misused, leading to fatigue, tightness, or stiffness in the throat muscles.
Individuals with laryngitis may experience a sensation of tightness or constriction in the throat, making it challenging to produce sound or speak clearly. The sore throat and vocal strain can be exacerbated by factors such as loud talking, singing, or prolonged speaking. Resting the voice and avoiding strenuous vocal activities can help alleviate these symptoms and promote healing.
It is crucial to address sore throat and vocal strain promptly, as neglecting these symptoms can prolong recovery and increase the risk of complications. A healthcare professional can provide guidance on managing these symptoms and developing strategies for optimal vocal care.
Complications of Laryngitis
Untreated or severe laryngitis can lead to complications, including respiratory distress, airway obstruction, and chronic vocal cord dysfunction, necessitating prompt medical attention to prevent long-term damage or life-threatening consequences.
Vocal Cord Damage
Vocal cord damage is a potential complication of laryngitis, resulting from chronic inflammation, scarring, or lesions on the vocal cords. This can lead to persistent voice changes, including hoarseness, breathiness, or vocal fatigue. In severe cases, vocal cord damage can cause significant voice loss or aphonia. The extent of damage can be assessed through laryngoscopy or stroboscopy, which provide detailed visualization of the vocal cords. Treatment for vocal cord damage depends on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. Mild cases may respond to voice therapy and conservative management, while more severe cases may require surgical intervention, such as laser treatment or microsurgery. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent further damage and optimize treatment outcomes. Vocal cord damage can have a significant impact on an individual’s quality of life, affecting communication, occupation, and overall well-being.
Throat Infection and Breathing Difficulties
A throat infection is a potential complication of laryngitis, which can spread to the surrounding tissues and cause breathing difficulties. This can lead to respiratory distress, including shortness of breath, wheezing, or stridor. In severe cases, a throat infection can cause airway obstruction, requiring immediate medical attention. Breathing difficulties can be exacerbated by swelling, inflammation, or scarring of the larynx, trachea, or bronchi. Individuals with pre-existing respiratory conditions, such as asthma or chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), are at increased risk of developing breathing difficulties. Treatment for throat infection and breathing difficulties typically involves antibiotics, bronchodilators, or corticosteroids, depending on the underlying cause and severity of the condition. In some cases, hospitalization may be necessary to manage respiratory distress and prevent further complications. Prompt medical attention is essential to prevent long-term damage and optimize treatment outcomes.
Diagnosis and Treatment of Laryngitis
Diagnosis involves a thorough medical history, physical examination, and visualization of the larynx through laryngoscopy or stroboscopy, followed by individualized treatment plans addressing underlying causes and alleviating symptoms effectively.
Rest and Voice Therapy
Voice rest is a crucial component in the treatment of laryngitis, allowing the vocal cords to recover from strain and inflammation. This entails avoiding loud talking, singing, or making excessive noise. A speech-language pathologist (SLP) can provide personalized voice therapy to promote healing and prevent future episodes of laryngitis.
Voice therapy may include exercises to improve breathing, relaxation techniques, and strategies to modify vocal technique. The SLP can also educate patients on proper vocal hygiene practices, such as staying hydrated, avoiding irritants, and managing stress. By incorporating voice rest and therapy into their treatment plan, individuals with laryngitis can alleviate symptoms, reduce the risk of complications, and achieve optimal vocal function.
Regular follow-up appointments with an SLP can help monitor progress, address concerns, and adjust the treatment plan as needed to ensure effective management of laryngitis and long-term vocal health.
Medications and Antibiotics
In the treatment of laryngitis, medications may be prescribed to alleviate symptoms, reduce inflammation, and combat infection. Pain relief medications, such as acetaminophen or ibuprofen, can help manage throat discomfort and pain.
Corticosteroids may be used to decrease swelling in the larynx, while antihistamines can provide relief from allergic reactions that may exacerbate laryngitis. Expectorants, such as guaifenesin, can aid in loosening and clearing mucus from the airways.
If a bacterial infection is present, antibiotics may be prescribed to target the underlying cause of laryngitis. It is essential to complete the full course of antibiotic treatment as directed by a healthcare professional to ensure effective eradication of the infection and prevent antibiotic resistance. Medications should only be taken under the guidance of a healthcare professional, as they can have side effects and interact with other medications.
Prevention of Laryngitis
Preventing laryngitis involves adopting healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, staying hydrated, managing stress, and avoiding exposure to environmental irritants and allergens that can strain the vocal cords.
Chronic Coughing and Vocal Strain
Chronic coughing and vocal strain are significant risk factors for developing laryngitis. Prolonged periods of coughing can cause irritation and inflammation to the vocal cords, leading to hoarseness and discomfort. Similarly, vocal strain from loud or prolonged speaking, singing, or shouting can also lead to laryngeal inflammation. It is essential to manage chronic coughs through medical treatment and adopt proper vocal hygiene techniques to prevent vocal strain.
This includes warming up the voice before use, taking regular breaks, staying hydrated, and avoiding loud noises. Additionally, individuals with persistent coughs should seek medical attention to diagnose and treat underlying conditions, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD) or respiratory infections, which can contribute to chronic coughing. By addressing these risk factors, individuals can reduce their likelihood of developing laryngitis and maintain optimal vocal health.
Good Hygiene Practices
Maintaining good hygiene practices is crucial in preventing the spread of laryngitis. This includes frequently washing hands with soap and water, especially after coming into contact with an individual with a respiratory infection. Additionally, avoiding close proximity to people with contagious illnesses and refraining from sharing food, drinks, or utensils can also reduce the risk of transmission.
It is also essential to regularly clean and disinfect surfaces and objects that may harbor bacteria and viruses, such as doorknobs, telephones, and keyboards. Furthermore, practicing good oral hygiene by brushing teeth at least twice a day and rinsing with antibacterial mouthwash can help prevent the spread of infections. By adhering to these good hygiene practices, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of contracting laryngitis and other respiratory infections, ultimately protecting their overall health and well-being.
I found this article well-researched., especially regarding potential underlying conditions contributing to laryngitis., Nonetheless., I think incorporating case studies could enhance reader understanding by providing concrete examples.
The section on vocal cord inflammation is particularly informative. I found it interesting how inflammation disrupts normal vocal cord vibration patterns. However, I think additional diagrams or illustrations would help readers better understand this concept.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of laryngitis, covering its causes, symptoms, and effects on vocal cord function. I appreciate how it emphasizes the importance of identifying underlying causes for effective treatment.
As someone who suffers from occasional bouts of laryngitis due to vocal strain during public speaking engagements., I appreciate how this article highlights prevention strategies through lifestyle modifications., though I would have liked more specific tips on maintaining good vocal hygiene.
The writing style is clear., concise., making complex concepts accessible even for non-medical professionals., One area for improvement could involve discussing emerging treatments for chronic cases.