Understanding Lumbar Microdiscectomy
Lumbar microdiscectomy is a surgical procedure designed to alleviate lower back pain and sciatica caused by a herniated disc compressing nerves in the lumbar spine.
Definition and Purpose
Lumbar microdiscectomy is a type of minimally invasive surgery aimed at relieving pressure on the spinal cord and nerve roots caused by a herniated disc. The primary purpose of this procedure is to remove the damaged or herniated disc material that is compressing the surrounding nerves, thereby alleviating symptoms such as lower back pain, numbness, tingling, and weakness in the legs.
The term “microdiscectomy” refers to the use of a microscope to visualize the disc and nerves during the procedure, allowing for a more precise and less invasive approach. By removing the offending disc material, the goal of lumbar microdiscectomy is to restore normal spinal function, relieve pain, and improve overall quality of life for individuals suffering from sciatica and other related conditions.
This procedure is often considered a viable treatment option for individuals who have not responded to conservative therapies or who are experiencing severe or debilitating symptoms.
Anatomy of the Lumbar Spine
The lumbar spine consists of five vertebrae (L1-L5), intervertebral discs, facet joints, and surrounding muscles, ligaments, and nerves that work together to provide stability and flexibility.
The Role of the Intervertebral Discs
The intervertebral discs play a crucial role in the lumbar spine, serving as shock absorbers and facilitating flexibility between adjacent vertebrae. Each disc consists of a tough outer layer (annulus fibrosus) and a soft, gel-like center (nucleus pulposus). The nucleus pulposus is responsible for absorbing and distributing compressive forces, while the annulus fibrosus provides stability and containment. As we age, the discs naturally degenerate, losing their water content and becoming less effective at absorbing shocks. This can lead to conditions such as spinal stenosis and herniated discs, which can put pressure on surrounding nerves and cause pain. Understanding the role of the intervertebral discs is essential for diagnosing and treating lumbar spine conditions.
The Procedure⁚ Lumbar Microdiscectomy
Lumbar microdiscectomy involves a minimally invasive surgery approach to remove the herniated disc material compressing nerves, providing effective spinal decompression and rapid sciatica relief.
Minimally Invasive Surgery for Spinal Decompression
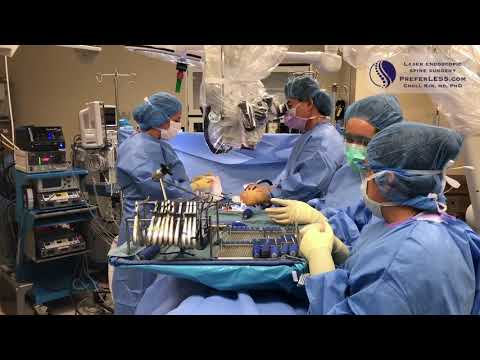
Lumbar microdiscectomy is a paradigm of minimally invasive surgery, leveraging advanced technologies to minimize tissue disruption and promote expedited recovery. By employing a posterior approach, surgeons can access the affected disc through a smaller incision, thereby reducing iatrogenic trauma to surrounding muscles and soft tissues. This technique enables precise disc removal, ensuring thorough spinal decompression while preserving the integrity of adjacent spinal segments. Consequently, patients experience diminished post-operative pain, accelerated healing, and improved functional outcomes. The minimally invasive nature of lumbar microdiscectomy has revolutionized the field of spine surgery, offering a safer, more efficacious alternative to traditional open surgical techniques. By reducing the risk of complications and promoting enhanced recovery, this approach has become the gold standard for treating lumbar spine pathology.
Surgical Techniques and Technologies
The efficacy of lumbar microdiscectomy is contingent upon the judicious employment of cutting-edge surgical techniques and technologies. Contemporary approaches often incorporate the use of operative microscopes or endoscopic visualization systems, which provide unparalleled magnification and illumination of the surgical site. Additionally, advances in electrophysiological monitoring enable real-time assessment of neural function, thereby minimizing the risk of iatrogenic nerve injury. Surgeons may also utilize intraoperative fluoroscopy or computed tomography to ensure accurate localization and precise discectomy. Furthermore, the integration of novel bipolar coagulation systems and ultrasonic aspirators facilitates efficient hemostasis and meticulous tissue handling. By harnessing these technological advancements, surgeons can optimize patient outcomes, reduce morbidity, and enhance the overall efficacy of lumbar microdiscectomy for treating herniated discs and attendant sciatica symptoms.
Candidacy for Lumbar Microdiscectomy
Candidacy for lumbar microdiscectomy is determined by a comprehensive evaluation of the patient’s medical history, physical examination, and diagnostic imaging results, such as MRI or CT scans.
Who Benefits from This Spine Procedure?
Patients with persistent or severe sciatica, leg pain, or numbness due to a herniated disc compressing nerve roots may benefit from lumbar microdiscectomy. Individuals who have tried conservative treatments, such as physical therapy, pain management, or epidural injections, without significant relief may also be candidates for this procedure. Additionally, patients experiencing significant limitations in their daily activities, such as difficulty walking or maintaining balance, may find lumbar microdiscectomy an effective solution. A thorough evaluation by a qualified orthopedic surgeon or neurosurgeon is necessary to determine if lumbar microdiscectomy is the best course of treatment for each individual case. By carefully selecting candidates, surgeons can optimize the likelihood of successful outcomes and long-term relief from debilitating symptoms. Proper patient selection is crucial to achieving the desired benefits of this spine procedure.
Recovery and Rehabilitation
Following lumbar microdiscectomy, patients typically undergo a structured recovery program involving pain management, physical therapy, and gradual return to normal activities to ensure optimal healing and spinal function.
Post-Surgery Expectations and Care
Following lumbar microdiscectomy, patients can expect to experience some level of discomfort, numbness, and weakness in the lower back and legs. A hospital stay of 1-2 days is typically required for monitoring and pain management. Upon discharge, patients are advised to follow a specific care plan, including wound care and medication management. A follow-up appointment with the surgeon is usually scheduled 1-2 weeks post-surgery to assess healing progress and remove any sutures or staples. Patients are also instructed to avoid heavy lifting, bending, and strenuous activities for 4-6 weeks to ensure proper healing and minimize the risk of complications. A gradual return to normal activities and work is encouraged, with most patients able to resume their daily routines within 2-3 months. It is essential to follow the surgeon’s instructions carefully to ensure a smooth and successful recovery.
Potential Risks and Complications
As with any surgical procedure, lumbar microdiscectomy carries potential risks and complications. These may include infection, bleeding, and nerve damage, which can result in numbness, weakness, or paralysis. Additionally, there is a risk of cerebrospinal fluid leak, herniation of an adjacent disc, and instability of the spine. Some patients may also experience ongoing pain or sciatica symptoms despite the surgery. Furthermore, there is a risk of allergic reactions to anesthesia and blood clots forming in the legs. While these complications are rare, it is essential to discuss them with the surgeon before undergoing the procedure. By understanding the potential risks and complications, patients can make an informed decision about their treatment and take steps to minimize their occurrence.
Success Rates and Outcomes
Lumbar microdiscectomy has a high success rate in alleviating sciatica symptoms and improving quality of life, with studies indicating a significant reduction in pain and disability in most patients.
Efficacy of Lumbar Microdiscectomy for Sciatica Relief
Numerous studies have demonstrated the efficacy of lumbar microdiscectomy in providing significant relief from sciatica symptoms. A systematic review of clinical trials revealed that patients who underwent microdiscectomy experienced substantial improvements in pain and functional outcomes, with a mean reduction in symptoms of 70-80%. Moreover, long-term follow-up studies have shown that the benefits of microdiscectomy can persist for several years, with some studies reporting sustained improvements in symptoms and quality of life at 5-10 years post-operatively. The efficacy of microdiscectomy is attributed to its ability to directly address the underlying cause of sciatica, namely the compression of the nerve root by a herniated disc. By removing the offending disc material, microdiscectomy can effectively alleviate pressure on the nerve, thereby reducing pain and restoring normal function.
Future Perspectives and Advancements
As the field of spine surgery continues to evolve, lumbar microdiscectomy is expected to benefit from several emerging trends and technologies. One area of research focus is the development of minimally invasive and percutaneous approaches, which aim to reduce tissue damage and promote faster recovery. Additionally, advances in spinal biologics and disc regeneration may offer new alternatives for treating degenerative disc disease. The integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning algorithms may also enhance surgical planning and execution. Furthermore, the increasing adoption of 3D printing technology is expected to improve the design and fabrication of spinal implants. As these innovations mature, they are likely to further refine the efficacy and safety of lumbar microdiscectomy, ultimately leading to better patient outcomes and improved quality of life for individuals suffering from spinal stenosis and related conditions.
I found this article informative but would have liked more details on post-operative care and potential complications associated with lumbar microdiscectomy.
Overall, this article does an excellent job describing lumbar microdiscectomy; however, it might be helpful to include information on alternative treatments or when surgery may not be necessary.
As someone who has undergone lumbar microdiscectomy myself, I can attest that this article accurately represents the procedure
While I appreciate this article
This article provides an excellent overview of lumbar microdiscectomy, clearly explaining its definition, purpose, and benefits. I appreciate how it breaks down complex medical concepts into easily understandable language.