A mitral valve prolapse can lead to severe cardiac problems if left untreated. It is crucial to understand the potential consequences, including heart failure, arrhythmia, and chest pain, to ensure timely medical intervention and prevention of complications.
Introduction to Mitral Valve Prolapse
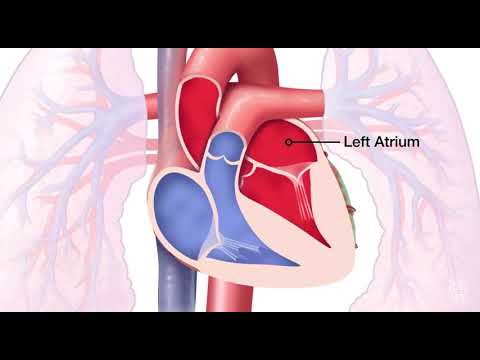
Mitral valve prolapse (MVP) is a relatively common heart condition characterized by the displacement of the mitral valve leaflets into the left atrium during systole. This condition affects approximately 2-3% of the general population, with a higher prevalence among women.
The mitral valve plays a crucial role in ensuring proper blood flow between the left atrium and ventricle. In a normal heart, the valve leaflets close tightly during systole, preventing backflow. However, in individuals with MVP, the leaflets do not close properly, leading to a characteristic bulging or prolapse into the atrium.
MVP can be classified into two main categories⁚ primary and secondary. Primary MVP is often associated with myxomatous degeneration, a condition where the valve tissue becomes abnormal and leads to prolapse. Secondary MVP, on the other hand, is typically seen in individuals with underlying conditions such as Marfan syndrome or coronary artery disease.
While many individuals with MVP remain asymptomatic, others may experience a range of symptoms that can significantly impact daily life. Understanding the complexities of MVP is essential for early diagnosis and effective management of this condition.
Causes and Risk Factors
Mitral valve prolapse can be caused by various factors, including genetic predisposition, myxomatous degeneration, connective tissue disorders, and coronary artery disease. Additionally, family history and age also play a significant role in increasing the risk of developing this condition.
Symptoms of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse often presents with a range of symptoms, which can vary in severity and impact on daily life. Common symptoms include⁚
- Chest pain or discomfort, often described as a sharp or stabbing sensation, particularly during periods of physical exertion or when lying down.
- Shortness of breath or difficulty breathing, especially during exercise or at high altitudes.
- Fatigue or feeling unusually tired, even after resting or engaging in light activities.
- Palpitations or irregular heartbeats, which can be felt as skipped beats, fluttering, or pounding in the chest.
- A heart murmur, which is an abnormal sound heard when listening to the heartbeat with a stethoscope.
It is essential to note that some individuals with mitral valve prolapse may not experience any noticeable symptoms, while others may exhibit severe symptoms that significantly impact their quality of life. If symptoms persist or worsen over time, it is crucial to seek medical attention for proper evaluation and treatment.
A thorough medical examination and diagnostic testing can help determine the presence and severity of mitral valve prolapse, allowing for timely intervention and prevention of potential complications.
Complications of Mitral Valve Prolapse
Mitral valve prolapse can lead to severe complications, including valve regurgitation, heart failure, and arrhythmia, which can significantly impact quality of life and increase the risk of morbidity and mortality if left untreated or poorly managed.
Valve Regurgitation
Mitral valve regurgitation is a condition where the mitral valve does not close properly, allowing blood to flow backward from the left ventricle into the left atrium. This can lead to an increase in pressure and volume in the left atrium, causing it to enlarge.
As a result, the heart must work harder to pump blood, which can lead to fatigue, shortness of breath, and swelling in the legs and feet. If left untreated, mitral valve regurgitation can lead to more severe complications, such as heart failure and arrhythmia.
The severity of mitral valve regurgitation can be classified into three categories⁚ mild, moderate, and severe. Mild regurgitation may not require treatment, while moderate to severe regurgitation may require medication or surgery to repair or replace the mitral valve.
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare professional can diagnose mitral valve regurgitation using echocardiography or cardiac catheterization and develop a treatment plan to manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
Early detection and treatment of mitral valve regurgitation can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage to the heart.
Heart Failure
Heart failure is a potential complication of mitral valve prolapse, where the heart is unable to pump enough blood to meet the body’s needs. This can occur when the mitral valve regurgitation causes the heart to work harder, leading to fatigue and decreased cardiac function.
The symptoms of heart failure caused by mitral valve prolapse may include shortness of breath, fatigue, swelling in the legs and feet, and a persistent cough. In severe cases, heart failure can lead to respiratory failure, which requires immediate medical attention.
There are several types of heart failure, including left-sided heart failure, right-sided heart failure, and congestive heart failure. The severity of heart failure can be classified using the New York Heart Association (NYHA) Functional Classification system.
Treatment for heart failure caused by mitral valve prolapse typically involves a combination of medications, lifestyle modifications, and in some cases, surgery. It is essential to work closely with a healthcare professional to manage symptoms and prevent further complications.
Early detection and treatment of heart failure can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of long-term damage to the heart.
A well-managed treatment plan can help individuals with heart failure lead active and fulfilling lives.
Arrhythmia
Arrhythmia, or an irregular heartbeat, is a potential complication of mitral valve prolapse. This can occur when the mitral valve does not close properly, disrupting the heart’s normal electrical conduction system.
There are several types of arrhythmias that can be associated with mitral valve prolapse, including atrial fibrillation, supraventricular tachycardia, and ventricular tachycardia. Symptoms of arrhythmia may include palpitations, skipped beats, or a feeling of the heart racing or pounding in the chest.
In some cases, arrhythmias caused by mitral valve prolapse can be asymptomatic, but still pose a risk to cardiovascular health. Untreated arrhythmias can lead to decreased cardiac function, increased risk of stroke, and other complications;
Diagnosing arrhythmias typically involves electrocardiogram (ECG) testing, Holter monitoring, or event monitoring. Treatment options may include medication, cardioversion, or catheter ablation, depending on the type and severity of the arrhythmia.
It is essential for individuals with mitral valve prolapse to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor for signs of arrhythmia and develop a treatment plan to manage symptoms and prevent complications.
Effective management of arrhythmias can help improve quality of life and reduce the risk of long-term cardiac damage.
Diagnosis and Treatment
Diagnosing mitral valve prolapse involves physical examination, echocardiogram, and cardiac catheterization. Treatment options include lifestyle modifications, medications, and surgery, such as mitral valve repair or replacement, to alleviate symptoms and prevent complications like heart murmur and disease progression.
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of mitral valve prolapse is essential for effective management and prevention of complications. By recognizing the causes, symptoms, and potential consequences of this heart condition, individuals can take proactive steps to maintain their cardiovascular health.
It is crucial to work closely with healthcare professionals to develop a personalized treatment plan, which may involve lifestyle modifications, medications, or surgical interventions. By doing so, individuals with mitral valve prolapse can alleviate symptoms, prevent disease progression, and reduce the risk of developing severe cardiac complications.
Furthermore, ongoing research and advancements in medical technology continue to improve diagnostic and therapeutic options for individuals with mitral valve prolapse. As a result, it is essential to stay informed about the latest developments and breakthroughs in the field of cardiology to ensure optimal management and care.
By prioritizing cardiovascular health and seeking timely medical attention when necessary, individuals with mitral valve prolapse can lead active, healthy lives and minimize the impact of this condition on their overall well-being.
The section on causes,risk factors,and classification types demonstrates thorough research.The inclusionof data regarding prevalence rates adds credibility.However,a critical aspect missing from this discussion involves addressing current debates within cardiology surrounding diagnostic criteria.
Overall,this piece does an outstanding job breaking down technical terms relatedtotheheartinto manageable piecesforlayreaders.Educatormateriallike thisis invaluableforraising awarenessaboutseriouscardiovascular diseases.
This article provides an excellent introduction to mitral valve prolapse (MVP), covering its definition, causes, symptoms, and classification types. The writing style is clear and concise, making it accessible to both medical professionals and non-experts interested in learning about this common heart condition.
I found this article helpful as someone who has recently been diagnosed with MVP.The explanation of how MVP affects blood flow between chambers was particularly useful.I wish there were more details about managing symptoms or future outlooks for those living with this condition.
As a cardiologist,I appreciate how this article emphasizes the importance of understanding MVP