Introduction to Noodle Consumption
Noodles have become a ubiquitous food globally, with instant noodles leading the trend. Their convenience and affordability make them a popular choice for many. However, frequent consumption raises concerns about potential health risks. Understanding noodle consumption patterns is crucial for assessing their impact on public health.
Nutrition Facts⁚ What’s Really in Your Noodles?
A closer examination of the nutritional content of instant noodles reveals a concerning profile. A typical serving of instant noodles is high in calories, carbohydrates, and fat, while being low in essential nutrients such as protein, fiber, and vitamins. The ingredients used in instant noodle production are often highly processed, including refined flour, vegetable oils, and seasonings high in sodium and sugar.
The seasoning packets that accompany instant noodles are particularly noteworthy for their high sodium content, often exceeding the recommended daily intake. Additionally, many instant noodles contain monosodium glutamate (MSG), a flavor enhancer linked to adverse health effects in some individuals.
Furthermore, the processing of instant noodles involves various chemical treatments, including bleaching and texturizing agents, which can lead to the formation of potentially carcinogenic compounds. The presence of artificial flavorings and colorings adds to the list of questionable ingredients.
It is essential to note that not all instant noodles are created equal, and some may be marketed as “healthier” options due to the inclusion of additional nutrients or fewer artificial ingredients. Nevertheless, even these alternatives should be consumed with caution, as the fundamental nutritional profile of instant noodles remains largely unaltered.
Understanding the nutritional facts behind instant noodles is a crucial step in assessing their potential health risks. As we delve deeper into the relationship between noodle consumption and health, it becomes clear that a more nuanced approach to nutrition is necessary to mitigate the risks associated with frequent instant noodle consumption.
Processed Foods and Their Impact on Health
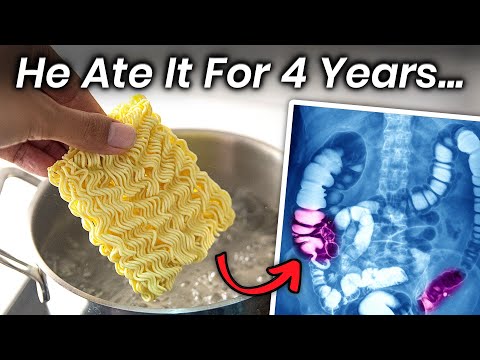
Consuming processed foods like instant noodles regularly can lead to a range of negative health outcomes. These products often contain unhealthy ingredients, added preservatives, and excessive sodium, which can disrupt normal bodily functions and increase the risk of chronic diseases when eaten excessively over time.
Health Risks Associated with Frequent Noodle Consumption
Frequent consumption of noodles, particularly instant noodles, has been linked to an increased risk of various health problems. Research studies have consistently shown that regular consumption of these products can lead to a decline in overall health and wellbeing.
The high caloric and fat content in noodles can contribute to weight gain and obesity, increasing the risk of developing conditions such as diabetes, cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer. Furthermore, the low essential nutrient content in noodles can lead to nutrient deficiencies over time, particularly if they are relied upon as a primary source of nutrition.
Additionally, the unhealthy ingredients present in many noodle products, such as monosodium glutamate (MSG) and other additives, can have adverse effects on health. These substances have been linked to headaches, digestive issues, and allergic reactions in some individuals.
Moreover, a diet dominated by noodles can lead to an imbalance of gut bacteria, which is crucial for maintaining optimal immune function and overall health. This imbalance can result in impaired digestion, reduced absorption of essential nutrients, and increased susceptibility to illnesses.
It is essential to recognize the potential health risks associated with frequent noodle consumption and take steps to maintain a balanced diet that includes a variety of whole, nutrient-dense foods to mitigate these risks.
High Sodium Intake⁚ A Major Concern
One of the most significant concerns associated with frequent noodle consumption is the high sodium intake that often accompanies it. Instant noodles, in particular, are notorious for their excessive sodium content, which can range from 800 to 1,200 milligrams per serving.
Prolonged consumption of high-sodium foods can lead to a range of health problems, including hypertension, cardiovascular disease, and stroke. The American Heart Association recommends consuming no more than 2,300 milligrams of sodium per day, with an ideal limit of 1,500 milligrams for those who are at risk or have existing conditions.
The high sodium content in noodles can be attributed to the presence of monosodium glutamate (MSG), soy sauce, and other seasonings used to enhance flavor. These ingredients not only contribute to the overall sodium content but also increase the risk of excessive sodium intake.
To put this into perspective, a single serving of instant noodles can account for up to 50% of the recommended daily sodium intake. This highlights the need for consumers to be mindful of their sodium intake and take steps to reduce their consumption of high-sodium foods, including noodles.
Reducing sodium intake can be achieved by opting for low-sodium alternatives, using herbs and spices to enhance flavor, and balancing noodle consumption with other nutrient-dense foods. By being aware of the risks associated with high sodium intake, individuals can take proactive steps to protect their health and wellbeing.
Digestive Problems and Nutrient Imbalance
Frequent noodle consumption can lead to digestive problems, such as bloating, constipation, and diarrhea, due to the high carbohydrate and low fiber content. Additionally, a diet dominated by noodles can result in nutrient imbalance, including inadequate intake of essential vitamins, minerals, and protein, compromising overall health and wellbeing.
Risk Factors⁚ Who is Most Susceptible to Noodle-Related Health Issues?
Certain individuals are more susceptible to noodle-related health issues due to various factors. These risk factors can be broadly categorized into demographic and lifestyle-related characteristics.
Demographically, children, pregnant women, and the elderly are more vulnerable to the negative effects of frequent noodle consumption. Children’s bodies are still developing, and a diet dominated by noodles can lead to nutrient deficiencies and stunted growth. Pregnant women require a balanced diet to support fetal development, and excessive noodle consumption can compromise this. The elderly may experience age-related declines in physical function, making them more susceptible to the adverse effects of noodle consumption.
Lifestyle-related factors also play a significant role in determining an individual’s susceptibility to noodle-related health issues. Those who lead sedentary lifestyles or have pre-existing medical conditions, such as hypertension or diabetes, are more likely to experience adverse effects from frequent noodle consumption. Additionally, individuals who consume noodles as a primary source of nutrition, rather than as an occasional supplement, are at higher risk of developing health problems.
Understanding these risk factors is crucial for developing targeted interventions and promoting healthy eating habits. By recognizing the characteristics that make certain individuals more susceptible to noodle-related health issues, healthcare professionals and policymakers can create effective strategies to mitigate these risks and promote overall well-being.
Vulnerable Populations⁚ Children, Pregnant Women, and the Elderly
Children, pregnant women, and the elderly are particularly vulnerable to the negative effects of frequent noodle consumption. In the case of children, a diet dominated by noodles can lead to inadequate nutrient intake, which can compromise growth and development.
Pregnant women, on the other hand, require a balanced diet that provides essential nutrients for fetal development. Excessive noodle consumption during pregnancy can increase the risk of gestational diabetes, hypertension, and other complications. Furthermore, the high sodium content in many instant noodles can exacerbate these conditions.
The elderly are also susceptible to the adverse effects of noodle consumption due to age-related declines in physical function. As people age, their metabolic rates slow down, and their bodies become less efficient at processing certain nutrients. A diet dominated by noodles can further compromise their nutritional status, leading to frailty, cognitive decline, and increased risk of chronic diseases.
It is essential to note that these vulnerable populations often have limited control over their dietary choices, relying on caregivers or family members for food provision. Therefore, it is crucial for caregivers and healthcare providers to be aware of the potential risks associated with noodle consumption and promote healthy eating habits in these populations.
By recognizing the unique needs and vulnerabilities of these populations, targeted interventions can be developed to promote healthier eating habits and mitigate the negative effects of noodle consumption.
Other Risk Factors⁚ Lifestyle and Pre-Existing Conditions
Sedentary lifestyle, smoking, and pre-existing conditions like hypertension, diabetes, and obesity can amplify the health risks associated with frequent noodle consumption. Individuals with these risk factors should exercise caution and consider healthier dietary alternatives to mitigate the negative effects of noodles on their overall health.
Moderation is Key
In conclusion, while noodles can be a convenient and enjoyable part of a balanced diet, frequent consumption can pose significant health risks. It is essential to practice moderation and mindful eating habits to minimize the negative effects of noodle consumption.
A well-informed approach to nutrition, taking into account individual risk factors and lifestyle choices, can help mitigate the dangers associated with regular noodle consumption. By making informed choices and adopting healthier dietary habits, individuals can reduce their risk of developing chronic diseases and maintain overall well-being.
Public health initiatives and education programs can also play a crucial role in promoting healthy eating habits and raising awareness about the potential risks of excessive noodle consumption. By working together, individuals, healthcare professionals, and policymakers can foster a culture of healthy eating and promote a balanced lifestyle for all.
Ultimately, the key to minimizing the health risks associated with noodle consumption lies in moderation and balance. By being mindful of our dietary choices and adopting healthier habits, we can enjoy noodles as an occasional treat while protecting our long-term health and well-being.
By adopting a balanced and informed approach to nutrition, we can navigate the complexities of modern food systems and make choices that promote optimal health, now and for generations to come.
I appreciate how this article breaks down the ingredients used in instant noodle production. It
I appreciate how this article emphasizes that not all instant noodles are created equal. It
As a health enthusiast, I
This article provides valuable insights into the world of instant noodle consumption. I look forward to reading more about this topic in future articles.
This article provides a thorough analysis of the nutritional content of instant noodles, highlighting their high calorie and sodium content. It
The section on MSG was informative, but I would have liked to see more discussion on its potential health effects.
I was surprised to learn about the chemical treatments involved in instant noodle processing. This article has definitely made me think twice about my food choices.
While I agree that instant noodles can be detrimental to our health, I think it