Introduction to Psoriasis Symptoms and Associated Risks
Persistent skin condition characterized by inflammatory response and skin lesions, increasing arthritis risk and joint inflammation, particularly in plaque psoriasis cases, necessitating timely psoriatic arthritis treatment consideration.
Understanding Psoriasis and Its Connection to Psoriatic Arthritis
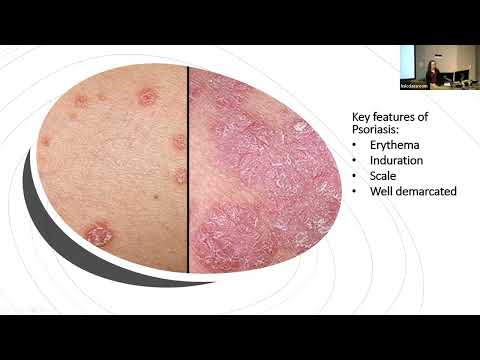
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune-mediated skin condition characterized by an abnormal inflammatory response, resulting in the formation of thickened, scaly skin lesions. This condition affects approximately 2-3% of the global population, with plaque psoriasis being the most common form. Research has established a significant connection between psoriasis and the development of psoriatic arthritis, a type of inflammatory arthritis that affects the joints.
Studies have shown that up to 30% of individuals with psoriasis will eventually develop psoriatic arthritis٫ highlighting the importance of early recognition and intervention. The exact mechanisms underlying this connection are not yet fully understood٫ but it is believed that a combination of genetic٫ environmental٫ and immunological factors contribute to the development of psoriatic arthritis in individuals with psoriasis. A comprehensive understanding of this relationship is essential for the effective management and treatment of both conditions.
The Autoimmune Nature of Psoriasis and Its Impact on Joints
Psoriasis is characterized by an abnormal autoimmune response, in which the immune system mistakenly targets healthy skin cells, leading to chronic inflammation and tissue damage. This autoimmune dysregulation can also affect the joints, leading to joint inflammation and damage.
The autoimmune nature of psoriasis is mediated by various immune cells, including T cells and dendritic cells, which produce pro-inflammatory cytokines that perpetuate the inflammatory response. These cytokines can also diffuse into the joints, triggering an inflammatory response and promoting the development of psoriatic arthritis. Furthermore, the chronic inflammation associated with psoriasis can lead to joint damage and degeneration over time, underscoring the importance of early intervention and management to mitigate the risk of psoriatic arthritis.
The interplay between the immune system, skin, and joints in psoriasis highlights the complex pathophysiology of this condition and the need for a multidisciplinary approach to manage its various manifestations.
Types of Psoriasis and Their Association with Psoriatic Arthritis
Plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, and psoriatic erythroderma are associated with varying degrees of psoriatic arthritis risk, with plaque psoriasis cartridges conferring the highest risk due to chronic inflammation and skin lesions.
Recognizing the Early Signs of Psoriatic Arthritis in Psoriasis Patients
Early detection of psoriatic arthritis is crucial to prevent long-term joint damage and disability. In patients with psoriasis, it is essential to monitor for signs of joint inflammation and arthritis symptoms, such as joint pain, swelling, and stiffness. Other indicators may include loss of range of motion, morning stiffness lasting over 30 minutes, and enthesitis (inflammation of the tendons and ligaments). Furthermore, the presence of nail changes, such as pitting and onycholysis, can be an early warning sign of psoriatic arthritis. A thorough physical examination, medical history, and laboratory tests can help diagnose psoriatic arthritis in its early stages, allowing for timely initiation of effective treatment and prevention of long-term complications.
Joint Pain and Swelling⁚ Common Indicators of Psoriatic Arthritis
Joint pain and swelling are two of the most common symptoms of psoriatic arthritis, occurring in up to 90% of patients. The pain is often described as dull, aching, or throbbing, and is typically accompanied by joint stiffness and limited mobility; The swelling is usually caused by inflammation in the joints, leading to redness, warmth, and tenderness to the touch. In some cases, the swelling can be severe enough to cause joint deformity and loss of function. The joints most commonly affected by psoriatic arthritis are the hands, feet, knees, elbows, and ankles. If left untreated, the chronic inflammation and joint damage associated with psoriatic arthritis can lead to long-term disability and decreased quality of life.
Other Warning Signs and Complications of Untreated Psoriatic Arthritis
Neglected psoriatic arthritis may lead to eye inflammation, osteoporosis, and increased cardiovascular risk, underscoring the importance of prompt diagnosis and treatment to mitigate these potential complications and comorbidities.
Managing Psoriasis and Reducing the Risk of Psoriatic Arthritis
Effective management of psoriasis symptoms is crucial in mitigating the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis. A comprehensive treatment plan should incorporate both pharmacological and non-pharmacological interventions. Topical treatments and light therapy can help control skin inflammation, while systemic medications may be necessary for more severe cases. In addition to these treatments, patients should be encouraged to adopt healthy lifestyle habits, such as maintaining a balanced diet, engaging in regular exercise, and managing stress levels.
Early detection and treatment of psoriatic arthritis are critical in preventing long-term joint damage and improving quality of life. By working closely with healthcare providers, patients can develop a personalized treatment plan that addresses their unique needs and reduces the risk of complications associated with psoriatic arthritis. Furthermore, ongoing monitoring and assessment of psoriasis symptoms and joint health are essential in ensuring optimal management and minimizing the risk of disease progression.
Lifestyle Modifications for Psoriasis Management and Arthritis Prevention
Certain lifestyle modifications can significantly impact the management of psoriasis symptoms and reduce the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis. Maintaining a healthy weight through a balanced diet and regular exercise can alleviate joint stress and promote overall well-being. A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids, whole grains, and fruits can help mitigate inflammation, while avoiding trigger foods can reduce skin condition flare-ups.
In addition to dietary changes, stress management techniques such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises can help regulate the immune system and reduce inflammation. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption can also improve overall health and reduce the risk of psoriatic arthritis. Furthermore, engaging in low-impact exercises such as swimming or cycling can help maintain joint mobility and reduce stiffness. By incorporating these lifestyle modifications, individuals with psoriasis can effectively manage their symptoms and reduce the risk of developing psoriatic arthritis.
Treatment Options for Psoriatic Arthritis⁚ Medications and Therapies
Psoriatic arthritis treatment involves a range of options, including nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), disease-modifying antirheumatic drugs (DMARDs), biologics, and physical therapies to manage joint inflammation and alleviate psoriasis symptoms effectively.
The Importance of Monitoring and Managing Psoriasis Symptoms
Effective management of psoriasis symptoms is crucial for preventing the development of psoriatic arthritis and mitigating its impact on quality of life. By understanding the connection between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, individuals can take proactive steps to monitor their condition and seek timely medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen.
A multidisciplinary approach, incorporating lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and regular follow-up appointments, can significantly reduce the risk of psoriatic arthritis and its associated complications.
It is essential for patients to work closely with their healthcare providers to develop a personalized treatment plan, addressing their unique needs and health goals. By prioritizing psoriasis management and maintaining open communication with healthcare professionals, individuals can minimize the risk of psoriatic arthritis and optimize their overall well-being.
Ultimately, a comprehensive and proactive approach to psoriasis care can significantly improve health outcomes and enhance quality of life for individuals affected by this chronic autoimmune disease.
Early Detection and Treatment of Psoriatic Arthritis in Psoriasis Patients
Timely identification and intervention are critical in managing psoriatic arthritis in patients with psoriasis. A thorough clinical evaluation, including a detailed medical history and physical examination, can help detect early signs of joint inflammation and arthritis.
Diagnostic imaging techniques, such as X-rays, ultrasound, or MRI, may be employed to confirm the presence of joint damage or inflammation. Laboratory tests, including rheumatoid factor and anti-CCP antibody assessments, can also aid in diagnosing psoriatic arthritis.
Upon diagnosis, a treatment plan should be initiated promptly, incorporating pharmacological agents, physical therapy, and lifestyle modifications as needed. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes, reducing the risk of long-term joint damage and disability. Regular follow-up appointments with a healthcare provider are essential to monitor disease progression and adjust treatment strategies as necessary.
By prioritizing early detection and treatment, individuals with psoriasis can minimize the impact of psoriatic arthritis and maintain optimal joint health and function.
Future Directions in Psoriasis and Psoriatic Arthritis Research and Treatment
Ongoing research endeavors aim to elucidate the complex interplay between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis, driving innovation in therapeutic strategies and disease management.
Emerging areas of investigation include the application of biologics and small-molecule inhibitors targeting specific molecular pathways implicated in inflammatory response and autoimmune disease progression.
Advances in personalized medicine and precision health are expected to enable tailored treatment approaches, accounting for individual variability in disease presentation, genetic predisposition, and environmental influences.
Furthermore, the development of novel biomarkers and imaging modalities will facilitate enhanced diagnostic accuracy and monitoring of disease activity, allowing for timely interventions and improved patient outcomes.
Interdisciplinary collaboration and knowledge sharing among researchers, clinicians, and patients will be essential in shaping the future of psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis care, ultimately reducing the burden of these conditions and improving quality of life for those affected.
This article demonstrates excellent knowledge on the topic; however, I felt that some sections were overly technical for non-experts like myself. Consider simplifying certain paragraphs or providing additional explanations for complex terms.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the connection between psoriasis and psoriatic arthritis. The author
Overall, I found this piece well-written with useful insights into both conditions; still – even though we learn about possible connections – we do not know enough specifics regarding causes behind these diseases.
I appreciate how this article highlights the importance of early recognition and intervention for individuals with psoriasis who are at risk of developing psoriatic arthritis. However, I would have liked to see more discussion on specific treatment options.
I was impressed by how well-researched this article was – it
As someone living with plaque psoriasis, I found this article informative and reassuring. The author