Ruptured Ear Drum⁚ Causes‚ Symptoms‚ and Treatment
A ruptured ear drum‚ also known as a tympanic membrane perforation‚ is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention. Conductive hearing loss and ear trauma are closely related to this condition‚ necessitating thorough evaluation and treatment.
Introduction
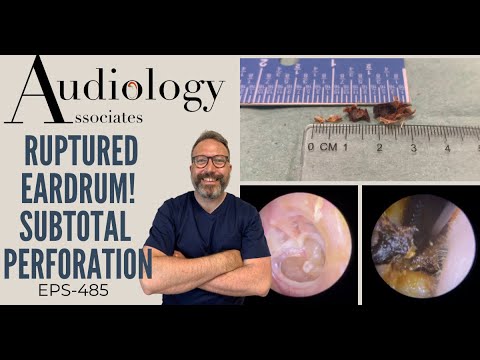
A ruptured ear drum is a medical condition characterized by a tear or perforation in the tympanic membrane‚ which separates the outer ear canal from the middle ear. This delicate structure plays a crucial role in sound transmission and hearing. The tympanic membrane is susceptible to damage from various causes‚ including ear trauma‚ infections‚ and Eustachian tube dysfunction.
The tympanic membrane is a complex structure composed of three layers⁚ an outer epithelial layer‚ a middle fibrous layer‚ and an inner mucosal layer; Its integrity is essential for maintaining normal middle ear pressure and facilitating sound conduction. When the tympanic membrane is compromised‚ it can lead to hearing loss‚ ear pain‚ and discharge.
It is essential to seek medical attention promptly if symptoms persist or worsen over time. A comprehensive evaluation by an ear‚ nose‚ and throat (ENT) specialist or an audiologist is necessary to determine the underlying cause and develop an effective treatment plan. Early intervention can significantly improve outcomes and prevent long-term complications.
Causes of a Ruptured Ear Drum
Ruptured ear drums can result from various causes‚ including ear trauma‚ middle ear infections‚ and Eustachian tube dysfunction. Foreign objects‚ loud noises‚ and sudden changes in air pressure can also contribute to this condition.
Ear Trauma
Ear trauma is a common cause of a ruptured ear drum. This can occur due to various reasons‚ including a severe head injury‚ a fall‚ or a car accident. Tympanic membrane perforation can also result from a direct blow to the ear‚ such as a punch or a slap. Additionally‚ foreign objects inserted into the ear canal‚ such as cotton swabs or fingers‚ can cause damage to the eardrum.
In some cases‚ ear trauma can also be caused by sudden and loud noises‚ such as an explosion or a gunshot. This type of trauma is often referred to as acoustic trauma. The sudden increase in air pressure can cause the eardrum to rupture‚ leading to hearing loss and other complications.
It is essential to seek medical attention immediately if ear trauma is suspected. A thorough examination by a healthcare professional can help determine the extent of the damage and guide further treatment.
A ruptured eardrum caused by ear trauma can lead to middle ear damage‚ which may require surgical intervention. Prompt treatment can help prevent long-term complications and promote healing.
Middle Ear Infections
Middle ear infections‚ also known as otitis media‚ are another common cause of a ruptured ear drum. These infections occur when bacteria or viruses infect the middle ear‚ causing inflammation and fluid buildup.
The increased pressure from the fluid can cause the eardrum to rupture‚ leading to a discharge of pus and debris from the ear canal. In some cases‚ the infection can spread to other parts of the ear‚ including the inner ear and the mastoid bone.
Eardrum rupture caused by middle ear infections can lead to conductive hearing loss‚ which may be temporary or permanent. Treatment for middle ear infections usually involves antibiotics to clear up the infection‚ and in some cases‚ surgical intervention may be necessary to repair the damaged eardrum.
It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms of a middle ear infection persist or worsen over time. Prompt treatment can help prevent complications and promote healing; A healthcare professional can diagnose middle ear infections using a combination of physical examination‚ medical history‚ and diagnostic tests.
Untreated middle ear infections can lead to serious complications‚ including chronic hearing loss and ear trauma. Early detection and treatment are crucial to preventing long-term damage.
Symptoms of a Ruptured Ear Drum
A ruptured ear drum can cause a range of symptoms‚ including sudden hearing loss‚ severe ear pain‚ and discharge from the ear canal. Middle ear damage may also lead to vertigo‚ tinnitus‚ and a feeling of fullness in the ear.
Hearing Loss
Hearing loss is a common symptom of a ruptured ear drum‚ particularly conductive hearing loss. This type of hearing loss occurs when sound waves are unable to reach the inner ear due to damage to the middle ear. The extent of hearing loss can vary depending on the severity of the rupture and the individual’s overall health.
In some cases‚ hearing loss may be temporary and resolve on its own once the rupture has healed. However‚ in more severe cases‚ hearing loss can be permanent and may require the use of hearing aids or other assistive devices.
It is essential for individuals who have experienced a ruptured ear drum to seek medical attention promptly to minimize the risk of long-term hearing loss. A healthcare professional can assess the extent of the damage and provide guidance on the best course of treatment to restore hearing and prevent further complications.
Early intervention and proper treatment can significantly improve outcomes and reduce the risk of permanent hearing loss. Therefore‚ it is crucial to prioritize prompt medical attention if symptoms of a ruptured ear drum occur.
Ear Pain and Discharge
Ear pain and discharge are common symptoms associated with a ruptured ear drum. The pain can range from mild to severe and is often described as sharp or stabbing. It may be exacerbated by certain movements‚ such as yawning or chewing.
Discharge from the ear‚ also known as otorrhea‚ may be clear‚ yellowish‚ or bloody‚ depending on the severity of the rupture and the presence of infection. In some cases‚ the discharge may have a foul odor‚ indicating a bacterial infection.
The ear pain and discharge can be distressing and affect daily activities. It is essential to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen over time. A healthcare professional can evaluate the ear and provide guidance on managing the symptoms and preventing further complications.
In addition to ear pain and discharge‚ some individuals may experience a sensation of fullness or blockage in the ear‚ which can be uncomfortable and affect hearing. Prompt medical attention can help alleviate these symptoms and promote healing.
Diagnosis and Treatment
An accurate diagnosis of a ruptured ear drum is crucial for effective treatment. A thorough evaluation by a healthcare professional will determine the best course of action to promote healing and prevent further complications.
Otoscopy and Tympanometry
Otoscopy and tympanometry are essential diagnostic tools used to evaluate the extent of a ruptured ear drum. Otoscopy involves the use of an otoscope to visually examine the ear canal and eardrum‚ allowing healthcare professionals to assess the severity of the perforation.
Tympanometry‚ on the other hand‚ is a non-invasive test that measures the movement of the eardrum and the reflexes of the middle ear muscles. This test helps to determine the presence and extent of middle ear damage‚ as well as the degree of hearing loss.
By combining the results of otoscopy and tympanometry‚ healthcare professionals can gain a comprehensive understanding of the condition and develop an effective treatment plan. These diagnostic tests are crucial in determining the best course of action to promote healing‚ prevent further complications‚ and restore optimal hearing function.
In some cases‚ additional tests such as audiometry or imaging studies may be necessary to fully evaluate the condition and guide treatment decisions. However‚ otoscopy and tympanometry remain the primary diagnostic tools for evaluating a ruptured ear drum.
Treatment Options
The primary goal of treatment for a ruptured ear drum is to promote healing‚ prevent infection‚ and restore optimal hearing function. In some cases‚ the condition may resolve on its own without medical intervention.
However‚ if the perforation is large or accompanied by significant hearing loss‚ surgical repair may be necessary. This typically involves a procedure called tympanoplasty‚ where a graft is used to repair or replace the damaged eardrum.
In addition to surgical intervention‚ treatment may also include antibiotics to prevent infection‚ as well as pain management medication to alleviate discomfort. It is essential to avoid water exposure and loud noises during the healing process to prevent further complications.
In some cases‚ a hearing aid may be recommended to manage conductive hearing loss until the condition resolves or surgical repair can be performed. A healthcare professional will work with the individual to develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to their specific needs and circumstances.
Regular follow-up appointments are crucial to monitor the healing progress and adjust the treatment plan as needed.
In conclusion‚ a ruptured ear drum is a serious condition that requires prompt medical attention to prevent long-term complications and promote optimal healing.
It is essential for individuals to be aware of the causes‚ symptoms‚ and treatment options available for this condition‚ as timely intervention can significantly impact outcomes. By seeking medical attention promptly‚ individuals can reduce the risk of permanent hearing loss and other complications.
Healthcare professionals play a crucial role in educating patients on the importance of proper ear care and providing personalized treatment plans to address the unique needs of each individual.
By working together‚ individuals and healthcare professionals can effectively manage and treat ruptured ear drums‚ ensuring the best possible outcomes and improving overall quality of life. Regular check-ups and preventive measures can also help to reduce the risk of future ear-related complications.
Ultimately‚ prioritizing ear health and seeking medical attention when necessary are essential steps in maintaining optimal auditory function and overall well-being.
I appreciate how this article emphasizes the need for comprehensive evaluation by an ENT specialist or audiologist for proper diagnosis and treatment planning.
This article provides an excellent overview of ruptured eardrums, their causes, symptoms, and treatment options. I appreciate how it emphasizes the importance of seeking medical attention promptly.
Overall, this article provides clear, concise information about ruptured eardrums, making it accessible to readers without extensive medical backgrounds.
As someone who has experienced conductive hearing loss due to eardrum damage, I appreciate how this article highlights the importance of early intervention in preventing long-term complications.
This article provides valuable insights into the relationship between eustachian tube dysfunction and ruptured eardrums.
I found this article informative, but I think it would benefit from more detailed explanations of the different types of treatments available for ruptured eardrums.
I think this article could benefit from more visual aids, such as diagrams or illustrations, to help readers better understand the concepts discussed.
This article does an excellent job explaining the anatomy of the tympanic membrane and its role in sound transmission.