Skin Function & Skin Structure⁚ What Do Individuals Need to Know About It?
Comprehending skin function and structure is crucial for maintaining optimal skin health. Individuals should be aware of the intricate relationships between skin layers, cells, and components to prevent and manage various skin conditions.
Introduction to Skin Anatomy
The human skin is a complex and dynamic organ, comprising multiple layers and components that work in harmony to maintain its integrity and functionality. As the largest organ of the body, the skin performs a multitude of vital functions, including thermoregulation, protection, and sensation. A comprehensive understanding of skin anatomy is essential for appreciating its diverse roles and responsibilities.
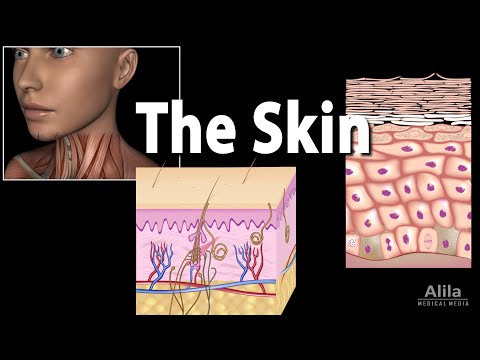
The skin’s structure is typically categorized into three primary layers⁚ the epidermis, dermis, and hypodermis. Each layer possesses distinct characteristics, cell types, and functions that contribute to the skin’s overall health and appearance. The study of skin anatomy is an ongoing field of research, with new discoveries continually shedding light on the intricacies of this fascinating organ. By grasping the fundamental concepts of skin anatomy, individuals can better comprehend the intricacies of skin function and develop effective strategies for promoting optimal skin health.
Understanding the Layers of the Skin
A thorough comprehension of the skin’s layered structure is essential for understanding its diverse functions and maintaining optimal skin health, as each layer possesses unique characteristics and plays a vital role in overall skin integrity.
The Epidermis⁚ Epidermis Function and Importance
The epidermis is the outermost layer of the skin, responsible for protecting the body from external factors such as water loss, temperature fluctuations, and pathogens. Comprising approximately 90% of the skin’s outermost layer, it plays a crucial role in maintaining skin integrity.
One of the primary functions of the epidermis is to act as a physical barrier, preventing the entry of foreign substances and microbes into the body. Additionally, it aids in regulating body temperature through the process of sweating and helps to maintain skin hydration levels.
The epidermis is composed of several sublayers, each with distinct characteristics and functions. The stratum corneum, the outermost sublayer, is responsible for the skin’s natural barrier function. Understanding the epidermis’ functions and importance is vital for maintaining optimal skin health and preventing various skin disorders.
As the body’s first line of defense, the epidermis requires proper care and maintenance to function effectively. Adequate hydration, protection from environmental stressors, and a balanced diet are essential for promoting epidermal health and overall skin well-being.
The Dermal Layer⁚ Understanding its Role in Skin Health
The dermal layer, situated beneath the epidermis, is a complex network of fibrous and non-fibrous elements that provide structural support and nourishment to the skin. Comprising approximately 90% of the skin’s thickness٫ it plays a pivotal role in maintaining skin elasticity and firmness.
The dermal layer is composed of two sublayers⁚ the papillary dermis and the reticular dermis. The papillary dermis, the thinner of the two, supplies the epidermis with oxygen and nutrients via a network of fine capillaries. The reticular dermis, comprising a dense mesh of collagen and elastin fibers, provides skin elasticity and resilience.
The dermal layer is also home to a variety of cell types, including fibroblasts, which produce collagen and elastin, and mast cells, which play a crucial role in the skin’s immune response. A comprehensive understanding of the dermal layer’s structure and function is essential for addressing various skin concerns, such as wrinkles, fine lines, and skin laxity.
By recognizing the dermal layer’s importance, individuals can take proactive steps to promote skin health, including protecting the skin from sun damage, using gentle skincare products, and maintaining a balanced lifestyle.
The Hypodermis⁚ Hypodermis Role in Temperature Regulation and Fat Storage
The hypodermis, also known as the subcutaneous tissue, is the innermost layer of the skin. It plays a vital role in regulating body temperature and storing energy in the form of fat. Composed of adipocytes, blood vessels, and connective tissue, the hypodermis acts as an insulating layer, helping to conserve heat in cold temperatures and dissipate it in warm temperatures.
The hypodermis also serves as a storage depot for lipids, which are metabolized to produce energy. In addition, it provides cushioning and support to underlying tissues and organs. The thickness of the hypodermis varies depending on factors such as age, sex, and body composition.
A well-functioning hypodermis is essential for maintaining overall health and well-being. Dysregulation of the hypodermis has been implicated in various conditions, including obesity, diabetes, and cardiovascular disease. Therefore, it is crucial to maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet and regular exercise, to support optimal hypodermis function.
Furthermore, understanding the role of the hypodermis in temperature regulation and fat storage can inform strategies for improving overall skin health and appearance.
Skin Cell Regeneration and Collagen Production
Effective skin cell regeneration and collagen production are vital for maintaining healthy, resilient skin. These processes enable the skin to repair and replace damaged cells, ensuring optimal skin elasticity, firmness, and radiance throughout life.
The Process of Skin Cell Regeneration and Turnover
The process of skin cell regeneration and turnover is a complex, highly regulated mechanism that ensures the maintenance of healthy, functional skin. It involves the coordinated effort of multiple cell types, including stem cells, keratinocytes, and melanocytes. The process begins with the proliferation of stem cells in the basal layer of the epidermis, which then differentiate into mature skin cells; As these cells migrate upwards through the epidermal layers, they undergo a series of morphological and biochemical changes, eventually reaching the skin’s surface, where they are shed and replaced by new cells. This continuous cycle of cell regeneration and turnover occurs every 28 days, on average, and is essential for maintaining the skin’s natural barrier function, preventing water loss, and regulating body temperature.
Throughout this process, the skin’s cellular composition is constantly being renewed, allowing for the removal of damaged or dysfunctional cells and the incorporation of new, healthy cells. This dynamic process is crucial for maintaining optimal skin health and preventing various skin disorders.
Collagen Production and its Importance in Skin Elasticity
Collagen production plays a pivotal role in maintaining skin elasticity and firmness. As the most abundant protein in the human body, collagen provides the structural framework for skin, bones, and connective tissue. In the skin, collagen fibers form a complex network that imparts elasticity, flexibility, and tensile strength, enabling the skin to snap back into place after stretching or contracting. The production of collagen is a highly regulated process, involving the coordinated effort of fibroblasts, growth factors, and enzymes.
Adequate collagen production is essential for maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin. However, collagen synthesis declines with age, leading to a loss of skin elasticity and the formation of wrinkles and fine lines. Factors such as UV exposure, smoking, and nutritional deficiencies can also compromise collagen production, further exacerbating skin aging. Therefore, stimulating collagen production through topical treatments, dietary interventions, or other means can help restore skin elasticity and promote a more radiant, youthful appearance.
Elastin Fibers⁚ The Key to Maintaining Skin Elasticity and Firmness
Elastin fibers are a crucial component of the skin’s extracellular matrix, playing a vital role in maintaining skin elasticity rebellion and firmness. These fibers are composed of the protein elastin, which is synthesized by fibroblasts and organized into a network of elastic fibers. Elastin fibers provide the skin with the ability to stretch and recoil, enabling it to adapt to changing facial expressions, movements, and environmental conditions.
The integrity of elastin fibers is essential for maintaining healthy, youthful-looking skin. However, elastin fibers are susceptible to degradation by enzymes, such as elastase, which can lead to a loss of skin elasticity and firmness. Furthermore, UV exposure, smoking, and chronological aging can also compromise elastin fiber integrity, contributing to the development of wrinkles and age-related skin changes. Understanding the importance of elastin fibers can inform the development of effective skincare strategies and treatments aimed at preserving skin elasticity and promoting a more radiant appearance.
The Importance of Skin Hydration and Moisture Barrier Function
Adequate skin hydration and a functioning moisture barrier are essential for maintaining healthy, resilient skin. This complex interplay regulates water balance, prevents dehydration, and protects against environmental stressors and irritants.
Skin Hydration Importance⁚ Maintaining the Skin’s Natural Barrier
Maintaining optimal skin hydration is crucial for preserving the skin’s natural barrier function. The stratum corneum, the outermost epidermal layer, plays a pivotal role in regulating water balance and preventing excessive water loss. Adequate hydration enables the skin to maintain its natural moisture barrier, ensuring the integrity of the stratum corneum and preventing the penetration of external aggressors. Dehydration, on the other hand, compromises the skin’s barrier function, leading to increased permeability and vulnerability to environmental stressors. Furthermore, skin hydration influences the skin’s mechanical properties, such as elasticity and suppleness. Proper hydration also facilitates the skin’s natural desquamation process, promoting the removal of dead skin cells and revealing radiant, healthy-looking skin. Consequently, prioritizing skin hydration is essential for maintaining a robust and resilient skin barrier, capable of withstanding internal and external challenges.
Moisture Barrier Function⁚ Preventing Water Loss and Protecting the Skin
The skin’s moisture barrier function is a critical mechanism that prevents excessive water loss and protects the skin from external aggressors. The stratum corneum’s lipid bilayer, composed of ceramides, cholesterol, and fatty acids, forms a hydrophobic barrier that inhibits water evaporation and retains moisture. This barrier also prevents the penetration of irritants, allergens, and microorganisms, safeguarding the skin against infections and inflammatory responses. Moreover, the moisture barrier function helps to regulate the skin’s pH levels, maintaining an acidic environment that inhibits the growth of pathogens. An intact moisture barrier also enables the skin to respond effectively to environmental changes, such as humidity and temperature fluctuations. By preserving the skin’s natural moisture barrier, individuals can protect their skin against dryness, irritation, and damage, ultimately maintaining healthy, resilient, and radiant skin. A compromised moisture barrier, on the other hand, can lead to a range of skin disorders and conditions.
Maintaining Skin pH Balance⁚ The Key to Healthy Skin
Maintaining the skin’s natural pH balance is essential for optimal skin health. The skin’s pH level is slightly acidic, ranging from 4.5 to 5.5, which allows it to function as a barrier against external aggressors. When the skin’s pH balance is disrupted, the skin’s natural barrier function is compromised, leading to increased susceptibility to irritation, dryness, and infection. Factors such as harsh skincare products, environmental stressors, and certain medical conditions can alter the skin’s pH levels, leading to skin disorders like acne, eczema, and dermatitis. To maintain skin pH balance, individuals should use gentle, pH-balanced skincare products, avoid excessive washing, and protect their skin from environmental stressors. Additionally, a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and omega-3 fatty acids can help support the skin’s natural pH balance. By maintaining skin pH balance, individuals can promote healthy skin, enhance its resilience, and reduce the risk of skin-related disorders.
Understanding Skin Function and Structure for Better Skin Health
In conclusion, a comprehensive understanding of skin function and structure is vital for achieving optimal skin health. By recognizing the intricate relationships within the skin, individuals can adopt informed strategies to promote skin wellness and prevent disorders.
Practical Tips for Maintaining Healthy Skin
To maintain healthy skin, it is essential to adopt a consistent skincare routine. This includes gentle cleansing, moisturizing, and protecting the skin from environmental stressors. Individuals should also prioritize sun protection, utilizing broad-spectrum sunscreen with a Sun Protection Factor (SPF) of 30 or higher.
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins supports skin health by providing essential nutrients and antioxidants. Adequate hydration is also crucial, with a recommended daily intake of at least eight glasses of water. Regular exercise, stress management, and sufficient sleep contribute to overall well-being and skin health.
Avoiding harsh skincare products, smoking, and excessive exposure to pollutants can also help prevent skin damage. Regular skin check-ups with a dermatologist can facilitate early detection and treatment of skin concerns, promoting optimal skin health and well-being. By incorporating these practical tips into daily life, individuals can foster healthy, resilient, and radiant skin.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of the skin
While this article provides a good introduction to skin anatomy, I felt that it was missing some key information about current research in the field.
I enjoyed reading this article because it was easy to understand despite being about a complex topic. The writing was clear and concise.
Overall, I thought this was a great article that effectively explained why understanding skin function and structure is important for maintaining healthy skin.
As a dermatologist, I found this article to be accurate and informative. However, I would have liked to see more discussion on common skin conditions and how they relate to skin anatomy.
As someone interested in skincare, I appreciated learning about how understanding skin anatomy can help me take better care of my own skin.
This article was well-written but could benefit from more visual aids such as diagrams or illustrations to help explain complex concepts.