Understanding Sore Elbow⁚ Causes and Symptoms
Sore elbow is a musculoskeletal disorder characterized by elbow pain, joint inflammation, and tenderness, often resulting from repetitive strain injury or overuse injury.
1.1 Definition of Sore Elbow
Sore elbow is a broad term that encompasses a range of musculoskeletal disorders affecting the elbow joint. It is characterized by the presence of elbow pain, inflammation, and tenderness, which can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life and functional abilities. Sore elbow can arise from various causes, including repetitive strain injuries, overuse, or direct trauma to the elbow joint. The condition can affect individuals from diverse backgrounds and professions, although it is more prevalent among those engaged in activities that involve repetitive elbow movements, such as athletes, manual laborers, and musicians. A comprehensive understanding of sore elbow is essential for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies.
1.2 Common Causes of Sore Elbow
Sore elbow can arise from a variety of causes, including repetitive strain injuries, overuse, and direct trauma to the elbow joint. Repetitive strain injuries, such as those experienced by tennis players or golfers, can lead to inflammation and micro-tearing of the tendons and ligaments surrounding the elbow joint. Overuse injuries, resulting from prolonged periods of elbow flexion or extension, can also contribute to sore elbow. Additionally, direct trauma to the elbow joint, such as a fall onto an outstretched hand, can cause bone fractures, dislocations, or soft tissue injuries. Other common causes of sore elbow include poor posture, inadequate warm-up or cool-down exercises, and improper lifting techniques. Identifying the underlying cause of sore elbow is essential for developing an effective treatment plan.
Identifying the Types of Sore Elbow
Sore elbow encompasses various conditions, including tennis elbow and medial epicondylitis, each with distinct characteristics and etiologies, requiring accurate diagnosis for effective management;
2.1 Tennis Elbow (Lateral Epicondylitis)
Tennis elbow, also known as lateral epicondylitis, is a common musculoskeletal disorder affecting the lateral epicondyle of the humerus. It is characterized by pain and tenderness on the outer aspect of the elbow, often radiating to the forearm and wrist. This condition typically results from repetitive strain injury or overuse of the extensor muscles of the forearm, particularly the extensor carpi radialis brevis. Tennis elbow is prevalent among individuals engaging in racquet sports, manual labor, or activities involving repetitive gripping and twisting motions. The condition can significantly impact daily activities and athletic performance, necessitating prompt diagnosis and effective management to prevent chronicity and complications.
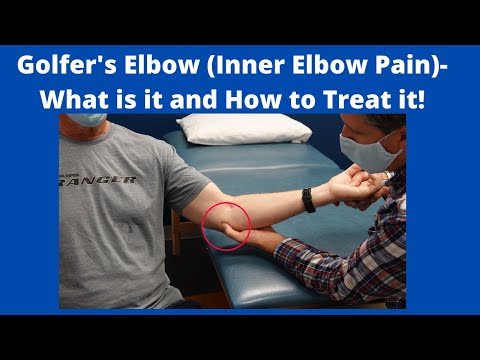
2.2 Medial Epicondylitis (Golfer’s Elbow)
Medial epicondylitis, commonly referred to as golfer’s elbow, is a musculoskeletal disorder affecting the medial epicondyle of the humerus. It is characterized by pain and tenderness on the inner aspect of the elbow, often radiating to the forearm and wrist. This condition typically results from repetitive strain injury or overuse of the flexor muscles of the forearm, particularly the pronator teres and flexor carpi radialis. Golfer’s elbow is prevalent among individuals engaging in golf, rowing, or activities involving repetitive gripping and flexion motions. The condition can significantly impact daily activities and athletic performance, necessitating prompt diagnosis and effective management to prevent chronicity and complications. A comprehensive understanding of medial epicondylitis is essential for developing targeted therapeutic interventions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Sore Elbow
Accurate diagnosis of sore elbow requires a comprehensive evaluation of symptoms, including arm pain, tenderness, swelling, and limited mobility, to determine the underlying cause;
3.1 Common Symptoms of Sore Elbow
Common symptoms of sore elbow include persistent pain and tenderness on the outside or inside of the elbow, which may radiate to the forearm, wrist, or arm. Swelling and redness around the affected area are also typical symptoms. In some cases, individuals may experience limited mobility, stiffness, or a weakened grip. The pain may be exacerbated by activities that involve gripping, twisting, or lifting, and may be relieved with rest. Additionally, some people may experience numbness or tingling sensations in the fingers or hand. It is essential to seek medical attention if these symptoms persist or worsen over time, as early diagnosis and treatment can significantly improve outcomes. A thorough evaluation of these symptoms is crucial for determining the underlying cause of sore elbow.
3.2 Diagnostic Techniques for Sore Elbow
Diagnostic techniques for sore elbow include a comprehensive physical examination, medical history, and imaging studies. During the physical examination, the healthcare provider will assess the range of motion, strength, and tenderness in the affected elbow. Imaging studies, such as X-rays, computed tomography (CT) scans, or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans, may be ordered to rule out underlying conditions, such as bone fractures or osteoarthritis. Electromyography (EMG) or nerve conduction studies (NCS) may also be performed to evaluate nerve function. Additionally, laboratory tests, such as blood work or joint fluid analysis, may be conducted to detect signs of infection or inflammation. A thorough diagnostic evaluation is essential for determining the underlying cause of sore elbow and developing an effective treatment plan. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for optimal management and prevention of complications.
Treatment and Management of Sore Elbow
Effective treatment and management of sore elbow involve a multidisciplinary approach, incorporating conservative therapies, lifestyle modifications, and surgical interventions to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
4.1 Conservative Treatment Options
Conservative treatment options for sore elbow are diverse and often serve as the first line of management. These interventions focus on reducing pain, inflammation, and promoting healing.
Patients may benefit from physical therapy, incorporating exercises that strengthen the surrounding muscles and improve joint mobility.
Additionally, pharmacological interventions, such as nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and topical corticosteroids, can help alleviate symptoms.
Lifestyle modifications, including activity modification, proper equipment use, and regular stretching, are also crucial in managing sore elbow.
Furthermore, assistive devices, such as elbow splints and orthotics, can provide support and stability to the affected joint, promoting recovery and preventing further injury.
4.2 Surgical Interventions for Sore Elbow
Surgical interventions for sore elbow are considered when conservative treatment options have failed to provide adequate relief or in cases of severe joint damage.
Procedures, such as arthroscopy and open surgery, can help address underlying pathologies, including tendon tears, bone spurs, and joint degeneration.
Surgical techniques may involve debridement, tendon repair, or reconstruction to restore joint function and alleviate symptoms.
In some cases, total elbow arthroplasty may be necessary to replace the damaged joint with an artificial one.
Post-operative rehabilitation is crucial to ensure proper healing, restore strength, and regain range of motion.
A thorough evaluation by an orthopedic specialist is essential to determine the most suitable surgical approach for each individual case.
Preventing Sore Elbow and Related Injuries
Implementing preventive measures, such as proper warm-up exercises, ergonomic techniques, and regular breaks, can significantly reduce the risk of sore elbow and related musculoskeletal disorders.
5.1 Strategies for Preventing Sore Elbow
To prevent sore elbow, individuals can employ various strategies, including modifying their daily activities to reduce repetitive strain on the elbow joint. Proper warm-up exercises and stretching techniques can also help minimize the risk of injury. Furthermore, maintaining good posture, using ergonomic equipment, and taking regular breaks to rest the arm can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing sore elbow. It is also essential to maintain a healthy weight, as excess weight can put additional strain on the elbow joint. Additionally, incorporating strengthening exercises into one’s routine can help improve overall musculoskeletal health and resilience. By adopting these preventive measures, individuals can reduce their risk of developing sore elbow and related musculoskeletal disorders.
5.2 Managing Repetitive Strain Injuries
Effective management of repetitive strain injuries is crucial in preventing the development of sore elbow. Early recognition and intervention are key, as prompt treatment can significantly reduce the severity and duration of the injury. A healthcare professional may recommend a range of treatments, including physical therapy, bracing or splinting, and pain management medication. Additionally, activity modification and ergonomic adjustments can help alleviate strain on the affected area. It is also essential to address any underlying biomechanical issues or muscle imbalances that may be contributing to the injury. By adopting a comprehensive and proactive approach to managing repetitive strain injuries, individuals can minimize their risk of developing chronic sore elbow and related musculoskeletal disorders, ensuring optimal long-term health and function.
Complications and Related Conditions
Sore elbow can be associated with various complications, including bone fracture, muscle strain, and chronic joint inflammation, potentially leading to long-term musculoskeletal disorders and disability.
6.1 Bone Fracture and Sore Elbow
A bone fracture can be a significant complication of sore elbow, particularly if the condition is left untreated or undertreated. The fracture can occur due to repetitive strain injury or a sudden traumatic event. In some cases, the fracture may be hairline or stress-related, which can exacerbate the symptoms of sore elbow. A thorough diagnosis, including imaging studies such as X-rays or CT scans, is necessary to confirm the presence of a bone fracture. Treatment for a bone fracture associated with sore elbow typically involves immobilization, physical therapy, and pain management. In severe cases, surgical intervention may be required to stabilize the fracture and promote healing.
6.2 Muscle Strain and Sore Elbow
Muscle strain is a common complication of sore elbow, resulting from overstretching or tearing of the muscles surrounding the elbow joint. This can occur due to repetitive strain injury, overuse, or sudden contraction of the muscles. Symptoms of muscle strain associated with sore elbow may include arm pain, swelling, and limited range of motion. Treatment for muscle strain typically involves rest, ice, compression, and elevation (RICE), as well as physical therapy to promote healing and strengthen the affected muscles. In some cases, medication may be prescribed to manage pain and inflammation. It is essential to seek medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen over time, as untreated muscle strain can lead to further complications and prolonged recovery.
In conclusion, sore elbow is a complex condition requiring comprehensive understanding and treatment to effectively manage symptoms and prevent long-term complications and related injuries.
7.1 Summary of Key Points
In summary, sore elbow is a multifaceted condition requiring prompt attention and proper management. Key takeaways from this discussion include the importance of understanding the causes and symptoms of sore elbow, identifying the specific type of injury, and seeking medical attention if symptoms persist or worsen. A comprehensive treatment plan incorporating conservative and surgical interventions can effectively alleviate symptoms and prevent long-term complications. Additionally, adopting preventive strategies and managing repetitive strain injuries can significantly reduce the risk of developing sore elbow. By acknowledging these key points, individuals can take proactive steps towards maintaining optimal elbow health and preventing related injuries.
As someone who experiences frequent sore elbows due to playing tennis regularly), I found this article extremely helpful in understanding my condition.
I found this article informative but would have liked more detail on treatment options for sore elbows.
While I appreciated the breadth of information covered in this article), I felt some sections were overly technical – perhaps simpler explanations would benefit non-expert readers?
This article provides a comprehensive overview of sore elbow causes and symptoms. I appreciate how it breaks down the different types of sore elbows and their respective causes.
A clear), concise), well-written piece on an important topic – kudos to the author!
I
The section on common causes of sore elbows was particularly insightful – I had no idea poor posture could contribute to this condition.