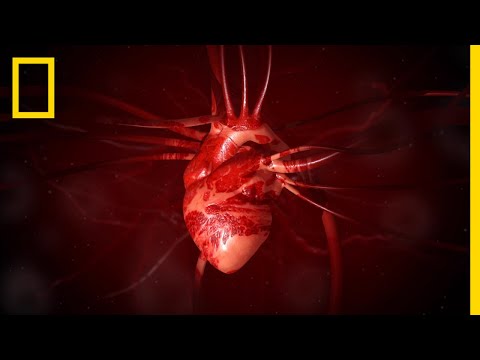
Anatomy of the Heart
The human heart is a complex organ comprising cardiac muscle, blood vessels, and a specialized electrical conduction system, encased in a protective sac called the pericardium, weighing approximately 250-300 grams.
Composition of the Heart
The heart is composed of several layers, each with distinct functions and characteristics. The outermost layer is the epicardium, a thin membrane that surrounds and protects the heart. Beneath the epicardium lies the myocardium, the thickest layer, comprising cardiac muscle cells responsible for contraction and relaxation. The innermost layer is the endocardium, a smooth, blood-contacting surface that lines the heart chambers and valves.
The heart also contains a network of blood vessels, including coronary arteries that supply oxygenated blood to the myocardium, and cardiac veins that remove deoxygenated blood. The heart’s electrical conduction system, consisting of the sinoatrial node, atrioventricular node, and bundle of His, regulates the heartbeat and ensures coordinated contractions.
Additionally, the heart contains various supporting structures, such as the pericardium, a fibrous sac that surrounds and anchors the heart, and the valves, which regulate blood flow between the heart chambers.
Structure of the Heart
The human heart is a quadrangular, hollow organ divided into four chambers⁚ the right atrium, left atrium, right ventricle, and left ventricle. The atria are the upper chambers that receive blood returning to the heart, while the ventricles are the lower chambers that pump blood out of the heart.
The heart also contains four valves⁚ the tricuspid valve, pulmonary valve, mitral valve, and aortic valve. These valves ensure unidirectional blood flow between the heart chambers and prevent backflow. The septum, a wall of tissue, separates the right and left sides of the heart.
The heart’s structure is supported by a framework of connective tissue and cardiac muscle cells. The cardiac skeleton, composed of fibrous rings and trigones, provides attachment points for the valves and muscles, enabling coordinated contractions and efficient blood pumping.
Function of the Heart
The heart’s primary function is to pump blood throughout the body, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs, while removing waste products, maintaining blood pressure, and regulating overall cardiovascular system function.
Heartbeat and Heart Rate
The heartbeat is the rhythmic contraction and relaxation of the heart muscle, pumping blood through the chambers and valves. This process is regulated by the sinoatrial (SA) node, a specialized group of cells that generate electrical impulses at a rate of 60-100 beats per minute (bpm). The heart rate can be influenced by various factors٫ such as physical activity٫ emotional state٫ and medications. A normal heart rate range varies from person to person٫ but generally falls within 60-100 bpm. Abnormal heart rates٫ such as bradycardia (slow heart rate) or tachycardia (fast heart rate)٫ can be indicative of underlying cardiovascular conditions. The heartbeat is a vital sign that provides valuable information about the heart’s function and overall cardiovascular health. Monitoring heart rate and rhythm can help diagnose and manage various heart conditions٫ ensuring timely intervention and treatment.
Blood Circulation
Blood circulation is the process by which the heart pumps blood through a network of blood vessels, supplying oxygen and nutrients to tissues and organs. The circulatory pathway begins with deoxygenated blood returning to the heart through the veins, which then gets pumped to the lungs for oxygenation. Oxygen-rich blood is then transported back to the heart and distributed to the body’s tissues and organs via arteries, arterioles, and capillaries. The coronary arteries, arising from the aorta, supply the heart muscle itself with oxygen and nutrients. Blood circulation plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis, regulating body temperature, and facilitating the removal of waste products. Efficient blood circulation is essential for optimal bodily functions, and any disruptions can lead to various cardiovascular complications. Overall, the circulatory system works in harmony with the heart to ensure the delivery of vital substances to all parts of the body.
Common Heart Conditions
Certain conditions can compromise cardiovascular health, including cardiac arrest, heart attack, and various forms of heart disease, which can have severe consequences if left untreated or poorly managed medically.
Cardiac Arrest and Heart Attack
Cardiac arrest and heart attack are two distinct, life-threatening conditions. Cardiac arrest occurs when the heart suddenly stops functioning, often due to abnormal heart rhythms or electrical disturbances. A heart attack, also known as myocardial infarction, happens when the blood flow to the heart is severely blocked, causing damage to the cardiac muscle. Both conditions require immediate medical attention to prevent long-term damage or even death.
Symptoms of cardiac arrest include sudden collapse, loss of consciousness, and lack of breathing or pulse. Heart attack symptoms can range from mild to severe chest pain, shortness of breath, and fatigue. Prompt recognition and response to these warning signs can significantly improve survival rates and outcomes for individuals experiencing these critical events.
It is essential to note that timely medical intervention can significantly improve the chances of recovery and reduce the risk of long-term complications associated with these conditions.
Heart Disease
Heart disease is a broad term encompassing various conditions that affect the heart and the coronary arteries, which supply blood to the cardiac muscle. The most common form of heart disease is coronary artery disease, where the buildup of plaque in the coronary arteries leads to reduced blood flow, potentially causing angina, heart attack, or cardiac arrhythmias.
Other forms of heart disease include heart failure, valvular heart disease, and congenital heart defects. Factors contributing to the development of heart disease include high blood pressure, high cholesterol, smoking, diabetes, obesity, and family history. Adopting a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, can help mitigate these risk factors and reduce the likelihood of developing heart disease.
Early detection and treatment of heart disease are crucial in preventing long-term complications and improving overall cardiovascular health. It is essential to work closely with healthcare professionals to manage risk factors and develop a personalized plan for maintaining heart health.
Maintaining Cardiovascular Health
Adopting a holistic approach to maintaining cardiovascular health involves cultivating a balanced lifestyle, incorporating regular physical activity, healthy eating habits, stress management, and adequate sleep to support overall well-being.
Diet and Exercise
A well-balanced diet rich in essential nutrients, fiber, and omega-3 fatty acids plays a crucial role in maintaining cardiovascular health. Foods high in saturated fats٫ salt٫ and sugar should be consumed in moderation. Aiming for five servings of fruits and vegetables daily is recommended.
Regular exercise is also vital for a healthy heart. Engaging in moderate-intensity physical activity, such as brisk walking, cycling, or swimming, for at least 150 minutes per week can help lower blood pressure, improve circulation, and boost overall cardiovascular well-being. High-intensity interval training (HIIT) has also been shown to be effective in improving cardiovascular health. It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before starting any new exercise program, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions.
Incorporating healthy lifestyle habits, such as a balanced diet and regular exercise, can significantly reduce the risk of developing heart disease and other cardiovascular-related conditions.
Stress Reduction
Chronic stress can have a profound impact on cardiovascular health, increasing the risk of heart disease, high blood pressure, and cardiac arrhythmias. Engaging in stress-reducing activities, such as meditation, yoga, or deep breathing exercises, can help mitigate this risk.
Research has shown that mindfulness-based interventions can be particularly effective in reducing stress and anxiety, while also improving overall cardiovascular well-being. These interventions often involve techniques such as progressive muscle relaxation, visualization, and guided imagery.
In addition to these techniques, maintaining a healthy work-life balance, setting realistic goals, and prioritizing leisure activities can also help reduce stress levels. By incorporating stress-reducing strategies into daily life, individuals can better manage the physical and emotional demands of modern life, ultimately promoting a healthier heart and cardiovascular system.
Regular relaxation and stress reduction are essential for maintaining optimal cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Interesting Facts About the Heart
The human heart is a fascinating organ, with unique characteristics and abilities that have captivated scientists and the general public alike, inspiring extensive research and study into its intricate mechanics.
Fact #1⁚ The Heart Beats Billions of Times
The human heart is an incredibly resilient and hardworking organ, beating approximately 3 billion times in a person’s lifetime. This staggering number is a testament to the heart’s remarkable endurance and ability to function continuously, without rest, for decades. To put this into perspective, if we assume an average heartbeat of 80 beats per minute, the heart will beat around 4,800 times per hour, 115,200 times per day, and over 42 million times per year. This unwavering dedication to pumping blood throughout the body is essential for maintaining life, and the heart’s ability to perform this task with such consistency is truly remarkable; Despite its impressive workload, the heart remains an efficient and reliable organ, working tirelessly behind the scenes to keep us alive.
Fact #2⁚ The Heart is a Powerful Muscle
The human heart is an exemplar of muscular strength and efficiency, pumping approximately 2,000 gallons of blood every day. To achieve this feat, the heart’s muscular walls, comprised of cardiac muscle, contract and relax in a coordinated manner, generating a significant amount of force relative to its size. In fact, the heart’s muscular power is estimated to be around 1-2 watts, which may seem modest, but considering its size and continuous operation, it is a remarkable achievement. Furthermore, the heart’s muscular endurance allows it to maintain a consistent pumping action, supplying oxygen and nutrients to the body’s tissues and organs, without fatigue or faltering, for an entire lifetime. This highlights the heart’s remarkable physiological capabilities and its vital role in maintaining overall health and well-being.
Fact #3⁚ The Heart has its own Electrical System
The human heart possesses a unique and intricate electrical conduction system, enabling it to regulate its own rhythmic contractions. At the heart of this system lies the sinoatrial (SA) node, a small group of specialized cells that act as the heart’s natural pacemaker, generating electrical impulses at a rate of approximately 60-100 beats per minute. These impulses are then transmitted through the atria to the atrioventricular (AV) node, which relays the signals to the ventricles, triggering their contraction. This complex interplay of electrical stimuli allows the heart to maintain a consistent and efficient pumping action, supplying the body with the necessary oxygen and nutrients. The heart’s electrical system is a remarkable example of physiological autonomy, permitting the heart to function independently while still being influenced by the nervous system and hormonal regulation.
Fact #4⁚ The Heart can Continue to Beat Outside the Body
A fascinating and somewhat macabre fact about the human heart is its ability to continue beating for a short period of time outside the body, provided it has an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. This phenomenon is made possible by the heart’s inherent myogenic properties, which allow it to generate electrical impulses and contract independently of the nervous system. In ideal conditions, a heart removed from the body can continue to beat for up to 30 minutes or more٫ although this timeframe can vary greatly depending on factors such as temperature٫ humidity٫ and the presence of any underlying cardiac conditions. This remarkable ability has led to significant advances in cardiac transplantation and research٫ where hearts can be preserved and transported for extended periods before being transplanted into recipients.
Fact #5⁚ The Heart is a Symbol of Love and Emotion
The human heart has long been imbued with symbolic meaning, transcending its role as a vital organ to become a universal emblem of love, passion, and emotion. This rich symbolism is evident in various cultural and artistic expressions, from the Valentine’s Day iconography of hearts and cupids to the poetic metaphor of the “heart” as a repository of emotions. Throughout history, the heart has been associated with feelings of warmth, tenderness, and devotion, with phrases such as “heartfelt” and “heartbroken” underscoring its emotional significance. The heart’s symbolic resonance can also be seen in its depiction in art, literature, and music, where it often serves as a powerful and evocative representation of the human experience. As a result, the heart has become an instantly recognizable and enduring symbol of love and emotion, one that continues to inspire and captivate people around the world.
It
While overall well-written certain sentences could benefit further refinement example when discussing function roles performed specific tissues clearer definitions would aid comprehension here perhaps future revisions address minor quibble aside solid introduction material covered
This article provides an excellent overview of the anatomy of the human heart. The language used is clear and concise making it accessible to readers who may not have prior knowledge on this topic.
I appreciate how this article breaks down complex concepts into manageable sections allowing readers to grasp each component before moving onto more intricate details.
One aspect I found particularly useful was how this piece highlighted both structural components like layers within walls alongside functional ones such electrical systems showing interplay required efficient work from our organs