Understanding Tooth Abscess⁚ A Comprehensive Guide
A tooth abscess is a serious dental condition characterized by the accumulation of pus in the tissues surrounding an infected tooth, requiring prompt attention to prevent further complications and ensure optimal oral health․
What is a Tooth Abscess?
A tooth abscess, also known as a dental abscess or periapical abscess, is a localized collection of pus in the tissues surrounding an infected tooth․ This occurs when bacteria invade the tooth pulp, causing an infection that spreads to the surrounding periodontal tissues․ The body’s natural defense mechanism is to isolate the infection by forming a pocket of pus, which can appear as a painful swelling or a lump on the gum tissue․ A tooth abscess can be acute or chronic, with acute abscesses developing rapidly and chronic abscesses persisting over time․ If left untreated, a tooth abscess can lead to severe consequences, including tooth loss, bone destruction, and potentially life-threatening systemic infections․ Prompt recognition and treatment of a tooth abscess are essential to prevent such complications and restore optimal oral health․
Causes and Risk Factors
Understanding the underlying causes and risk factors of tooth abscess is crucial for prevention and effective management, as it enables individuals to take proactive measures to mitigate their susceptibility to this dental condition․
Common Causes of Tooth Abscess
Tooth abscesses are often the result of an untreated dental cavity, gum disease, or a cracked tooth, allowing bacteria to penetrate the tooth pulp and cause infection․ Additionally, poor oral hygiene, inadequate dental care, and a diet high in sugar can contribute to the development of a tooth abscess․
Trauma to the mouth, such as a blow to the face, can also lead to a tooth abscess by causing damage to the tooth or surrounding tissue․ Furthermore, dental procedures, including extractions or root canals, can sometimes lead to the formation of a tooth abscess if not performed properly․
In rare cases, a tooth abscess can be caused by an underlying medical condition, such as diabetes or a compromised immune system․ Understanding the common causes of tooth abscess is essential for prevention and prompt treatment, helping to prevent further complications and ensure optimal oral health․
Risk Factors for Developing a Tooth Abscess
Certain individuals are more susceptible to developing a tooth abscess due to various risk factors․ Poor oral hygiene and inadequate dental care increase the likelihood of developing a tooth abscess, as bacteria can accumulate and cause infection․
Smoking and tobacco use also significantly increase the risk of developing a tooth abscess, as they impair the body’s ability to fight infection․ Additionally, individuals with compromised immune systems, such as those with diabetes or HIV/AIDS, are more prone to developing a tooth abscess․
Genetic predisposition, gum disease, and previous dental trauma also contribute to an individual’s risk of developing a tooth abscess․ Furthermore, poor diet and nutrition, particularly a diet high in sugar and processed foods, can increase the risk of developing a tooth abscess․ Identifying these risk factors is essential for taking preventive measures and reducing the likelihood of developing a tooth abscess․
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Accurate diagnosis of a tooth abscess involves identifying characteristic symptoms, conducting thorough clinical examinations, and utilizing diagnostic imaging techniques to confirm the presence of an abscess and develop an effective treatment plan;
Recognizing the Symptoms of a Tooth Abscess
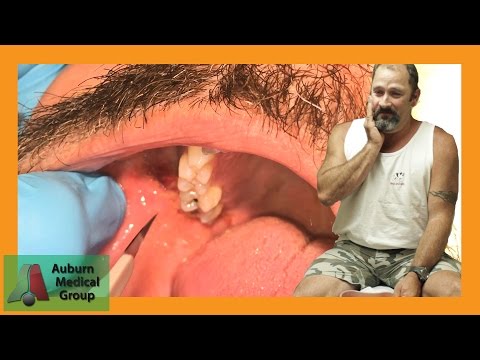
A tooth abscess typically presents with a range of symptoms, including severe toothache or mouth pain, which can radiate to the ear, jaw, or surrounding teeth․ The pain often worsens over time and may be exacerbated by biting or chewing․ Additional symptoms may include sensitivity to hot or cold temperatures, swelling of the face, cheek, or gums, and pus or discharge in the affected area․ In some cases, patients may experience fever, swollen lymph nodes, or a general feeling of malaise․ It is essential to seek dental attention immediately if any of these symptoms occur, as prompt treatment can help prevent further complications and ensure optimal outcomes․ A thorough evaluation by a dental professional is necessary to confirm the diagnosis and develop an effective treatment plan․
Diagnosing a Tooth Abscess
A diagnosis of a tooth abscess is typically made through a combination of clinical evaluation, medical history, and diagnostic imaging․ During the examination, the dentist will visually inspect the affected tooth and surrounding tissues, looking for signs of swelling, redness, or pus․ They may also use a dental probe to assess the depth of any pockets that may have formed between the tooth and gum․ Radiographic images, such as X-rays or cone beam computed tomography (CBCT) scans, may be ordered to confirm the presence of an abscess and evaluate the extent of the infection․ In some cases, the dentist may also perform a pulp vitality test to assess the health of the pulp tissue within the affected tooth․ A definitive diagnosis is essential for developing an effective treatment plan and preventing further complications․
Treatment and Management
Effective treatment and management of a tooth abscess involve eliminating the infection, alleviating symptoms, and restoring oral health through various dental interventions and strategies tailored to the individual’s needs․
Treatment Options for a Tooth Abscess
The primary objective of treating a tooth abscess is to eliminate the infection and prevent further complications․ Treatment options may include drainage of the abscess, which involves making an incision in the gum tissue to allow for the release of pus․ Antibiotics may be prescribed to combat bacterial infections and promote healing․ In some cases, a root canal procedure or tooth extraction may be necessary to remove the infected tooth or pulp tissue․ Additionally, pain management strategies such as analgesics or anti-inflammatory medications may be employed to alleviate discomfort and swelling․ It is essential to follow a dentist’s instructions carefully to ensure effective treatment and minimize the risk of recurrence․ A comprehensive treatment plan will address the underlying causes of the abscess and provide a roadmap for recovery and long-term oral health․
Managing a Dental Emergency
In the event of a dental emergency such as a tooth abscess, it is crucial to seek immediate attention from a qualified dental professional․ While awaiting treatment, individuals can take steps to manage their symptoms and alleviate discomfort․ Rinsing the mouth with warm salt water can help reduce swelling and promote drainage․ Over-the-counter pain medications such as ibuprofen or acetaminophen can be taken to manage pain and inflammation․ Applying a cold compress to the affected area can also provide relief․ It is essential to avoid attempting to drain the abscess or extract the infected tooth, as this can lead to further complications․ A dental emergency service or on-call dentist can provide guidance and support during this critical period․ By taking prompt action and seeking professional help, individuals can mitigate the risks associated with a tooth abscess and achieve a favorable outcome․
Prevention and Oral Health
Maintaining good oral hygiene practices, including regular brushing and flossing, is essential for preventing tooth abscesses and promoting overall oral health and well-being, reducing the risk of dental complications;
Maintaining Good Oral Health
To prevent tooth abscesses, it is crucial to maintain good oral health through regular brushing and flossing․ This helps remove plaque, bacteria, and food particles that can accumulate on teeth and cause infections․ A fluoride toothpaste and mouthwash can also aid in strengthening tooth enamel and reducing the risk of decay․ Additionally, regular dental check-ups are essential for identifying potential oral health issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and prevention of complications․ A balanced diet low in sugar and acidic foods can also contribute to maintaining healthy teeth and gums․ Furthermore, avoiding tobacco and nicotine products can significantly reduce the risk of oral health problems, including tooth abscesses․ By adopting these habits, individuals can ensure optimal oral health and reduce the likelihood of developing a tooth abscess․
Preventing Tooth Abscesses
Beyond regular oral hygiene practices, several measures can be taken to prevent tooth abscesses․ One key step is to address any dental issues promptly, such as filling cavities or treating gum disease․ Individuals with a history of dental problems should consider visiting their dentist more frequently for check-ups and cleanings․ Wearing a mouthguard during sports or activities that may result in tooth trauma can also help prevent tooth abscesses․ Moreover, avoiding biting or chewing on hard objects, such as ice or hard candy, can reduce the risk of tooth damage․ In cases where a tooth has been damaged or chipped, seeking immediate dental attention can help prevent the development of an abscess․ By taking these proactive steps, individuals can significantly lower their risk of developing a tooth abscess and maintain optimal oral health․
In conclusion, understanding tooth abscesses is crucial for maintaining optimal oral health, and by being aware of the causes, symptoms, and treatment options, individuals can take proactive steps to prevent and manage this condition effectively․
The Importance of Prompt Treatment
Prompt treatment of a tooth abscess is essential to prevent further complications and ensure optimal outcomes․ Delaying treatment can lead to the spread of infection, resulting in more severe consequences such as cellulitis, osteomyelitis, or even life-threatening conditions like sepsis․ Furthermore, prompt treatment can help alleviate symptoms, reduce pain, and prevent long-term damage to the surrounding tissues and teeth․ In addition, timely intervention can also reduce the need for more extensive and costly procedures, such as surgical drainage or tooth extraction․ It is crucial to seek immediate dental attention if symptoms of a tooth abscess are suspected, as prompt treatment can significantly impact the prognosis and overall oral health․ By prioritizing prompt treatment, individuals can minimize the risk of complications and ensure a faster and more effective recovery․
This article provides an excellent overview of tooth abscesses. I particularly appreciated the explanation of the causes and risk factors associated with this condition.
While I found this article informative overall some sections felt repetitive could benefit from condensing information
I was impressed by the comprehensive nature of this guide. The section on understanding tooth abscess was clear and concise.
This article highlights the importance of good oral hygiene in preventing tooth abscesses. I appreciate how it emphasizes proactive measures individuals can take.
As someone who has experienced a tooth abscess firsthand, I found this article informative and accurate. However, I would have liked more information on treatment options.
The explanation of acute versus chronic tooth abscesses was helpful however more examples would aid understanding