What is Arteriosclerosis?
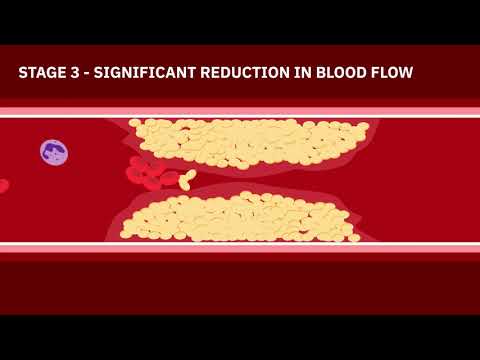
Arteriosclerosis refers to the hardening and thickening of arteries due to plaque buildup, leading to restricted blood flow and increased risk of cardiovascular disease, including heart attack and stroke, ultimately compromising cardiac health.
Cardiovascular Disease Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of arteriosclerosis, including advanced age, family history, obesity, physical inactivity, diabetes, and stress, which can exacerbate high blood pressure, atherosclerosis, and overall vascular disease susceptibility.
High Blood Pressure
High blood pressure, or hypertension, is a significant risk factor for the development of arteriosclerosis. Prolonged elevation of blood pressure can cause damage to the inner lining of blood vessels, leading to the formation of plaque and atherosclerosis.
As blood pressure increases, it puts additional strain on the heart, forcing it to work harder to pump blood throughout the body. This can result in cardiac hypertrophy, a thickening of the heart muscle that can lead to decreased cardiac function over time.
Furthermore, high blood pressure can also cause blood vessels to become narrower and more rigid, reducing blood flow to vital organs and increasing the risk of blood vessel blockage, heart attack, and stroke. Effective management of high blood pressure through lifestyle modifications and medication is crucial in preventing the progression of arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease.
High Cholesterol
High cholesterol is a primary risk factor for the development of arteriosclerosis, as it can lead to the accumulation of low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol in the walls of arteries. This can initiate an inflammatory response, attracting macrophages and promoting the formation of foam cells, which contribute to the growth of atherosclerotic plaques.
Elevated levels of LDL cholesterol can also increase the production of free radicals, leading to oxidative stress and further damage to the endothelial lining of blood vessels. Conversely, high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol has been shown to have protective effects, facilitating the removal of excess cholesterol from the bloodstream and reducing the risk of atherosclerosis.
Maintaining healthy cholesterol levels through a balanced diet, regular exercise, and lipid-lowering therapy can help mitigate the risk of arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. It is essential to monitor cholesterol profiles regularly and address any abnormalities promptly to prevent the progression of atherosclerotic disease.
Smoking
Cigarette smoking is a significant risk factor for the development of arteriosclerosis, as it promotes vascular inflammation, oxidative stress, and endothelial dysfunction. The chemicals present in tobacco smoke can damage the inner lining of blood vessels, making them more susceptible to the accumulation of atherosclerotic plaques.
Smoking also increases the production of vasoconstrictors, which can narrow blood vessels and reduce blood flow to vital organs. Furthermore, smoking can lower levels of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) cholesterol, reducing the body’s ability to remove excess cholesterol from the bloodstream.
Quitting smoking can significantly reduce the risk of arteriosclerosis and cardiovascular disease. Smoking cessation programs, counseling, and pharmacological interventions can help individuals overcome nicotine addiction and adopt a healthier lifestyle. It is essential to emphasize the importance of smoking cessation in the prevention and management of atherosclerotic disease, as it can have a profound impact on cardiovascular health and overall well-being.
Consequences of Arteriosclerosis
Arteriosclerosis can lead to severe consequences, including blood vessel blockage, organ damage, and impaired cardiac function, ultimately compromising overall vascular health and increasing the risk of life-threatening complications and mortality.
Heart Attack and Stroke
Atherosclerotic plaque buildup in coronary arteries can lead to a heart attack, causing damage to the heart muscle and potentially life-threatening complications. Similarly, plaque accumulation in cerebral arteries can result in a stroke, characterized by impaired blood flow to the brain and subsequent tissue damage.
The risk of heart attack and stroke is significantly increased in individuals with advanced arteriosclerosis, as the narrowed arteries are more susceptible to blockage by blood clots or other debris. Prompt medical attention is essential in the event of a heart attack or stroke, as timely treatment can minimize tissue damage and improve outcomes.
It is crucial for individuals with a history of arteriosclerosis to work closely with their healthcare provider to manage cardiovascular risk factors and prevent these devastating consequences. A comprehensive treatment plan, including lifestyle modifications and pharmacological interventions, can help mitigate the risk of heart attack and stroke;
Vascular Disease
Arteriosclerosis can lead to the development of vascular disease, characterized by impaired blood flow to various organs and tissues. The reduced perfusion can result in tissue ischemia, leading to symptoms such as pain, numbness, and weakness in the affected limbs.
Peripheral artery disease (PAD) is a common manifestation of vascular disease, typically affecting the lower extremities. PAD can significantly impact an individual’s quality of life, limiting mobility and increasing the risk of complications such as gangrene and amputation.
The progression of vascular disease can be slowed or halted through a combination of lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and revascularization procedures. Early detection and treatment are crucial in preventing long-term damage and improving outcomes for individuals with vascular disease. A comprehensive management plan should be developed in collaboration with a healthcare provider to address the unique needs of each patient.
Prevention and Treatment
Effective prevention and treatment of arteriosclerosis involve a multifaceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, pharmacological interventions, and medical procedures, aimed at reducing cardiovascular risk factors and promoting overall cardiac health and well-being.
Lifestyle Changes
Implementing lifestyle changes is crucial in preventing and managing arteriosclerosis. A well-balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can help lower cholesterol levels and blood pressure. Regular physical activity, such as walking, jogging, or cycling, can also improve cardiovascular health.
In addition to dietary modifications and exercise, individuals should aim to maintain a healthy weight, manage stress levels, and get sufficient sleep. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also essential in reducing the risk of cardiovascular disease.
Furthermore, incorporating stress-reducing activities, such as meditation or yoga, into daily routines can help mitigate the negative effects of stress on cardiac health. By adopting these lifestyle changes, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of developing arteriosclerosis and associated cardiovascular complications.
It is essential to consult with a healthcare professional before initiating any new diet or exercise program, especially for individuals with pre-existing medical conditions or concerns. A personalized approach to lifestyle modification can ensure optimal results and minimize potential risks.
Medical Treatment
Medical treatment for arteriosclerosis typically involves a combination of medications and interventional procedures. Cholesterol-lowering medications, such as statins, are commonly prescribed to reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol levels and slow disease progression.
Beta blockers and calcium channel blockers may be used to manage high blood pressure, while antiplatelet agents and anticoagulants can help prevent blood clots from forming. In some cases, medications to manage symptoms of cardiovascular disease, such as angina or heart failure, may also be necessary.
Interventional procedures, including angioplasty and stenting, may be performed to restore blood flow to affected areas. In severe cases, surgical bypass grafting or endarterectomy may be required to remove plaque buildup and improve circulation.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a personalized treatment plan, as the most effective approach will depend on the individual’s specific condition, medical history, and overall health status. Regular monitoring and follow-up appointments are crucial to ensuring optimal treatment outcomes and preventing complications.
I appreciate how this article breaks down complex medical concepts into easy-to-understand language. However, I would have liked to see more discussion on the role of nutrition in preventing or managing arteriosclerosis.
As a healthcare professional, I found this article to be accurate and well-researched. The section on high cholesterol was particularly well-written, explaining the mechanisms by which LDL cholesterol contributes to atherosclerotic plaque formation.
Overall I found this article well-written but would suggest adding visual aids such as diagrams or illustrations could enhance understanding key concepts related artery hardening.
This article provides a comprehensive overview of arteriosclerosis, its risk factors, and its impact on cardiovascular health. The section on high blood pressure is particularly informative, highlighting the importance of managing hypertension through lifestyle modifications and medication.
I found this article to be informative but somewhat lacking in depth. For example, I would have liked to see more discussion on emerging treatments for arteriosclerosis or new research developments in this area.
This article does an excellent job highlighting the importance of addressing modifiable risk factors for arteriosclerosis such as physical inactivity and stress management techniques such as meditation or yoga could have been explored further.