What is the Normal BSP Reading for Pregnant Women? You Must Know!
Maintaining normal blood sugar levels during pregnancy is crucial for the health of both mother and fetus. Understanding BSP levels and their significance can help prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy.
Introduction
Pregnancy is a complex and delicate process that requires careful monitoring of various physiological parameters to ensure the health and well-being of both the mother and the fetus. One crucial aspect of prenatal care is the management of blood sugar levels, also known as Blood Sugar Percentage (BSP) levels. Abnormal BSP levels during pregnancy can have significant consequences, including an increased risk of gestational diabetes, pregnancy complications, and adverse fetal outcomes.
As such, it is essential for pregnant women to understand the importance of maintaining normal BSP levels and to be aware of the risks associated with abnormal levels. Furthermore, healthcare providers must be vigilant in monitoring BSP levels and providing timely interventions to prevent complications and ensure optimal outcomes. This article aims to provide an overview of BSP levels in pregnancy, including the normal range, the importance of monitoring, and the potential risks associated with abnormal levels.
By understanding BSP levels and their significance, pregnant women can take an active role in maintaining their health and ensuring a healthy pregnancy.
Understanding BSP Levels in Pregnancy
BSP levels play a crucial role in pregnancy, influencing fetal development and maternal health. Understanding the factors that affect BSP levels and their impact on pregnancy outcomes is essential for effective prenatal care and management.
What are BSP Levels?
BSP levels, also known as blood sugar levels or blood glucose levels, refer to the concentration of glucose present in the blood. In pregnancy, BSP levels are a critical indicator of maternal and fetal health. Glucose is a primary source of energy for the body’s cells, and its levels are tightly regulated by hormones such as insulin.
During pregnancy, hormonal changes can affect insulin sensitivity, leading to fluctuations in BSP levels. If left unmanaged, abnormal BSP levels can increase the risk of gestational diabetes, a condition characterized by high blood sugar levels during pregnancy. Understanding BSP levels is crucial for identifying and managing potential complications, ensuring a healthy pregnancy and optimal fetal development.
Healthcare providers closely monitor BSP levels throughout pregnancy, using various tests and assessments to evaluate maternal and fetal well-being. By maintaining normal BSP levels, pregnant women can reduce their risk of pregnancy-related complications and promote a healthy outcome for themselves and their baby.
Importance of Normal BSP Levels
Maintaining normal BSP levels is crucial for a healthy pregnancy. Abnormal BSP levels can have far-reaching consequences, affecting both maternal and fetal well-being. When BSP levels are within the normal range, it ensures that the body’s cells receive the necessary energy for optimal functioning.
Normal BSP levels also play a critical role in fetal development. The fetus relies on glucose from the mother’s bloodstream for growth and development. Abnormal BSP levels can disrupt this process, potentially leading to birth defects, low birth weight, or other complications.
Furthermore, normal BSP levels reduce the risk of pregnancy-related complications, such as gestational diabetes, preeclampsia, and premature labor. By maintaining normal BSP levels, pregnant women can minimize their risk of these complications and promote a healthy pregnancy outcome; Regular prenatal care and monitoring of BSP levels are essential for identifying any potential issues and taking prompt action to address them.
Overall, maintaining normal BSP levels is vital for ensuring a healthy pregnancy and optimal fetal development.
Normal Blood Glucose Levels in Pregnancy
Normal blood glucose levels in pregnancy vary depending on the stage of gestation and the individual woman. Understanding these levels is essential for maintaining a healthy pregnancy and preventing complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels.
What are Normal BSP Levels?
Normal blood sugar levels during pregnancy, also known as blood glucose levels, typically range from 70 to 140 milligrams per deciliter (mg/dL) for women without a history of diabetes. However, these levels may vary depending on the stage of gestation and the individual woman’s health.
In the first trimester, normal fasting blood glucose levels are typically below 95 mg/dL, while one hour after eating, levels should be below 180 mg/dL. In the second and third trimesters, normal fasting levels may be slightly higher, ranging from 95 to 105 mg/dL.
It is essential for pregnant women to work closely with their healthcare providers to establish a personalized target range for blood glucose levels. This can help prevent complications associated with abnormal blood sugar levels and ensure a healthy pregnancy. Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels can also help identify any potential issues early on, allowing for prompt treatment and management.
Understanding normal BSP levels can provide valuable insights into a woman’s overall health during pregnancy, enabling her to make informed decisions about her care and take proactive steps to maintain a healthy pregnancy.
Glucose Screening Test
A glucose screening test is a routine prenatal test used to assess a pregnant woman’s risk of developing gestational diabetes. The test typically occurs between 24 and 28 weeks of gestation and involves consuming a sweet liquid containing glucose.
One hour after consumption, a blood sample is taken to measure the body’s ability to process glucose. If the results indicate an elevated blood glucose level, further testing may be necessary to confirm the diagnosis of gestational diabetes.
The glucose screening test is not a diagnostic test, but rather a screening tool to identify women who are at risk of developing gestational diabetes. Women with a history of gestational diabetes, obesity, or other risk factors may require earlier or more frequent testing.
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists recommends that all pregnant women undergo glucose screening, as gestational diabetes can have significant consequences for both mother and fetus if left untreated. Early detection and management can significantly reduce the risk of complications associated with gestational diabetes.
A healthcare provider will discuss the results of the glucose screening test with the patient and determine the best course of action for her individual situation.
High-Risk Pregnancy and BSP Levels
Pregnancies complicated by pre-existing medical conditions, obesity, or a history of gestational diabetes are considered high-risk. Close monitoring of BSP levels is crucial in these cases to prevent and manage potential complications.
Factors that Increase the Risk of Gestational Diabetes
Certain factors increase a pregnant woman’s risk of developing gestational diabetes. These include⁚
- A family history of diabetes, particularly in first-degree relatives
- Obesity, defined as a body mass index (BMI) of 30 or higher
- Previous history of gestational diabetes or delivering a baby over 4 kg
- Age 35 or older at the time of pregnancy
- Belonging to an ethnic group with a high prevalence of diabetes, such as Hispanic or African American
- Polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS) or other conditions associated with insulin resistance
Women with these risk factors should be closely monitored for signs of gestational diabetes and undergo regular glucose screening tests to ensure early detection and management.
Early identification of gestational diabetes allows for prompt intervention, reducing the risk of complications for both mother and fetus. Understanding individual risk factors is essential for effective prenatal care and a healthy pregnancy outcome.
Pregnancy Complications and BSP Levels
Abnormal BSP levels during pregnancy can lead to various complications for both mother and fetus. These complications include⁚
- Preeclampsia, a condition characterized by high blood pressure and damage to organs such as the kidneys and liver
- Preterm labor, which increases the risk of respiratory distress and other health problems in the newborn
- Fetal macrosomia, a condition where the baby grows too large, making delivery more challenging
- Increased risk of cesarean delivery and associated surgical complications
Furthermore, uncontrolled BSP levels can also affect fetal development, potentially leading to birth defects or an increased risk of stillbirth.
Tight control of BSP levels is essential to prevent these complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome. Women with gestational diabetes should work closely with their healthcare provider to manage their condition and minimize the risk of adverse effects on both mother and fetus.
Regular prenatal care and careful monitoring of BSP levels are crucial to preventing pregnancy complications and ensuring a successful pregnancy outcome.
In conclusion, maintaining normal BSP levels during pregnancy is crucial for the health and well-being of both mother and fetus. Understanding the importance of BSP levels and managing them effectively can help prevent complications and ensure a healthy pregnancy outcome.
It is essential for pregnant women to work closely with their healthcare provider to monitor and manage their BSP levels, particularly if they have been diagnosed with gestational diabetes.
By prioritizing prenatal care and taking proactive steps to manage BSP levels, women can reduce their risk of pregnancy complications and promote a healthy and successful pregnancy outcome.
Furthermore, raising awareness about the importance of BSP levels during pregnancy can help empower women to take control of their health and make informed decisions about their care.
Ultimately, a healthy pregnancy outcome requires a collaborative effort between healthcare providers, pregnant women, and their families. By working together, we can promote optimal health outcomes for mothers and babies alike.
Early detection and management of abnormal BSP levels are critical in preventing adverse pregnancy outcomes and ensuring a healthy start for newborns.
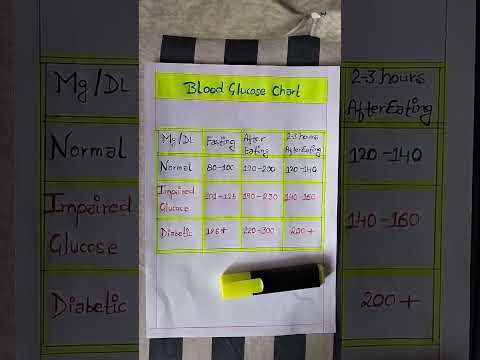
This article reinforced my understanding of BSP level management during pregnancy; however, I believe further discussion on postpartum implications would enhance its value.
I appreciate this article
I found this article informative, but I would like to see more discussion on the specific risks associated with abnormal BSP levels during different stages of pregnancy.
As a pregnant woman, I appreciate this article
The article provides a comprehensive overview of BSP levels during pregnancy; however, I think it would benefit from additional discussion on gestational diabetes screening guidelines.
This article highlights the critical role healthcare providers play in monitoring BSP levels during pregnancy. I agree that timely interventions are essential for preventing complications.
This article provides valuable insights into the importance of monitoring blood sugar levels during pregnancy. As a healthcare provider, I appreciate the emphasis on timely interventions to prevent complications.